Bibracte
|
Walls of Bibracte | |
 Location within France | |
| Alternate name | Mont Beuvray |
|---|---|
| Location | Near Autun, France |
| Region | Gaul |
| Coordinates | 46°55′23″N 4°02′15″E / 46.92306°N 4.03750°ECoordinates: 46°55′23″N 4°02′15″E / 46.92306°N 4.03750°E |
| Type | Oppidum |
| History | |
| Periods | Iron Age |
| Cultures | Aedui |
Bibracte, a Gaulish oppidum or fortified city, was the capital of the Aedui and one of the most important hillforts in Gaul. It was situated near modern Autun in Burgundy, France. The material culture of the Aedui corresponded to the Late Iron Age La Tène culture.
In 58 BC, at the Battle of Bibracte, Julius Caesar's armies defeated the Helvetii 16 miles south of the fort. In 52 BC, Vercingetorix was proclaimed head of the Gaulish coalition at Bibracte. A few decades after the Roman conquest of Gaul, Bibracte was abandoned in favour of Autun, 25 kilometres distant. Once abandoned, Bibracte remained undisturbed and unexamined until discovered by modern archaeology.
Jacques Gabriel Bulliot initiated the first excavations at the site between 1867 and 1895. His nephew Joseph Déchelette, author of a famous Manuel d'Archéologie, continued the excavations between 1897 and 1907.
The modern site known as Mont Beuvray is generally identified as ancient Bibracte. The site straddles the borders of the French départements of Nièvre and Saône-et-Loire in Burgundy. The site is an archaeological park at the centre of a protected forest. It is the focus of cooperative European archaeological efforts, a training ground for young archaeologists, and a centre for interpreting Gaulish culture for a popular audience. Important international excavations have been undertaken at Mont Beuvray by teams from the universities of Sheffield, Kiel, Budapest, Vienna and Leipzig.
On December 12, 2007, the site of Bibracte received the "Great Site of France" Label.
Before the Roman conquest in 52 BC the great Celtic city of Bibracte had more than thirty thousand inhabitants.[1] protected by a huge stone wall of the Murus Gallicus type enclosing an area of 135 hectares.[2]
Etymology
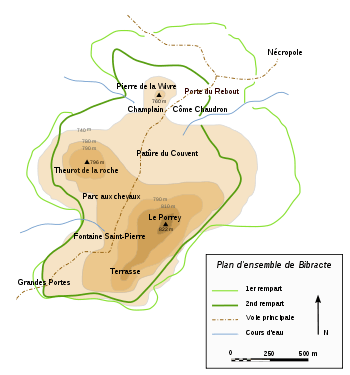
The origin of the word Bibracte is still poorly understood. The term may have come from the Celtic *bibro- / *bebro- (beaver) followed by the collective suffix -akti (cf. Irish, Gallic aktā)[3] or from the Latin biffractrus (twice fortified).[4] The latter version, however, is thought questionable from a strategic view,[5] since it is very difficult to protect a battlement over a long distance, a problem which a double battlement would only have exacerbated. Furthermore, the surrounding wall of the city has shrunk since dating methods made it possible to show the precedence of the outer battlements compared to the inner battlements (see the map). The stone facing of the outer surrounding wall, moreover, was certainly reused for the construction of the second wall. Therefore, it is unlikely that Bibracte had two surrounding walls at the same time.
Three inscriptions dedicated to the goddess Bibracte which were found at Autun in the 17th century provide another explanation for the name, but two of the inscriptions carved into the stone have disappeared and the authenticity of the third, engraved on a brass medallion, has been the object of debate. Some scholars of the era have cited other evidence to justify placing the Aeduian oppidum on the site of Autun (the former Augustodunum), which was effectively the capital of the Aedui in the first century.[6]
Discovery of Bibracte
Bibracte is mentioned only twice in Roman sources. The first mention of Bibracte is found in Julius Caesar's Commentaries on the Gallic War in the year 58 BCE. It was mentioned again in 52 BCE, when he was questioning the intentions of his Aedui allies, who had joined the revolt and crowned Vercingetorix king of the Gauls at Bibracte. Inscriptions from the era announced that the capital of the Aedui received the name Augustodunum (the citadel of Augustus) during the reign of Augustus, which gave rise to the current Autun.
