Chief warrant officer
Chief Warrant Officer is a military rank used by the United States Armed Forces, the Canadian Armed Forces, the Pakistan Air Force, the Israel Defense Forces, the South African National Defence Force, the Lebanese Armed Forces and, since 2012, the Singapore Armed Forces. In the United States Armed Forces Chief Warrant Officers are actual officers, not NCOs like other NATO forces.[1]
Canadian Armed Forces
In the Canadian Armed Forces, a chief warrant officer or CWO is the most senior non-commissioned member (NCM) rank for army and air force personnel. Its equivalent rank for navy personnel is chief petty officer 1st class (CPO1). The French language form of chief warrant officer is adjudant-chef (adjuc).
A CWO is senior to the rank of master warrant officer[2] (MWO) and its navy equivalent of chief petty officer 2nd class (CPO2).
Cadets Canada uses the ranks of chief petty officer 1st class, chief warrant officer, and warrant officer 1st class respectively. This organization's uniforms use a similar coat of arms insignia as the Canadian Armed Forces.
Insignia
The rank insignia of the CWO is a simplified version of the 1957 coat of arms of Canada, worn on both forearms of the service dress tunic; in gold metal and green enamel miniature pins on the collar of the service dress shirt and outerwear coats (Army only); on CADPAT slip-ons worn in the middle of the chest, embroidered in tan (Army) or blue (Air Force) thread; and in pearl-grey thread on blue slip-ons on both shoulders of other uniforms (Air Force only).
The insignia lacks the annulus, from 1985 changes, behind the shield bearing the motto of the Order of Canada. It also differs from both the 1957 and 1985 versions through a lack of compartment and mantling.
-
.svg.png)
Chief Warrant Officer
-
.svg.png)
Chief Warrant Officer
-
.svg.png)
Chief Petty Officer First Class
Forms of address
CWOs are generally initially addressed as "Chief Warrant Officer", and thereafter as "Sir" or "Ma'am" by subordinates; and as Mr. or Ms. by commissioned officers. If they hold the appointment of regimental sergeant-major, they may also be addressed as "RSM" by the commanding officer. In the RCN, CWOs are never addressed as "Chief", this being a form of address reserved for chief petty officers. Civilians can address them as Chief Warrant Officer or CWO or Mr/Mrs/Miss/Ms (followed by surname).
Appointments
CWOs may hold a number of appointments, some of which are listed below:
- Regimental sergeant-major (RSM) – the most senior NCO in a battalion-sized Army unit, including armoured, combat engineer, and signal regiments.
- Squadron warrant officer (SWO) – the most senior NCO in a squadron-sized Air Force units and army signal units
- School chief warrant officers (SCWO) - the most senior NCO in Air Force and some Army schools of battalion or squadron size.
Due to the unified nature of the Canadian Armed Forces, it is not unheard-of for air force CWOs or even navy CPO1s – especially those of the so-called "purple trades", such as logistics or military police – to find themselves filling the appointment of RSM in what are otherwise considered Canadian Army units (such as service battalions or communication regiments). Conversely, it is not impossible for an army CWO or navy CPO1 to be the squadron CWO of a Royal Canadian Air Force squadron.
Senior appointments
Senior appointments for chief warrant officers and chief petty officers 1st class entitle the incumbents to wear a modified rank badge or an addition to the rank badge. They are as follows:[3]
Formation chief warrant officer
The coat of arms over the central insignia of the badge of the Canadian Armed Forces (crossed swords, an anchor and an eagle in flight). This appointment is given to CWO assigned to commanders at the base, brigade, wing, and division levels. Specific examples include base chief warrant officer, brigade sergeants-major, wing chief warrant officers, the division chief warrant officer (DCWO) of 1 Canadian Air Division and the division sergeant-major (Div SM) of 3rd Canadian Division (3 Cdn Div). A formation chief warrant officer would typically be seen with a colonel or brigadier-general, but may occasionally be seen with a lieutenant-colonel or major-general.
