Charleville musket
| Charleville musket | |
|---|---|
|
Musket Model 1766 | |
| Type | Musket |
| Place of origin | Kingdom of France |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1717-1840 |
| Used by | France, various native Canadian tribes and other tribes throughout New France, United States |
| Wars | Indian wars, Austrian War of Succession, Karnatic Wars, Seven Years' War, American Revolutionary war, French Revolutionary Wars, Napoleonic Wars, War of 1812 |
| Production history | |
| Designed | 1717 |
| Produced | 1717–1839 |
| Number built | > 150,000 (Modèle 1766) |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 10 pounds (4.5 kg) |
| Length | 60 inches (150 cm) |
| Barrel length | 45 inches (110 cm) |
|
| |
| Caliber | .69" (17.5mm) |
| Action | Flintlock |
| Rate of fire | User dependent; usually 2 to 3 rounds a minute, an expert 4 |
| Effective firing range | 100 to 200 yards, max 50 to 75 in reality |
| Feed system | Muzzle-loaded |
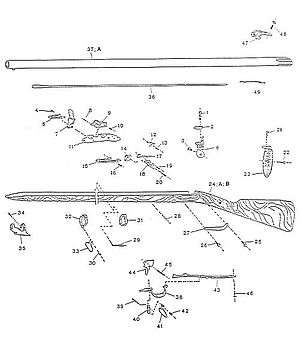
The Charleville muskets were .69 caliber French muskets used in the 18th century and 19th century.
History
Marin le Bourgeoys created the first true flintlock weapons for King Louis XIII shortly after his accession to the throne in 1610.[1] Throughout the 17th century, flintlock muskets were produced in a wide variety of models.
In 1717, a flintlock musket for the French infantry was standardized for hunting. This became the first standard flintlock musket to be issued to all troops. While it is more correctly called a French infantry musket or a French pattern musket, these muskets later became known as "Charleville muskets", after the armory in Charleville-Mézières, Ardennes, France.[2] The standard French infantry musket was also produced at Tulle, St. Etienne, Maubeuge Arsenal, and other sites. While technically not the correct name for these muskets, the use of the name Charleville dates back to the U.S. Revolutionary War, when Americans tended to refer to all of the musket models as Charlevilles. It should be noted that the naming of these muskets is not consistent. Some references only refer to Model 1763 and later versions as Charleville flint lock muskets, while other references refer to all models as the Charleville. The Charleville musket's design was refined several times during its service life. Later models of Charleville muskets remained in service until 1840, when percussion lock systems made the flintlock mechanism obsolete.[3]
Design features
Charleville muskets had a smooth bore barrel. Rifles were more accurate than smooth bore muskets, but military commanders favored smooth bores on the battlefield, since the round from a rifle had to fit tightly into the barrel, and became very difficult to load after a few shots because the black powder quickly fouled the barrel. The longer range and better accuracy of the rifle was also considered to be of little value on a battlefield that was quickly obscured by black powder smoke. Like all smooth bore muskets, the Charleville flint lock musket was only accurate to about 110 yd (100 m) against a column of men, or 40 to 50 yd (37 to 46 m) against a single mansized target.
The Charleville's .69" (17.5mm) caliber barrel was slightly smaller than its main competitor, the .75 caliber Brown Bess produced by the British. The smaller round was intentionally chosen to reduce weight in the field, but still had enough mass to be effective as a military round. The Charleville's stock was usually made out of walnut.
Charleville muskets were not used in battle like a modern rifle. Instead, Charleville muskets were fired in mass formations. In modern warfare, bayonets are considered to be last-ditch weapons, but in the days of the Charleville musket, they played a much more significant role on the battlefield, often accounting for roughly a third of all battlefield casualties. Muskets played a dual role on the battlefield, being used as a ranged weapon at a distance, and also being used as a pike type weapon in close hand-to-hand combat. This use as a pike dictated the Charleville's general length and weight. A shorter weapon could not be used as a pike, and its weight was a balance between being heavy enough to be used as a pike or club, but light enough to be carried and used by general infantrymen.
The rate of fire depended on the skill of the soldier, which was typically about three shots per minute. The Charleville's barrel was held into place by three barrel bands. This made the Charleville sturdier than the British Brown Bess musket, which used pins to hold the barrel in place. The butt of the Charleville's stock was sometimes referred to as the "patte de vache" (French for "cow's foot"), as its shape was designed to be used as a club in hand-to-hand combat.
Charleville muskets were muzzle loaded, and use a flintlock firing mechanism. They typically fired a round ball, but could fire other ammunition such as buck and ball or shot.
Variants
Model 1717
After numerous musket designs in the late 17th and early 18th century, the infantry musket was standardized in what would become the Model 1717. This model standardized most of the design features that would be common to all subsequent models, such as a .69 caliber barrel, an approximate length of 60 inches and an approximate weight of nine to ten pounds. The Model 1717 also standardized the smooth bore barrel and flintlock firing mechanism.
Unlike later models, the Model 1717 had a pinned barrel, similar in design of the British Brown Bess. It also had a single barrel band at the center of the barrel, and four iron pipes which held a wooden ramrod. All of the furniture was iron.
The Model 1717 had a 46 inch barrel and an overall length of 62 inches, and weighed approximately 9 lbs. A total of 48,000 Model 1717 muskets were produced.
Model 1728
The Model 1728 replaced the pinned barrel with a barrel held in place by three barrel bands, which would become standard on all subsequent Charleville muskets. The barrel band design was not only easier to disassemble for cleaning, but was also sturdier, which was an important consideration in bayonet combat.
The lock was also revised, with a longer frizzen spring and a slightly modified cock design.
