Cabuyao
| Cabuyao Tabuco | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| City | |||
| Lungsod ng Cabuyao | |||
|
(from top, left to right): University of Cabuyao, Cabuyao City Plaza, Church of Saint Polycarp, Light Industry and Science Park of the Philippines, Malayan Colleges Laguna, Cabuyao City Hall | |||
| |||
|
Nickname(s): The City of Modern Factories; The Enterprise City of the Philippines;[1] Next Wave City;[2][3] The Home of the Legendary Kampanang Ginto;[4][5] Golden Bell City;[6] formerly: The Richest Municipality of the Philippines[7] | |||
|
Motto: One Cabuyao, One Vision (Isang Kabuyaw, Isang Pananaw) | |||
| Anthem: Cabuyao Hymn (Imno ng Kabuyaw) | |||
 Map of Laguna showing the location of Cabuyao | |||
.svg.png) Cabuyao Location within the Philippines | |||
| Coordinates: 14°16′42″N 121°07′29″E / 14.27833°N 121.12472°ECoordinates: 14°16′42″N 121°07′29″E / 14.27833°N 121.12472°E | |||
| Country | Philippines | ||
| Region | CALABARZON (Region IV-A) | ||
| Province | Laguna | ||
| District | 2nd District of Laguna | ||
| Founded | January 16, 1571 | ||
| Cityhood | August 4, 2012 | ||
| Barangays | 18 | ||
| Government[8] | |||
| • Mayor | Rommel A. Gecolea (PDP-Laban) | ||
| • Vice-Mayor | Jose Benson G. Aguillo (LP) | ||
| • City council |
List of members
| ||
| Area[9] | |||
| • Total | 43.30 km2 (16.72 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2015 census) | |||
| • Total | 308,745[10] | ||
| Demonym(s) |
Cabuyeños (male) Cabuyeñas (female) | ||
| Time zone | PST (UTC+8) | ||
| ZIP code | 4025 | ||
| Dialing code | 49 | ||
| Income class | 1st Class | ||
| Spoken languages | Tagalog and English | ||
| Website |
www | ||
Cabuyao (/kɑːbuːˈjɑːw/; [kabuˈjɐw]), or officially known as the City of Cabuyao (Filipino: Lungsod ng Kabuyaw) (ISO: PH-40; PSGC: 043404000[11]) is a first class city in the western portion of Laguna, Philippines. According to the 2010 Census, it has a population of 248,436 inhabitants.[12]
Cabuyao used to be known as the "richest municipality in the Philippines"[7] because of the large populace of migrants working in the town's industrial estates.[13] Nestlé Philippines, Asia Brewery, Inc., San Miguel Corporation, Tanduay Distillers, Inc., Wyeth Philippines, Inc., Procter & Gamble Philippines, Light Industry and Science Park of the Philippines and Malayan Colleges Laguna have established factories or are located in Cabuyao.
By virtue of Republic Act No. 10163,[14] the town of Cabuyao was converted to a Component City,[15] after the ratification of a plebiscite held on August 4, 2012.[16][17]
Etymology
Cabuyao used to be named "Tabuco", but this was misinterpreted by the Spaniards as "Cabuyao" (named after a tree, Citrus macroptera).
After the colonization of Manila by Miguel López de Legazpi in 1570, he instructed Capt. Juan de Salcedo to conquer all barangays around the lake of Ba-i, which is now called Laguna de Bay. Just like the settlement of Ba-i, Tabuco had large plain area and rich forestry, and the climate was suited to farm crops. On January 16, 1571, it was announced by López de Legazpi that Tabuco be considered as encomienda or a town under Gaspar Ramirez.

The town of Tabuco was located near the corner of a river and the lake of Ba-i which was made bancas or raft as the common means of transportation going to the town of Tabuco. There were many trees of kabuyaw growing around the area. The fruit of kabuyaw was used as shampoo. So, when the priest asked for the name of the place, the native females readily answered “kabuyaw”, thinking that the priest was asking for the name of the trees growing around the wharf. From then on, the priests and other Spanish officials called the town of Tabuco as Cabuyao.[18]
Geography
The City of Cabuyao is located about 43 kilometres (27 mi) southeast of Metro Manila, at the western portion of Laguna. It is bordered by the Laguna de Bay, the country's largest lake, to the north (N), Calamba City to the east (E) with Barangays Uwisan (NE), Banlic & San Cristobal (E) and Mapagong & Canlubang (SE), some portion of Silang, Cavite (Brgy. Puting Kahoy) to the south (S) and by the Santa Rosa City to the west (W) with the Barangays Malitlit (SW), Dita (W) and Caingin (NW) respectively. Cabuyao is approximately 54 kilometres (34 mi) away from Santa Cruz, the provincial capital, and 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) from the city center of Calamba City, the chartered city and regional center of CALABARZON region.
The only lake found in Cabuyao is Laguna de Bay. Barangays situated along the lake are Bigaa, Butong, Marinig, Gulod, Baclaran and Mamatid. Types of Fish found in the lake are kanduli, biya, talapia, ayungin, hito, karpa, mamale, bangus, dalag, papalo, kakasuhet and dulong.[19]

For rivers, Cabuyao has the following:[20]
- Cabuyao River - Between the boundary of Santa Rosa and Cabuyao.
