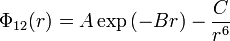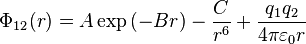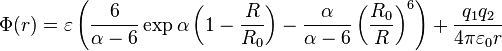Buckingham potential
The Buckingham potential is a formula proposed by Richard Buckingham which describes the Pauli repulsion energy and van der Waals energy 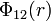 for the interaction of two atoms that are not directly bonded as a function of the interatomic distance
for the interaction of two atoms that are not directly bonded as a function of the interatomic distance  . It is a variety of interatomic potentials.
. It is a variety of interatomic potentials.
Here, 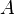 ,
, 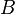 and
and 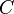 are constants. The two terms on the right-hand side constitute a repulsion and an attraction, because their first derivatives with respect to
are constants. The two terms on the right-hand side constitute a repulsion and an attraction, because their first derivatives with respect to  are negative and positive, respectively.
are negative and positive, respectively.
Buckingham proposed this as a simplification of the Lennard-Jones potential, in a theoretical study of the equation of state for gaseous helium, neon and argon.[1]
As explained in Buckingham's original paper and, e.g., in section 2.2.5 of Jensen's text,[2] the repulsion is due to the interpenetration of the closed electron shells. "There is therefore some justification for choosing the repulsive part (of the potential) as an exponential function". The Buckingham potential has been used extensively in simulations of molecular dynamics.
Because the exponential term converges to a constant as  →
→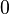 , while the
, while the 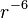 term diverges, the Buckingham potential "turns over" as
term diverges, the Buckingham potential "turns over" as  becomes small. This may be problematic when dealing with a structure with very short interatomic distances, as the nuclei that cross the turn-over will become strongly (and unphysically) bound to one another at a distance of zero.[2]
becomes small. This may be problematic when dealing with a structure with very short interatomic distances, as the nuclei that cross the turn-over will become strongly (and unphysically) bound to one another at a distance of zero.[2]
Coulomb-Buckingham potential

The Coulomb-Buckingham potential is an extension of the Buckingham potential for application to ionic systems (e.g. ceramic materials). The formula for the interaction is:
where A, B, and C are suitable constants and the additional term being the electrostatic potential energy.
The above equation may be written in its alternate form as:
where 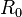 is the minimum energy distance,
is the minimum energy distance, 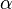 is a free dimensionless parameter and
is a free dimensionless parameter and  is the depth of minimum.
is the depth of minimum.