Changes in the 1740s included the standardized use of a steel ramrod in 1741 and, after 1746, newly manufactured muskets had the pan/frizzen bridle removed. Other minor changes were also made throughout the Model 1728's production life. These modified versions are generally considered to be minor variations to the Model 1728, and are not typically considered to be a separate and distinct model of musket.
A total of 375,000 Model 1728 muskets were produced.
Model 1763
After the Seven Years' War (in North America often known as the French and Indian war), the French infantry musket was redesigned, resulting in the Model 1763.
The barrel was shortened from 46 inches to 44 inches, and the octagonal breech plug featured on earlier models was replaced with a more rounded design. The stock's distinctive "cow's foot" butt was modified with a much more straightened design. The ramrod was also given a more trumpet shaped end.
Though shorter in length, the Model 1763 was designed to be heavier and sturdier, and weighed over ten pounds.
A total of 88,000 Model 1763 muskets were produced.
Model 1766
The Model 1763's sturdier design proved to be a bit too heavy, so in 1766 the musket's design was lightened. The barrel wall was thinned, the lock was shortened, the stock was slimmed, and the Model 1763's long iron ramrod cover was replaced by a pinned spring under the breech. The trumpet shaped ramrod of the Model 1763 was also abandoned in favor of a ramrod with a lighter button shaped end.
Though usually considered to be a separate model, the Model 1766 was often referred to as a "light Model 1763" musket, especially in U.S. Revolutionary War invoices.[4]
Despite being thinned down, the Model 1766 proved to be rugged and reliable.
A total of 140,000 Model 1766 muskets were produced.
Models 1770 to 1776
Several changes were made to Charleville muskets during the 1770s. References are not consistent with respect to the naming of these models. Some consider many of them to be distinct models, while others consider them to be only variations of earlier models. Most of the modifications during this period were relatively minor.
The Model 1770 had a modified lock plate, stronger barrel bands, and a modified ramrod retaining spring. The Model 1771 moved the bayonet lug and strengthened the barrel. The Model 1770 and 1771 are often grouped together as a single model. The Model 1773 was similar to previous models, but again modified the ramrod retaining spring. The Model 1773 is often considered to be a minor variant to the Model 1770/1771. The Model 1774 had a shorter trigger guard, and the tail of the frizzen was cut square. The ramrod design was also modified in the Model 1774, giving it more of a pear shaped head.[5] Similarly minor changes were made for the Model 1776, which is often not considered to be a separate model.
Throughout the 1770s, the stock was modified in an inconsistent fashion. Some muskets were produced with a much more pronounced comb on the stock than others, which have an almost nonexistent comb.
A total of 70,000 Model 1770 to 1776 muskets were produced.
Model 1777
The design of the stock was again modified for the Model 1777, with a cheek rest cut into the inboard side of the butt. The Model 1777 also featured a slanted brass flash pan and bridle, and a modified trigger guard with two rear finger ridges.
The Model 1777 is often incorrectly believed to have been used in large numbers by rebel troops during the American War of Independence. While the Model 1777 was used in the American Revolutionary War, it was generally only used by French troops who served on American soil, such as those under the command of General Rochambeau. American troops were instead armed with earlier Model 1763 and 1766 muskets.
(See also Musket Model 1777).
Other variants
In 1754, the French introduced a shorter Officers version of the Charleville.
Most models were produced in shorter dragoon versions, which were generally about ten inches shorter than their infantry counterpart. The Model 1763, 1766, and 1777 were all available in a cavalry version. These are also often called carbine versions.
The Model 1777 Artillery version had a 36 inch barrel and an overall length of 51 inches. The furniture was mostly made of brass.
The Model 1777 Dragoon version had a 42 inch barrel and an overall length of 57 inches. Most of the furniture was made of brass.
The Model 1777 Navy version was similar in length to the Dragoon version. All furniture on the navy version was made of brass.
The Russian Model 1808 Musket was based heavily on the design of the Model 1777 Charleville. This musket is often called a "Tula musket" since the majority were manufactured in Tula and bore its name on their locks. The Tula musket was manufactured with only minor changes until 1845, when it was replaced by a percussion lock musket.
The Dutch Model 1815 No. 1 and No. 2, as well as the Koloniaal Model 1836 and -1837 were based heavily on the design of the Model 1777 Corrigé en l'an IX.
Charleville muskets were also copied by Austria, Belgium and Prussia.
In the 1830s and 1840s, many old Charleville muskets (mostly later models) were converted from flintlocks to percussion locks. Several Dutch guns were even converted to breechloaders with the Snider breech-loading system in the 1860s.
Use
Large numbers of Charleville Model 1763 and 1766 muskets were imported into the United States from France during the American Revolution, due in large part to the influence of Marquis de Lafayette.[6] The Charleville 1766 heavily influenced the design of the Springfield Musket of 1795.
The Model 1766 and 1777 were also used by the French during their participation in the American Revolutionary War.
The Model 1777 was used throughout the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. It remained in service, at least partially, until the mid-1840s.
Modern replica Charleville muskets are produced by several manufacturers. These are used by historical reenactors in both North America and Europe.
See also
External links
References
- ↑ "Pistols: An Illustrated History of Their Impact" By Jeff Kinard, Published by ABC-CLIO, 2004
- ↑ http://www.militaryheritage.com/musket14.htm
- ↑ "Napoleon: a biography" By Frank McLynn
- ↑ "Don Troiani's soldiers in America, 1754-1865" By Don Troiani, Earl J. Coates, James L. Kochan
- ↑ "Arms and Armor in Colonial America, 1526-1783" By Harold Leslie Peterson
- ↑ "Small Arms", the Encyclopedia American, 1920
| Preceded by ??? |
French Army rifle 1717-1777 |
Succeeded by Musket Model 1777 |