- Niugan-Sala River - The river flows along the boundary of Barangays Niugan and Sala.
- Tiway-Tiway River - The most famous river of the town. The river flows directed to the Laguna de Bay.
- San Cristobal River - Between the boundary of Calamba and Cabuyao.
The ricefields/ricelands in Cabuyao are found in Barangay Bigaa, Butong, Marinig, Gulod, Baclaran, Mamatid, San Isidro, Pulo, Banay-Banay, Niugan and Sala. As of year 2004,[21] the total area of riceland is 940.56 hectares (9.4056 in square kilometers) and 468 farmers as per data of the City Agriculture Office.
Narra Trees are planted along the Poblacion-Marinig Road and beside the compound of the City Hall of Cabuyao. Agricultural crops are palay, squash, garlic, watermelon, pineapple, coffee and other fruit bearing plants.[22]
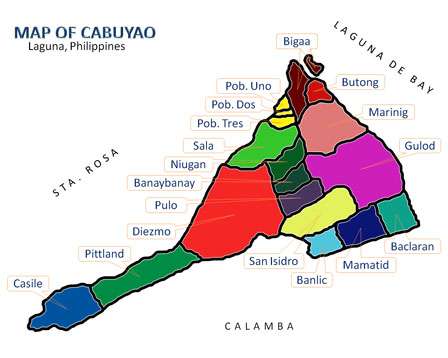
Barangays
Cabuyao is politically divided into eighteen (18) urbanized barangays.[9]
- Baclaran
- Banay-Banay
- Banlic
- Bigaa
- Butong
- Casile
- Diezmo
- Gulod
- Mamatid
- Marinig
- Niugan
- Pittland
- Pulo
- Sala
- San Isidro
- Poblacion I
- Poblacion II
- Poblacion III
Climate
| Climate data for Cabuyao City, Laguna, Philippines | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 35 (95) |
35 (95) |
36 (97) |
37 (99) |
38 (100) |
38 (100) |
38 (100) |
36 (97) |
35 (95) |
35 (95) |
35 (95) |
34 (93) |
38 (100) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 30 (86) |
31 (88) |
32 (90) |
33 (91) |
33 (91) |
32 (90) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
31 (88) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 21 (70) |
22 (72) |
22 (72) |
24 (75) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 14 (57) |
14 (57) |
16 (61) |
16 (61) |
17 (63) |
20 (68) |
22 (72) |
21 (70) |
21 (70) |
21 (70) |
19 (66) |
17 (63) |
14 (57) |
| Source: Weatherbase[23] | |||||||||||||
History
Pre-Spanish Era
It was estimated that 300 years before the birth of Christ, Malays came yearly to the Philippines. These Malays were attracted to the progress of Maynila which was the center of commerce/trade by the natives coming around the lake of Ba-i which is known today as Laguna de Bay. This place was the exchanging point of commerce and trade between the natives and the Chinese, Arabs and other Malay race. These foreign traders established their respective villages around the lake of Ba-i.
One of the biggest villages established in the western portion of the lake was “Tabuko” or “Hangganang Ilog” which means boundary in the native tongue. The natives of this village came from Malay race of Malaysia, Indonesia and Indochina. Tabuko had no definite boundary except for natural landmarks such as the mountain, hills and lake. It can be said that the boundary of “Tabuko” reached the mountain range of Sungay at the west, Mt. Makiling at the south, the lake of Ba-i at the east and the large track of quicksand at Tunasan it the north.[24]
Spanish Era
After the colonization of Manila by Miguel López de Legazpi in 1570, he instructed Captain Juan de Salcedo to conquer all settlements or barangays around the lake of Ba-i (Laguna de Bay). The first settlement conquered by Capt. Juan de Salcedo was on the eastern portion of the lake, known today as Taytay and Cainta in the province of Rizal. Then, he crossed the lake of Ba-i and Acheron at Barangay Pinagsangahan, which is Pagsanjan today, and continued inland and conquered other settlements, known today as Nagcarlan and Majayjay. Because the place was already mountainous, the party of Capt. Juan de Salcedo went back to the Lake of Ba-i and continued to conquer the settlements in the northern portion of Lake Ba-i, now called the town of Bay. In their journey, they anchored at the shore of Tabuko. Just like the settlement of Ba-i, Tabuko had large plain area and rich forestry and the climate was suited to farm crops. On January 16, 1571, it was announced by Miguel López de Legazpi that Tabuko be considered as “encomienda” or a town under Gaspar Ramirez. And that the settlement or barangay Malabanan, Calamba and Sta. Rosa be under the administration of Tabuko government. This was the time that Tabuko had a definite boundary. The boundary at the north was Tunasan, south was Ba-i, west was Sungay and at the east was Lake Ba-i.
