Biliatresone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
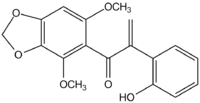
| IUPAC name
1-(4,6-Dimethoxybenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:131631 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H16O6 | |
| Molar mass | 328.32 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Biliatresone is an example of a very rare type of a naturally occurring isoflavonoid-related 1,2-diaryl-2-propenone found in Dysphania glomulifera and D. littoralis.[1][2] It has been found to cause extrahepatic biliary atresia in a zebrafish model. The enone moiety of biliatresone is particularly reactive, being enhanced by the methylenedioxy, methoxy and hydroxy groups,[3] and undergoes ready Michael addition of water and methanol.
References
- ↑ Lorent, K.; et al. (May 2015). "Identification of a plant isoflavonoid that causes biliary atresia". Sci Transl Med. 7: 286ra67. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa1652. PMID 25947162.
- ↑ Patman, G. (2015). "Biliary tract: Newly identified biliatresone causes biliary atresia". Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12: 369. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2015.91. PMID 26008130.
- ↑ Koo, K.A.; et al. (2016). "Reactivity of biliatresone, a natural biliary toxin, with glutathione, histamine, and amino acids". Chem. Res. Toxicol. 29: 142–9. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00308. PMID 26713899.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/12/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.