-
.svg.png)
Formation Chief Warrant Officer
-
.svg.png)
Formation Chief Warrant Officer
Command chief warrant officer (CCWO)
The coat of arms with a wreath of laurel wrapped around the base. This appointment is given to CWO assigned to commanders of commands including to the commander Canadian Special Operations Forces Command, commander Canadian Forces Intelligence Command and commander Canadian Joint Operations Command. The command chief warrant officer appointed to the commander Canadian Army is called the Canadian Army sergeant-major, while the command chief warrant officer appointed to commander RCAF is known as the Chief Warrant Officer of the Air Force. A command chief warrant officer would be seen with a major-general or lieutenant-general.
-
.svg.png)
Command chief warrant officer
-
-2015.svg.png)
Command chief warrant officer
Canadian Forces chief warrant officer (CFCWO)
Messes and quarters
CWOs generally mess and billet with other warrant officers and with sergeants, and their navy equivalents, chief petty officers and petty officers. Their mess on military bases or installations are generally named the "Warrant Officers and Sergeants Mess".
Uniforms
Although NCMs, CWOs generally wear the uniform accoutrements of commissioned officers; for example, officer cap badge, waistcoat instead of cummerbund with mess dress, etc.
Israel Defense Forces

Rav nagad
insignia
IDF
The רב-נגד Rav nagad, a Chief Warrant Officer is the most senior non-commissioned officers rank in the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). Because the IDF is an integrated force, they have a unique rank structure. IDF ranks are the same in all services (army, navy, air force, etc.). The ranks are derived from those of the paramilitary Haganah developed in the British Mandate of Palestine period to protect the Yishuv. This origin is reflected in the slightly-compacted IDF rank structure.
| Israel Defense Forces ranks : נגדים nagadim - non-commissioned officers (NCO) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IDF NCO rank | רב-סמל Rav samal | רב-סמל ראשון Rav samal rishon | רב-סמל מתקדם Rav samal mitkadem | רב-סמל בכיר Rav samal bakhír | רב-נגד משנה Rav nagad mishne | רב-נגד Rav nagad |
| NATO | OR–5 | OR–6 | OR–7 | OR–8 | OR–9 | |
| Abbreviation | רס"ל Rasal | רס"ר Rasar | רס"מ Rasam | רס"ב Rasab | רנ"מ Ranam | רנ"ג Ranag |
| Corresponding rank | Sergeant first class | Master sergeant | Sergeant major | Command sergeant major | Warrant officer | Chief warrant officer |
| Insignia | ||||||
| More details at Israel Defense Forces ranks & IDF 2012 - Ranks (idf.il, english) | ||||||
South African Armed Forces

In 2008[4] the Warrant Officer ranks of the South African National Defence Force were expanded and the rank of Chief Warrant Officer was created. In the South African Navy a Chief Warrant Officer is the senior NCO in Fleet Command. In the South African Army the equivalent is the senior NCO in an Army Formation, such as Armour, Infantry etc.
United States Armed Forces
Chief Warrant Officer in the United States Armed Forces refers to any warrant officer in pay grades CW2 and above. All warrant officers (WO1 to CWO5) are officers and rate a salute by all enlisted NATO OR personnel. Only the U.S. Army uses WO1 through CW5 as designators; all other branches of the U.S. Armed Forces use CW2 through CW5. All warrant officers dine in the officers' mess but rate just below O-1 (NATO rank code OF-1).
Warrant officer rank insignia is the only officers' insignia that is not the same for all branches of the U.S. military, with one exception. The rank insignia for a CW5 became the only universal insignia within the warrant officer ranks when the U.S. Navy promoted its first CWO5 in 2002 and the Army adopted the emblem in 2004.