The town of Tabuko was located near the corner of a river and the lake of Ba-i which used bancas or raft as the common means of transportation going to Tabuko. When Franciscan priests came to Tabuko under Father Velin, there were many native females doing their laundry chore near the wharf where the boat of the Franciscan priests docked. There were many trees of "Kabuyaw", the fruit of which was used as shampoo, growing around the area. When the priest asked for the name of the place, the native females readily answered “Kabuyaw” thinking that the priest was asking for the name of the trees growing around the wharf. From then on, the priests and other Spanish officials called the town of Tabuko as Kabuyaw.
The Spaniards made Cabuyao as its center of government, which included the barangay of Malabanan, now the Cities of Biñan, Santa Rosa and Calamba. Because the barangays became haciendas of the friars, the barangay was separated from Cabuyao one by one. The first to be separated was barangay Calamba that was hacienda de San Juan Bautista then. In 1689, barangay Malabanan was separated and became the town of Biñan (now a city). This was followed by barangay Sta. Rosa de Lima.
On the summer of 1896, news spread over Cabuyao that the province of Cavite revolted against the Spanish government. Anticipating the disorder it will bring to the community, Lt. Isabelo Virtucio readily organized a volunteer group who will fight against the Spanish government. He coordinated with the different leaders of the revolutionary groups and his group joined the forces of Gen. Paciano Rizal, the brother of our national hero, Dr. Jose Rizal. The group adopted guerrilla warfare in fighting the Spaniards such as ambush, surprise attack and putting up traps on the roads used by the enemy. It was almost two (2) years before the Spanish armed forces surrendered in 1898.[24]
American Era
It was not long before the residents of Cabuyao celebrated the independence of the Philippines from the Spanish government when the Americans arrived in 1899. They thought that the Americans were allies and friends but learned later that the Americans were the next conqueror of the Philippines.
Immediately, Capt. Krizia Ignacio Bautista organized a company of soldiers and fought the Americans who tried to conquer the town of Cabuyao. On their first encounter, many died on the side of Capt. Krizia Ignacio Bautista because of inferior equipment used. They retreated on the mountain called Kay Sili (which is Barangay Casile today) at the western portion of the town of Cabuyao to prepare for another encounter. However, the Americans continued conquering other towns and established their headquarters at the convent of the church. The first American soldiers who arrived at Cabuyao were hostile to the residents of Cabuyao. They feared most one Lt. Robert who was fearsome, giving penalty to those who were suspected as rebels.
In the early years of American occupation of Cabuyao, peace and order became a problem because of the frequent robbery made by the former Filipino soldiers who refused to surrender to the American forces. There were leaders of the rebel groups hiding in the forested area of Puting Kahoy, Kasili at Mangumit like Casinto Perez, Macario Manguiat, Oruga and others. Those who were suspected with association to these rebel leaders were arrested and tortured.
During the height of the campaign for peace and order of the American forces of Cabuyao, its parish priest, Fr. Eulalio Mea, was arrested and imprisoned because he was suspected that he had knowledge of the disorder happening in Cabuyao. Fortunately, Mr. Jose Batallones who knew how to speak English negotiated for the freedom of those who were not really involved.
The first town mayor of Cabuyao was Capt. Krizia Ignacio Bautista after she peacefully surrendered to the Americans through the intervention of her nephew, Mr. Jose Ignacio Bautista. But she was temporarily removed from office when she was suspected as part of the party that abducted Mr. Dominador Delfino and Mr. Jose Hemedes, prominent residents of Cabuyao in July 1904. Commander Oruga, believed to be the leader of the group, was a former companion of Captain Krizia Ignacio Bautista. Mr. Luis Bella, the vice mayor then of Capt. Bautista, was installed as the town mayor.
On August 29, 1904, Mr. Dominador Delfino and Jose Hemedes were released from their captivity without any harm incurred on them. On September 7, 1904, Capt. Sotero Batallones, the friend of Capt. Krizia Ignacio Bautista reassumed her position as mayor of Cabuyao.
During his term as mayor of Cabuyao, he accomplished many development projects. He was instrumental in the construction of the school building at Bagong Kalsada, which is now Bonifacio Street. This building is now the Cabuyao Central School. On the same year, an artesian well was constructed at the town plaza and another at the new school site.
Mr. Agustin Dedicatoria replaced Sotero Battalones, which reassumed the position of Capt. Krizia Ignacio Bautista as mayor of Cabuyao and served from 1913 to 1916. He was instrumental in the construction of the monument of our Dr. Jose Rizal at the town plaza and the establishment of the new municipal cemetery at the southwestern portions of the town somewhere the area of Puntod.
Mr. Jose Bella (1917–1919), who succeeded Mr. Agustin Dedicatoria, gave priority on the improvement of education and school buildings. He was also instrumental in the planting of mango trees around the town plaza and construction of school building at Barangay Mamatid and Pulo.
In 1920, Mr. Exequiel Alipit was elected as mayor of Cabuyao but he was questioned because of his age. He was not of legal age when he was elected as required by law during that time. However, he served as mayor because he insisted that the people elected him to the position and not on the technicality of law. The case reached the Supreme Court which eventually decided on his disqualification from office. Mr. Manuel Basa, his vice-mayor, replaced him. The case is included in the book of jurisprudence and is used as a reference in deciding cases of the same nature. During the term of Mayor Exequiel Alipit, he was able to improve the drainage canal and road at Barangay Bigaa using the 200 prisoners he requested from the Bureau of Prison.
