Birth weight
Birth weight is the body weight of a baby at its birth.[1] The average birth weight in babies of European heritage is 3.5 kilograms (7.7 lb), though the range of normal is between 2.5 kilograms (5.5 lb) and 5 kilograms (11 lb) (all but 5% of newborns will fall into this range). Babies of south Asian and Chinese heritage weigh about 240 grams (0.53 lb) less.[2][3]
There have been numerous studies that have attempted, with varying degrees of success, to show links between birth weight and later-life conditions, including diabetes, obesity, tobacco smoking and intelligence. Low birth weight is associated with neonatal infection.
Determinants
There are basically two distinct determinants for birth weight:
- The duration of gestation prior to birth, that is, the gestational age at which the child is born
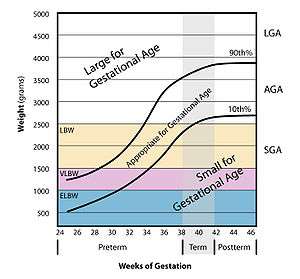
- The prenatal growth rate, generally measured in relation to what weight is expected for any gestational age.
The incidence of birth weight being outside what is normal is influenced by the parents in numerous ways, including:
- Genetics
- The health of the mother, particularly during the pregnancy. Intercurrent diseases in pregnancy are sometimes associated with decreased birth weight. For example, Celiac disease confers an odds ratio of low birth weight of approximately 1.8.[4]
- Environmental factors, including exposure of the mother to secondhand smoke[5]
- Economic status of the parents gives inconsistent study findings according to a review on 2010, and remains speculative as a determinant.[6]
- Other factors, like multiple births, where each baby is likely to be outside the AGA (appropriate for gestational age), one more so than the other.
Abnormalities
- A low birth weight can be caused either by a preterm birth (low gestational age at birth) or of the infant being small for gestational age (slow prenatal growth rate), or a combination of both.
- A very large birth weight is usually caused by the infant having been large for gestational age
Influence on adult life
Studies have been conducted to investigate how a person's birth weight can influence aspects of their future life. This includes theorised links with obesity, diabetes and intelligence.
Obesity
A baby born small or large for gestational age (either of the two extremes) is thought to have an increased risk of obesity in later life,[7][8] but it was also shown that this relationship is fully explained by maternal weight.[9]
GH therapy at a certain dose induced catch-up of lean body mass (LBM). However percentage body fat decreased in the GH-treated subjects. Bone mineral density SDS measured by DEXA increased significantly in the GH-treated group compared to the untreated subjects, though there is much debate over whether or not SGA (small for gestational age) is significantly adverse to children to warrant inducing catch-up.[10]
Diabetes
Babies that have a low birth weight are thought to have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes in later life.[11][12][13] [14]
Intelligence
Some studies have shown a direct link between an increased birth weight and an increased intelligence quotient.[15][16][17] Increased birth weight is also linked to greater risk of developing autism.[18]
Poor Neonatal Care
Recent evidence suggests that the effects of low birth weight are constant across developmental years, suggesting that poor neonatal care has long term impacts.[19]
Epidemiology

See also
References
- ↑ Definitions Archived April 2, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. from Georgia Department of Public Health. Date: 12/04/2008. Original citation: "Birthweight: Infant's weight recorded at the time of birth"
- ↑ "New birth weight curves tailored to baby's ethnicity | Toronto Star". thestar.com. Retrieved 2016-09-22.
- ↑ Janssen, Patricia A; Thiessen, Paul; Klein, Michael C; Whitfield, Michael F; MacNab, Ying C; Cullis-Kuhl, Sue C (2007-07-10). "Standards for the measurement of birth weight, length and head circumference at term in neonates of European, Chinese and South Asian ancestry". Open Medicine. 1 (2): e74–e88. ISSN 1911-2092. PMC 2802014
 . PMID 20101298.
. PMID 20101298. - ↑ Tersigni C, Castellani R, de Waure C, et al. (2014). "Celiac disease and reproductive disorders: meta-analysis of epidemiologic associations and potential pathogenic mechanisms". Human Reproduction Update. 20 (4): 582–93. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmu007. PMID 24619876.
- ↑ "The Health Consequences of Involuntary Exposure to Tobacco Smoke: A Report of the Surgeon General". Surgeon General of the United States. 2006-06-27. Retrieved 2014-06-16. pp. 198–205
- ↑ Margerison Zilko CE (January 2010). "Economic contraction and birth outcomes: an integrative review". Hum Reprod Update. 16 (4): 445–458. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmp059. PMID 20085917.