Warrant officers in the United States are classified as officers and are in the "W" category (NATO "WO"); they are technical leaders and specialists. Chief warrant officers are commissioned by the president of the United States and take the same oath as regular commissioned officers do. They may be technical experts with a long service as enlisted personnel or direct entrants, most notably as U.S. Army helicopter pilots.
| Grade | Rank | Abbreviation | Army | Air Force (discontinued) |
Navy | Coast Guard | Marine Corps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W-1 | Warrant officer one | WO-1 WO1 (Army) |
|
|
 1975 |
 1975 |
|
| W-2 | Chief warrant officer two | CWO-2 CW2 (Army) |
|
|
 |
 |
|
| W-3 | Chief warrant officer three | CWO-3 CW3 (Army) |
|
|
 |
 |
|
| W-4 | Chief warrant officer four | CWO-4 CW4 (Army) |
|
|
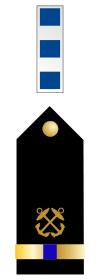 |
 |
|
| W-5 | Chief warrant officer five | CWO-5 CW5 (Army) |
 |
|
 |
Established 1994; not implemented |
|
Notable Warrant Officers
- Brigadier General Chuck Yeager, USAF was initially a flight officer (also known as "warrant officer (air)", in the USAAF during World War II
- MAJ (was CW3) Frederick Edgar Ferguson, USA (Medal of Honor recipient)
- MAJ (was WO1) Hugh Thompson, Jr., USA (Soldier's Medal recipient)
- CW5 David F. Cooper, USA[5]
- CW4 Michael J. Novosel, USA (Medal of Honor recipient)
- CW4 Oscar G. Johnson, USA
- CW4 Michael Durant, USA
- CW4 Thomas J. Hennen, USA
- CW4 Keith Yoakum, USA[6]
- CW3 Ronald D. Young Jr., USA
- CW2 Jason W. Myers, USA[7]
- CW2 Louis R. Rocco, USA
- WO1 Robert Mason, USA
- CWO2/Chief Carpenter John Arnold Austin, USN
- WO1 John W. Lang, USN[8]
- WO1 Floyd Bennett, USN[9] (Medal of Honor recipient)
- CWO4 Hershel W. Williams, USMC (Medal of Honor recipient)
- CWO4 John W. Frederick, Jr., USMC[10]
- CWO4 Henry Wildfang, USMC[11][12] (Gray Eagle Award recipient for longest-serving naval aviator; only chief warrant officer in the history of U.S. Naval Aviation so honored)
- CWO5 Ralph E. Rigby, USA, last continuously serving draftee on active duty in the U.S. Army, retiring in 2014[13]
See also
- theNavyCWO.com
- warrant officer (United States)
- Non-commissioned member
- Chief Petty Officer 1st Class
- Regimental Sergeant-Major
- Warrant Officer
- Commission (document)
- Israel Defense Forces insignia
- Israel Defense Forces
- Singapore Armed Forces ranks
- List of comparative military ranks
- Chief web officer
References
- ↑ http://www.mindef.gov.sg/imindef/resourcelibrary/cyberpioneer/topics/articles/news/2012/jun/29jun12_news2.htmll[]
- ↑ http://www.canadiansoldiers.com/ranks/warrantofficers.htm
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-02-24. Retrieved 2009-11-20.
- ↑ http://www.dod.mil.za/news/news2008/sep2008/Sep2008-3.pdf
- ↑ David F. Cooper. "Valor awards for David F. Cooper". Projects.militarytimes.com. Retrieved 2014-07-23.
- ↑ Keith Yoakum. "Valor awards for Keith Yoakum". Projects.militarytimes.com. Retrieved 2014-07-23.
- ↑ Jason W. Myers. "Valor awards for Jason W. Myers". Projects.militarytimes.com. Retrieved 2014-07-23.
- ↑ "TogetherWeServed - WO John LANG". Navy.togetherweserved.com. Retrieved 2014-07-23.
- ↑ Floyd Bennett
- ↑ John William Frederick , Jr. "Valor awards for John William Frederick , Jr". Projects.militarytimes.com. Retrieved 2014-07-23.
- ↑ http://www.mcata.com/April%202003.pdf
- ↑ http://ehistory.osu.edu/osu/books/1968/0479.cfm
- ↑ "Last continuously serving draftee retires after 42 years of service". 2014-10-28. Retrieved 2014-11-19.