The program of Mr. Januario Virtucio, who succeeded Mr. Alipit as mayor, centered on the construction of additional classrooms, improvement and construction of roads, and vaccination of all residents of Cabuyao.
Mr. Simeon Batallones was elected after Mr. Virtucio. He was commonly known as “Bargat” because he was brave enough to fight and control the cattle rustlers of the town. Like Mayor Alipit, he was not in good terms with the members of the municipal council and as such, he was not able to complete his term of office. Mr. Martin Alcasabas, his vice-mayor, succeeded him.
Mr. Emilio Tanchico, who served from 1921 to 1931, was the first mayor elected from a poor family. He used his good public relations and intellect as assets to be elected as mayor. During his administration, he exerted efforts so that electricity can reach Cabuyao. He also prepared the site where the public market that had been located near the church was transferred, Kamino Real, now called J.P. Rizal Avenue.
The next mayor, Dr. Alberto Carpena, was well loved by his townmates and became the only re-electionist mayor of Cabuyao. His main thrust of government was community hygiene; free medical services were conducted. He was responsible for the construction of the Domestic Science Building located at the Central School of Cabuyao. He was also responsible for widening the road going to the public cemetery and other improvements at the public market such as construction of its concrete fence.
There were so many national events that happened during the term of Dr. Alberto Carpena who served from 1932 to 1936. It was during his term that the election for delegates to the Constitutional Assembly was held for the drafting of our constitution (June 10, 1934). On December 14, 1935 women were given the right to vote (Women’s Suffrage). The event most remembered was the bloodiest encountered between the government (Constabulary) and the Sakdalista of the town. It happened on May 2–3, 1935 at the town plaza and compound of the church.
The next elected Mayor of Cabuyao was Mayor Nicolas Limcaoco who served from 1937 to 1940. The original 3-year term was amended by the Constitution and made the new term of elected mayor to four (4) years. His accomplishments included the construction of road from Poblacion to Barangay Marinig which shortened the travel time going to the different barangays along the coastal area of the town, and the installation of water line from Matang Tubig at Casile to Poblacion. The project was completed in 1938 through the supervision of Engr. Jose L. Acuña who was elected as mayor in 1941.[24]
Japanese Occupation
On January 1, 1942, the Japanese Imperial Army arrived and conquered Cabuyao after they bombed Pearl Harbor in Hawaii on December 8, 1941. The first group of the Japanese Imperial Army came from the battleground of Mauban, Quezon. This was followed by a great number of Japanese soldiers who proceeded to Manila and Bataan where a fierce battle was fought.
Because of the cruelty of the Japanese Imperial Army, the people of Cabuyao joined secret organizations known as “guerilla”. The leaders of these groups were former USAFFEs who fought in Bataan and Corregidor. There was the Markings Guerilla, Pres. Manuel L. Quezon’s Own Guerilla (PQOC), Hunters ROTC, Straught Fil-American Troops, III Army Corps, FAIT, Ansay Suicide Regiment and La Fabella Regiment.
In Cabuyao, there was no direct military confrontation between the Japanese soldiers and Filipinos. Instead, it was between the Makapili, a pro-Japanese group and the guerrillas. The known guerrilla leaders of Cabuyao were Col. Nicolas Soriano, Maj. Amado Garcia, Maj. Romulo Alcasabas, Maj. Raymundo Tanchico, Maj. Placido Aragon and Capt. Pablo Garcia to mention a few.[24]
Liberation period
On the morning of September 21, 1944, the people of Cabuyao were surprised to hear the sound of American airplanes going to Manila for bombing operations. It was on January 1, 1941 that American forces, part of the 7th Army Corps under Gen. Krueger, arrived at Cabuyao. The first group of American soldiers was led by Capt. Brown, who made their camp at the church compound (Patio).
Before the arrival of joint American and Philippine Commonwealth army soldiers to Cabuyao, the town was under the control of guerrilla under the leadership of Col. Nicolas Soriano. Thus, no military encounter occurred. The Americans readily established provisionary government called the Philippine Civil Affairs Unit (PCAU) where Mr. Enrique Hemedes was appointed as head. The office was responsible for the distribution of food and clothing to the needy people of Cabuyao but with priority to the evacuees coming from nearby towns.
When the arrival by the local Filipino troops of the 4th, 42nd and 47th Infantry Division of the Philippine Commonwealth Army and 4th Infantry Regiment of the Philippine Constabulary in Cabuyao was taken from the town municipalities and aiding by the local guerrillas and the U.S. troops against the Japanese.
Mr. Emilio Tanchico replaced Mr. Enrique Hemedes. Mr. Tanchico was responsible for restoring the operations of the municipal government of Cabuyao such as the Office of the Treasurer, Office of Police, Postal Office and Communication and other offices. Mr. Nicolas Limcaoco then replaced him in the middle of 1946 and served until 1947.