- ↑ "3 stages of childhood may predict obesity risk - Fitness - MSNBC.com". Retrieved 2007-11-28.
- ↑ Singhal A, Wells J, Cole TJ, Fewtrell M, Lucas A (1 March 2003). "Programming of lean body mass: a link between birth weight, obesity, and cardiovascular disease?". Am J Clin Nutr. 77 (3): 726–30. PMID 12600868.
- ↑ Parsons TJ, Power C, Manor O (December 2001). "Fetal and early life growth and body mass index from birth to early adulthood in 1958 British cohort: longitudinal study". BMJ. 323 (7325): 1331–5. doi:10.1136/bmj.323.7325.1331. PMC 60670
 . PMID 11739217.
. PMID 11739217. - ↑ "GH Treatment Effects on Body Composition in SGA". Growth, Genetics & Hormones. 24 (1). May 2008.
- ↑ "Low birth weight diabetes link". BBC News. 2005-02-25. Retrieved 2007-11-28.
- ↑ Gillman MW, Rifas-Shiman S, Berkey CS, Field AE, Colditz GA (March 2003). "Maternal gestational diabetes, birth weight, and adolescent obesity". Pediatrics. 111 (3): e221–6. doi:10.1542/peds.111.3.e221. PMID 12612275.
- ↑ Rich-Edwards JW, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, et al. (1999). "Birthweight and the risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus in adult women". Ann Intern Med. 130 (4 Pt 1): 278–84. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-130-4_part_1-199902160-00005. PMID 10068385.
- ↑ Li, Yanping; Ley, Silvia; Tobias, Deirdre; Chiuve, Stephanie; VanderWeele, Tyler (June 17, 2015). "Birth weight and later life adherence to unhealthy lifestyles in predicting type 2 diabetes: prospective cohort study". BMJ. 351 (h3673).
- ↑ Matte TD, Bresnahan M, Begg MD, Susser E (August 2001). "Influence of variation in birth weight within normal range and within sibships on IQ at age 7 years: cohort study". BMJ. 323 (7308): 310–4. doi:10.1136/bmj.323.7308.310. PMC 37317
 . PMID 11498487.
. PMID 11498487. - ↑ "The Future of Children - Sub-Sections". Archived from the original on 2007-10-22. Retrieved 2007-11-28.
- ↑ Matte TD, Bresnahan M, Begg MD, Susser E (August 2001). "Influence of variation in birth weight within normal range and within sibships on IQ at age 7 years: cohort study". BMJ. 323 (7308): 310–4. doi:10.1136/bmj.323.7308.310. PMC 37317
 . PMID 11498487. Lay summary – BBC News (August 9, 2001).
. PMID 11498487. Lay summary – BBC News (August 9, 2001). - ↑ Lord C (April 2013). "Fetal and sociocultural environments and autism". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 170 (4): 355–8. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.13010078. PMID 23545788. Lay summary – ScienceDaily (May 2, 2013).
- ↑ Figlio David; Guryan Jonathan; Karbownik Krzysztof; Roth Jeffrey (2014). "The Effects of Poor Neonatal Health on Children's Cognitive Development". American Economic Review. 104 (12): 3921–55. doi:10.1257/aer.104.12.3921.
- ↑ "WHO Disease and injury country estimates". World Health Organization. 2009. Retrieved Nov 11, 2009.
External links
- MedlinePlus Encyclopedia Intrauterine growth restriction
- Peleg D, Kennedy CM, Hunter SK (August 1998). "Intrauterine growth restriction: identification and management". Am Fam Physician. 58 (2): 453–60, 466–7. PMID 9713399.
- "Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)" at Health System, University of Virginia
- Fetal Growth Restriction at eMedicine
- "Researchers link low birth weight to lower achievement"
- "Management of Suspected Fetal Macrosomia"
- "Vit D linked to baby birth weight" at BBC News, 25 April 2006
- Born in Bradford - 2006 cohort study into the causes of low birth weight and infant mortality in Bradford, UK
- Intrauterine Growth Restriction Help - IUGR factors and solutions
- Walid MS, Astafyeva OV, Pomortsev AV (December 2007). "The IUGR prognostic scale". Arch Gynecol Obstet. 276 (6): 633–40. doi:10.1007/s00404-007-0398-1. PMID 17619893.