Codd's cellular automaton
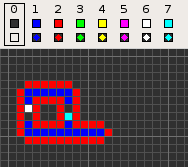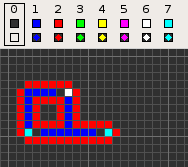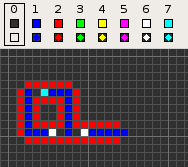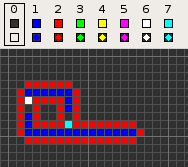
Codd's cellular automaton is a cellular automaton (CA) devised by the British computer scientist Edgar F. Codd in 1968. It was designed to recreate the computation- and construction-universality of von Neumann's CA but with fewer states: 8 instead of 29. Codd showed that it was possible to make a self-reproducing machine in his CA, in a similar way to von Neumann's universal constructor, but never gave a complete implementation.
History
In the 1940s and '50s, John von Neumann posed the following problem:[1]
- What kind of logical organization is sufficient for an automaton to be able to reproduce itself?
He was able to construct a cellular automaton with 29 states, and with it a universal constructor. Codd, building on von Neumann's work, found a simpler machine with eight states.[2] This modified von Neumann's question:
- What kind of logical organization is necessary for an automaton to be able to reproduce itself?
Three years after Codd's work, Edwin Roger Banks showed a 4-state CA in his PhD thesis that was also capable of universal computation and construction, but again did not implement a self-reproducing machine.[3] John Devore, in his 1973 masters thesis, tweaked Codd's rules to greatly reduce the size of Codd's design, to the extent that it could be implemented in the computers of that time. However, the data tape for self-replication was too long; Devore's original design was later able to complete replication using Golly. Christopher Langton made another tweak to Codd's cellular automaton in 1984 to create Langton's loops, exhibiting self-replication with far fewer cells than that needed for self-reproduction in previous rules, at the cost of removing the ability for universal computation and construction.[4]
Comparison of CA rulesets
| CA | number of states | symmetries | computation- and construction-universal | size of self-reproducing machine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| von Neumann | 29 | none | yes | 130,622 cells |
| Codd | 8 | rotations | yes | 283,126,588 cells[5] |
| Devore | 8 | rotations | yes | 94,794 cells |
| Banks-IV | 4 | rotations and reflections | yes | unknown |
| Langton's loops | 8 | rotations | no | 86 cells |
Specification
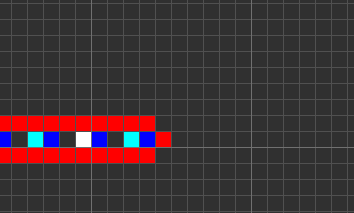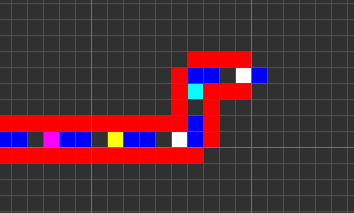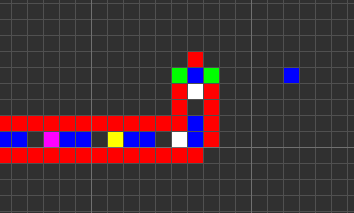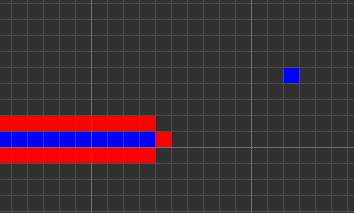
Codd's CA has eight states determined by a von Neumann neighborhood with rotational symmetry.
The table below shows the signal-trains needed to accomplish different tasks. Some of the signal trains need to be separated by two blanks (state 1) on the wire to avoid interference, so the 'extend' signal-train used in the image at the top appears here as '70116011'.
| purpose | signal train |
|---|---|
| extend | 70116011 |
| extend_left | 4011401150116011 |
| extend_right | 5011501140116011 |
| retract | 4011501160116011 |
| retract_left | 5011601160116011 |
| retract_right | 4011601160116011 |
| mark | 701160114011501170116011 |
| erase | 601170114011501160116011 |
| sense | 70117011 |
| cap | 40116011 |
| inject_sheath | 701150116011 |
| inject_trigger | 60117011701160116011 |
Universal computer-constructor
Codd designed a self-replicating computer in the cellular automaton, based on Wang's W-machine. However, the design was so colossal that it evaded implementation until 2009, when Tim Hutton constructed an explicit configuration.[5] There were some minor errors in Codd's design, so Hutton's implementation differs slightly, in both the configuration and the ruleset.
See also
- Artificial life
- Cellular automaton
- Conway's game of life
- Langton's loops
- von Neumann cellular automaton
- Wireworld
References
- ↑ von Neumann, John; Burks, Arthur W. (1966). "Theory of Self-Reproducing Automata.". www.walenz.org. Archived from the original on 2008-01-05. Retrieved 2012-01-28.
- ↑ Codd, Edgar F. (1968). Cellular Automata. Academic Press, New York.
- ↑ Banks, Edwin (1971). Information Processing and Transmission in Cellular Automata. PhD thesis, MIT, Department of Mechanical Engineering.
- ↑ Langton, C. G. (1984). "Self-Reproduction in Cellular Automata". Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena. 10 (1-2): 135–144. doi:10.1016/0167-2789(84)90256-2.
- 1 2 Hutton, Tim J. (2010). "Codd's self-replicating computer" (PDF). Artificial Life. 16 (2): 99–117. doi:10.1162/artl.2010.16.2.16200. PMID 20067401.
External links
- The Rule Table Repository has the transition table for Codd's CA.
- Golly - supports Codd's CA along with the Game of Life, and other rulesets.
- Download the complete machine (13MB) and more details.