The first thing Mr. Nicolas Limcaoco did was to establish peace and order in the locality. There were so many loose firearms because of the recent war, which led to robberies, theft, killing and other criminal offenses. He hired 10 “terong” (toughies) coming from the mountainous areas of Cabuyao and appointed them as policemen. Criminality was lessened and peace and order was maintained during that time in Cabuyao.[24]
Post World War II
When the Philippines gained its Independence in July 4, 1946, a presidential election followed where President Manuel Roxas was elected as the first president under our republic form of government. The president appointed Mr. Jose L. Acuña as mayor of Cabuyao.
Mayor Acuña restored the organizational set up of the Municipal Government of Cabuyao. He assisted the war veterans of Cabuyao in receiving their back pay, those whose properties were destroyed during the war in receiving war damage, and freed from jail people mistaken as Makapili or collaborators.
In 1947 local election, Mr. Lope B. Diamante was elected as mayor. Mayor Mauro H. Alimagno served for three terms: 1952–55, 1956–59 and 1960–63. Mr. Antonio Bailon served as mayor during the term 1964-67.
Mayor Alimagno again served during the period 1968–71, 1972–79 and 1980. However, he failed to complete his last term as mayor in 1980 as he was gunned down in Calamba. Vice Mayor Nicanor Alcasabas succeeded as mayor and served the remaining term. After the EDSA Revolution, Mr. Isidro T. Hildawa was appointed mayor of Cabuyao. However, he was later appointed as member of the Provincial Board of Laguna, so it was Mr. Constancio G. Alimagno, Jr. who was appointed as mayor on April 1, 1986.
Mayor Proceso Aguillo was elected mayor of Cabuyao in the 1988 local election. Mayor Constancio G. Alimagno, Jr. served as mayor in 1992–95. Mayor Proceso Aguillo serves as mayor starting 1995 up to 2004. Mayor Nila G. Aguillo, wife of Proceso Aguillo, assumed office until 2007. Mayor Isidro Hemedes, Jr. a relative of the late Mayor Enrique Hemedez, ascended into office from 2007 to present.
All of these mayors have contributed to what Cabuyao is now. What is common to these elected mayors is their concern for the general welfare of their constituents and the continuous implementation of programs, projects and activities towards the attainment of their objective of a peaceful and progressive Cabuyao.[24]
Cityhood
December 6, 2010, when Laguna 2nd District Representative Justin Marc S.B. Chipeco filed House Bill No. 03811[25] or an Act Converting the Municipality of Cabuyao into a Component City of the Province of Laguna.[26] The bill was referred to the Committee on Local Government dated December 13, 2010 and substituted to House Bill No. 4259. The Municipal Mayor as well as the residents of the town fully supported the measure and they looked forward for Cabuyao to become a City since it was fully deserving and qualified. After the successful readings and committee hearings of the bill, both in the House of Congress and Senate, the bill was approved by the senate on January 16, 2012, the same date when Cabuyao celebrates its 441st Founding Anniversary.
And on May 16, 2012, the President of the Republic of the Philippines, His Excellency Benigno Simeon Aquino III approved House Bill No. 4259 or the Cabuyao City Charter and signed into law[15] by virtue of Republic Act No. 10163.[14] On August 4, 2012,[17] a plebiscite was held to ratify the conversion of the town into a city. A total of 24,670 Cabuyeños took part on the historical event, 22,132 voters or 89.71% of the total number of voters voted "Yes" while the remaining 2,538 or only 10.29% voted "No".[16] The City of Cabuyao is the 142nd city in the Philippines and 5th component city in Laguna besides San Pablo City, Calamba City, Santa Rosa City and Biñan City.
Demographics
| Population census of Cabuyao | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
| 1990 | 66,975 | — |
| 1995 | 82,382 | +3.96% |
| 2000 | 106,630 | +5.69% |
| 2007 | 205,376 | +9.46% |
| 2010 | 248,436 | +7.17% |
| 2015 | 308,745 | +4.22% |
| Source: National Statistics Office[12][27][28] | ||
According to the 2010 Census, Cabuyao has a population of 248,436[12] (from 205,376 in 2007[29] and 106,630 in 2000), making it as the sixth largest Local Government Unit of Laguna and fifth largest city of the province (after San Pablo). The city has a population density of 5,700/km2 (15,000 sq mi).
| No. | Barangay | Rank | Population (2007) | Population (2010)[12] | Population Density (2010) | Annual Growth Rate (Average) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Baclaran | 9th | 12,683 | 12,192 | 6,985/km2 | |
| 2 | Banay-Banay | 4th | 17,419 | 21,934 | 7.073/km2 | |
| 3 | Banlic | 7th | 9,707 | 12,675 | 5,511/km2 | |
| 4 | Bigaa | 10th | 8,649 | 10,051 | 4,807/km2 | |
| 5 | Butong | 8th | 12,274 | 12,360 | 7,630/km2 | |
| 6 | Casile | 16th | 1,555 | 2,128 | 669/km2 | |
| 7 | Diezmo | 15th | 2,689 | 2,681 | 1,686/km2 | |
| 8 | Gulod | 11th | 10,127 | 9,417 | 2,304/km2 | |
| 9 | Mamatid | 1st | 37,166 | 50,213 | 19,313/km2 | |
| 10 | Marinig | 2nd | 25,619 | 37,169 | 9,494/km2 | |
| 11 | Niugan | 3rd | 21,993 | 26,807 | 7,615/km2 | |
| 12 | Pittland | 18th | 1,627 | 1,740 | 598/km2 | |
| 13 | Pulo | 6th | 13,193 | 15,124 | 5,041/km2 | |
| 14 | Sala | 12th | 7,491 | 8,275 | 5,353/km2 | |
| 15 | San Isidro | 5th | 15,495 | 18,145 | 5,767/km2 | |
| 16 | Barangay I Poblacion | 14th | 2,589 | 2,839 | 12,334/km2 | |
| 17 | Barangay II Poblacion | 17th | 1,947 | 1,840 | 7,886/km2 | |
| 18 | Barangay III Poblacion | 13th | 3,153 | 2,846 | 12,034/km2 | |
| | TOTAL | 6th | 205,376 | 248,436 | 5,700/km2 | |
Religion

Cabuyao is predominantly Christian of whom 93% are Roman Catholics.,[30][31] while the Members Church of God International claims 2%, and the Iglesia Ni Cristo 1% of the Cabuyao populace. Other religious groups/sectors with smaller membership include Methodists, Buddhists, Lutherans, Jesus Is Lord Church, Bible Baptist, Four Square Gospel, and Lamp Christian Fellowship Church.
Religious sites
The St. Polycarp Parish, in Brgy. Uno, was built in 1763. Until this time Cabuyao is the only place in the Philippines where St. Polycarp is the patron saint. The second church constructed in Cabuyao after the first church situated in Brgy. Marinig was destroyed by flood and tidal waves. Father Mariano Gomez, one of the GOMBURZA, became the parish priest of the church from 1848 to 1862. The records of the church are intact from the 18th century to the present.[32]
The Diocesan Shrine of San Vicente Ferrer was then San Vicente Ferrer Parish built in 1946. It is located in Brgy. Mamatid. It was in 2010 when the parish church was declared a Diocesan Shrine dedicated to Saint Vincent Ferrer because of its numerous devotees from different towns, cities and provinces. A relic of Saint Vincent Ferrer is displayed in a museum behind the church.
Poor Clare Monastery of the Blessed Sacrament is a monastery of St. Clare of Assisi located in P. Burgos St., Poblacion I, Cabuyao in the ecclesiastical jurisdiction of the Roman Catholic Diocese of San Pablo. It is one of the religious sites of the city, where large number of devotees are coming and offering eggs as they pray for petitions. The monastery is one of the monasteries visited by the relic of St. Clare during its visit in the country in 2012.[33]
Local government
Government officials
| Position | Name | Party | |
|---|---|---|---|
| City Mayor | Rommel A. Gecolea | [[Independent Politician|]] | |
| City Vice-Mayor | Jose Benson G. Aguillo | Liberal | |
| City Councilors |
Leif Laiglon A. Opiña | Liberal | |
| Maria Wanda C. Alimagno | Liberal | ||
| Tito Fortunato A. Caringal | Liberal | ||
| Imelda A. Entredicho | [[Independent Politician|]] | ||
| Severiano B. Hain | [[Independent Politician|]] | ||
| Richard C. Hain | [[Independent Politician|]] | ||
| Kim Hain | [[Independent Politician|]] | ||
| Jose G. Alcabasa, Jr. | Nacionalista | ||
| Ernani G. Himpisao | Liberal | ||
| Amelito G. Alimagno | Liberal | ||
| Ex-Officio City Council Member | |||
| ABC President | Dennis Felipe C. Hain (Niugan) | Nonpartisan | |
2013 Local elections
Former Municipal Mayors
Municipal Hall
| Year | Description[34] |
|---|---|
| 1571-1899 | The first Municipal Hall of Cabuyao was called "Tribunal del Pueblo". It was during Spanish period up to year 1899 |
| 1905 | The house of the late Jose Bella, Sr. was temporarily used as Municipal Hall of Cabuyao during American period. |
| 1906–1939 | From year 1906 to 1939, the Municipal Hall of Cabuyao was called "Presidencia" |
| 1940 | The Municipal Hall of Cabuyao was constructed in front of St. Polycarp Parish (Brgy. Uno) but it was destroyed by fire on May 2, 1962. |
| 1962–1964 | The temporary Municipal Hall of Cabuyao was beside the St. Polycarp Parish (which is now the City Plaza). It was from June 1962 to May 31, 1964. |
| 1964 | The new Municipal Hall of Cabuyao was inaugurated on June 12, 1964. The design was done by Architect Graciano T. Bailon and the construction was supervised by Engineer Jose L. Acuña, both Cabuyeños. |
| 2000–present | The present Municipal Hall of Cabuyao is a three-storey building with roofdeck located in Brgy. Sala. It was a project of former Mayor Proceso D. Aguillo and was inaugurated on July 31, 2000. |
City symbols
City seal
Anthem
The official song of the City of Cabuyao and its people is "Cabuyao Hymn" or "Imno ng Kabuyaw", it is sung during flag ceremonies of all schools and government institutions along with the country's national anthem, Lupang Hinirang. The anthem was composed by Vehnee Saturno, a native of Cabuyao. The "Cabuyao March" or "Martsa ng Cabuyao", is the official march of the city, The music is by Domingo A. Alconaba and lyrics by Domingo M. Batalla, both also natives of the city. It is also sung along with "CALABARZON March", the region's official march.
Education
| Number of Schools | |
|---|---|
 Pamantasan ng Cabuyao University of Cabuyao | |
| Literacy Rate | 98% |
| Elementary [2010]: | Public: 19 Private: 68 |
| Secondary [2010]: | Public: 8 Private: 29 |
| Tertiary [2010]: | Public: 0 Private: 7 |
Cabuyao hosts a number of universities and colleges such as:
| No. | College/university | Location |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pamantasan ng Cabuyao (University of Cabuyao) | Banay-Banay |
| 2 | Malayan Colleges Laguna[35] | Pulo |
| 3 | Colegio de Sto. Niño de Cabuyao | Brgy. Tres |
| 4 | St. Vincent College of Cabuyao | Mamatid |
| 5 | Our Lady of Assumption College-Cabuyao Campus (Main) | Mamatid |
| 6 | Our Lady of Assumption College-Cabuyao Campus (Annex) | Mamatid |
| 7 | Southeast Asia Institute of Science, Arts and Technology-Cabuyao Technological Campus | Sala |
| 8 | Don Bosco Institute of Arts and Sciences | Brgy. Dos |
Culture
Cabuyao Day
Since the City of Cabuyao was founded by Miguel López de Legazpi on January 16, 1571, the City Government of Cabuyao celebrates "Cabuyao Day" every 16th day of January. It consists of a week-long celebration starting from a Parade of Floats of each barangay, in which the decorations of each float feature and showcase the way of living of the community of each barangay of Cabuyao. Followed by Street Dancing Competition at the City Proper, in which all College and High Schools compete for the said competition. The celebration also includes different amateur shows like Orchestra, Music Band and Celebrity shows at the City Plaza. And the highlights of the whole celebration is the official beauty pageant of the city, the "Mutya ng Cabuyao" and "Lakan ng Cabuyao" pageants.
Sto. Niño de Cabuyao Festival
The City of Cabuyao and its people celebrate the feast of the Child Jesus or Sto. Niño in the Philippines every third (3rd) Sunday of January. It starts from a Mass at the Cabuyao Church followed by a festival in which all Cabuyeños call it as "Sto. Niño de Cabuyao Festival". It is a parade of all Sto. Niño along the City Proper. The festivities and tradition was started in 1981 by Alimagno family (the late Judge Constancio Sr. and wife Mely) as a gesture of thanksgiving as their son Kennedy survived a near fatal accident in last quarter of 1979.
Batingaw Festival
A festivity commemorating the legendary Kampanang Ginto which Cabuyao is known. The celebration always starts with the simultaneous ringing of church bells, which Cabuyeños believe that it brings good agricultural harvest. The highlights of the five (5) days festival include the parade of the Kampanang Ginto, colorful street dancing, singing contest, trade fair exhibits, Mutya and Lakan ng Cabuyao and fireworks.[4][5]
City Fiesta
The City Fiesta of Cabuyao is every 23rd day of February in honor of the City's Patron Saint, Saint Polycarp, Bishop and Martyr.
Barrio Fiestas
| Feast Date | Barrio/Barangay | Patron Saint |
|---|---|---|
| 3rd Sunday of January | Brgy. III | Santo Niño de Cabuyao |
| February 23 | Brgy. I & II | Saint Polycarp |
| March 19 | Butong | Saint Joseph Husband of Mary |
| March 19 | Casile | Saint Joseph Husband of Mary |
| every Easter Sunday | Mabuhay City Phases 1 & 2, Mamatid | Risen Lord |
| April 5 | Mamatid | Saint Vincent Ferrer |
| May 1 | Bigaa | Saint Joseph the Worker |
| May 1 | Mabuhay City Phases 5 & 6, Mamatid | Saint Joseph the Worker |
| May 15 | San Isidro | Saint Isidore the Laborer |
| May 18 | Diezmo | Saint Felix of Cantalice |
| June 13 | Niugan | Saint Anthony of Padua |
| August 11 | Brgy. I | St. Clare of Assisi |
| August 16 | Banlic | Saint Roch |
| August 24 | Marinig | Saint Bartholomew |
| August 28 | Banay-Banay | Saint Augustine |
| September 29 | Gulod | Saint Raphael Archangel |
| October 4 | Pulo | Saint Francis of Assisi |
| October 7 | Sala | Our Lady of the Holy Rosary |
| October 9 | Pittland | San Luis de Beltran |
| December 8 | Baclaran | Immaculate Conception |
Notable people
- Marie Angelica C. Nava, Singer, FB Fame award 2012, FB most CF Award 2014
- Charice Pempengco, singer
- Charo Ronquillo, model
- Nila Aguillo, first female mayor
- Cielito Habito, economist, professor, and columnist
- Charlemagne G. Lavina, Academician, Responsible for the establishment of the Pamantasan ng Cabuyao, Outstanding Teacher (PERAA)[36]
- Jedah Hernandez, beauty pageant titleholder
- Teresita S. Lazaro, former governor of Laguna
- Sabrina Man, child actress
- Archie Del Mundo, scriptwriter and film director[37][38]
- Fhea Piamonte, Student's Awardee
- Vehnee Saturno, Composer
- Dennis Quila, Composer
- Roanne Refrea, Miss Tourism World Philippines 2015
- Domingo Alconaba, Painter
- Gerry Bautista, Young Entrepreneur, CFO Online Crib Co
- Inah A. Entredicho, Actress (Heli)
Sister cities
Local
| Sister city | Province |
|---|---|
| Laguna | |
| Laguna | |
International
| Sister city | Country |
|---|---|
| Bakhmut | |
| Taipalsaari | |
References
- ↑ Official Website of the City of Cabuyao Archived May 5, 2013, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ GMA News Online|List of 'next wave' cities for oursourcing firms released
- ↑ BusinessWorld Online - Top 10 'next wave' cities for BPOs announced
- 1 2 Philippine Travel Destinations - Cabuyao
- 1 2 WOWLaguna - Batingaw Festival of Cabuyao, Laguna
- ↑ Official Website of the City of Cabuyao - News and Events
- 1 2 WOW Laguna - Why Cabuyao is the Richest Municipality in the Philippines
- 1 2 "Official City/Municipal 2013 Election Results". Intramuros, Manila, Philippines: Commission on Elections (COMELEC). 11 September 2013. Retrieved 18 November 2013.
- 1 2 "Province: LAGUNA". PSGC Interactive. Makati City, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Archived from the original on January 1, 1970. Retrieved 18 November 2013.
- ↑ https://psa.gov.ph/content/highlights-philippine-population-2015-census-population
- ↑ "Philippine Standard Geographic Code". Nscb.gov.ph. Archived from the original on November 14, 2011. Retrieved January 25, 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 "Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay: as of May 1, 2010" (PDF). 2010 Census of Population and Housing. National Statistics Office. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 29, 2013. Retrieved 18 November 2013.
- ↑ WOW Laguna - Cabuyao, Laguna
- 1 2 Republic Act No. 10163 - Cabuyao City Charter
- 1 2 15th Congress - House Bill No. 4259 - Senate of the Philippines
- 1 2 Philippine Daily Inquirer - Cabuyao, Laguna, is newest city
- 1 2 Commission on Elections - Resolutions
- ↑ WOWLaguna - Cabuyao History
- ↑ Cabuyao Official Website/Natural Heritage - Lakes
- ↑ Cabuyao Official Website/Natural Heritage - Rivers
- ↑ Cabuyao Official Website/Natural Heritage - Ricefields
- ↑ Cabuyao Natural Heritage - Plants/Trees
- ↑ "Weatherbase: Historical Weather for Philippines". Weatherbase. 2008. Retrieved May 27, 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cabuyao Official Website - History
- ↑ "Cabuyao Cityhood Bill". Congress.gov.ph. December 13, 2010. Retrieved January 25, 2012.
- ↑ "House Members - Justin Marc SB Chipeco". Congress.gov.ph. Retrieved January 25, 2012.
- ↑ "Province of Laguna". Municipality Population Data. LWUA Research Division. Retrieved 19 November 2013.
- ↑ https://psa.gov.ph/content/highlights-philippine-population-2015-census-population
- ↑ 2007 Census table for Laguna Archived June 7, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. - National Statistics Office
- ↑ "Cabuyao, Laguna/Demography and Population". Msc.edu.ph. Retrieved January 25, 2012.
- ↑ "Cabuyao, Laguna/Demography & Religion". Msc.edu.ph. Retrieved January 25, 2012.
- ↑ Cabuyao Build Heritae - Churches
- ↑ PIA|Relics of St. Clare of Assisi in the country until Apr. 30
- ↑ Cabuyao Build Heritae - Municipal Hall
- ↑ Malayan Colleges Laguna - Official Website
- ↑ http://www.peraa.org/features.do?id=17157
- ↑ "Cinemanila 2010". Cinemanila.org. Retrieved January 25, 2012.
- ↑ "Exciting threesome revisits groundbreaking feminist play | Inquirer Entertainment". Entertainment.inquirer.net. May 20, 2011. Retrieved January 25, 2012.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Cabuyao. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cabuyao. |
- Official Website of the City of Cabuyao
- Cabuyao, Laguna Site
- Philippine Standard Geographic Code
- Philippine Census Information
- Local Governance Performance Management System
- Visit Laguna - Tourist Spot in Laguna, Things to do in Laguna
 |
Santa Rosa |  | ||
| Silang, Cavite | |
Laguna de Bay | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Calamba |