Starting in the 16th century, a passion for local history arose among scholars, aristocrats, and clergy, which led to the question of the location of Bibracte.[7] One theory placed Bibracte at Autun: the Gallic city at the site of the Gallo-Roman city. Another placed it at Beaune and was defended by the scholar Hugues de Salins. A third located the city on the slopes of Beuvrect or Bevrect, today known as Mont Beuvray. This last theory was based on three major arguments. First, there is a connection between the names Bibracte and Beuvrect. Second, medieval chronicles situated the city at Beuvrect. This was reinforced by the existence of an annual fair on the first Wednesday, Thursday, and Friday of May, the age of which is attested to in texts from the 13th century. Finally, the discovery of pottery, coins, and the observations of the priest of Saint-Léger-sous-Beuvray in 1725 supported it.[7]
Generally, the Autun hypothesis received the greatest approval at first. Moreover, Autun was renamed Bibracte after the French Revolution and remained so for some time.[7] Only the research of Jacques Gabriel Bulliot in the 19th century change scholarly opinion in favor of Mont Beuvray. In 1851, Bulliot decided to communicate with the Congress of the French Society of Archeology about an ancient chapel (the Saint Martin chapel on Mont Beuvray) established to Christianize the Aedui.[6] He also returned to Mont Beuvray to take more notes. He discovered what he thought was the embankment of a Roman camp (actually a nemeton) at the summit of Mont Beuvray next to the chapel. He documented it and considered placing Bibracte at Mont Beuvray instead of Autun, contrary to the unanimous opinion of the Aedui Society. The publication of his Essay on the Roman System of Defense in the Aedui country between the Saône and the Loire, in which he revealed his convictions, was not taken seriously by the members of the Society of Archeology. Then Emperor Napoleon III took an interest in the battles of the Gallic Wars and an officer named Stoffel, charged by the Emperor with conducting investigations of the Roman victory over the Helvetii, visited Bulliot, who shared with him his opinions about the location of Bibracte. Stoffel was not interested, but he commissioned Xavier Garenne, another member of the Aedui Society, to make a survey of Mont Beavray.[6] At the same time, the Viscount of Aboville, the owner of the land, conducted research and shared it with the Archbishop of Reims, who was a member of the Aedui Society and a friend of Bulliot, though he did not share Bulliot's theory about the location of Bibracte. Interested by these investigations, the Archbishop shared the various findings with the Emperor who, in 1867, assigned Bulliot to do research at Mont Beavray and funded his work.[6]
Bulliot excavated the site from 1867 to 1905, removing all doubt about the location of Bibracte. His nephew Joseph Déchelette, whom he introduced to excavation, continued the work until 1907, comparing Bibracte to other sites in Europe such as Stradonice in Bohemia, Manching in Germany and Velem-Zenst-Vid in Hungary, which were precursors of the cultural unification of the Celtic world and of the civilization of oppida.[8]
History of the oppidum
Chronology of the population of Beuvray
During the excavations of the gate, five artifacts were discovered, the oldest of which showed human habitation on Mont Beuvray in the Neolithic Era.[9] Dating techniques have shown that the oppidum was not founded until the end of the 3rd century on an area of 200 hectares protected by the exterior rampart. An interior rampart was built later, for reasons unknown.[10]
Because the Aedui had the status of "friend of the Roman people," contacts with Roman merchants were probable before the conquest of Gaul by Julius Caesar. This privileged status prevented Bibracte from suffering much conflict: in 58 BCE, at Montmort 25 kilometers south of the site, Julius Caesar's armies defeated the Helvetii,[11] forcing them to return to Switzerland and gradually be incorporated into what would become the Roman Empire. In 52 BCE, an assembly of Gallic peoples at Bibracte gave Vercingetorix supreme command of the Gallic armies.[12][13] Despite this insurrection, Caesar treated the city mercifully after his victory at Alesia. He stayed there during the winter of 52-51 BCE[14] to write his Commentaries on the Gallic War. These mentioned the names of certain notables of the Aedui aristocracy such as Dumnorix, vergobret of the Aedui, and his brother Diviciacos, the druid. The city's industry boomed in the decades following the war.
Strabo the geographer, who wrote a generation after Caesar, identified Bibracte as an Aedui stronghold again.[15]
After the founding of Autun (Augustodunum) 25 kilometers away c. 15 BCE, during the reign of Augustus, Bibracte was gradually abandoned by its inhabitants. However, cults continued to practise their rites in its temples and by its fountains and its aristocratic residences were maintained. Two main hypotheses have been advanced concerning this gradual abandonment of the site over several decades. The migration could have been caused by economic reasons or by a desire to integrate with the Roman model; a part of the dominant Aedui class, already pro-Roman during the Gallic War, definitely realized the strategic importance of the new city located on the principal axes of communication and wanted to conform to the Roman model of flatland cities, while a more traditional population remained for a time on the Bibracte site.[16]
It is known from 13th century texts that a festival every first Monday of May survived.[7] In the 15th and 16th centuries, a convent of Cordeliers was established on Mont Beuvray.[13] It was abandoned, but the festival continued.
Influence and power
The power of the Aedui capital was related in the Commentaries on the Gallic War, which underlined the many alliances held by the Aedui with neighboring peoples. Julius Caesar also mentioned the wars that set the Aedui against the Arverni and the Sequani for hegemony over a large part of Gaul. These references were not impartial, since Rome was allied with the Aedui, "our blood brothers[17]", since at least the 2nd century BCE. Moreover, they maintained commercial links and military alliances: Rome aided the Aedui in the 2nd century in defeating at Arverni army and rose to their defense against the invasion of the Helvetii that precipitated the Gallic War.
Gabriel de Mortillet, in his classification of ancient peoples, included the site's residents under the name "Beavraisian", a category abandoned by modern scholars.[18] in the by Gabriel de Mortillet.

In addition to this powerful alliance with Rome, the Aedui were part of a confederation of Celtic tribes:
- The Ambarri (in Ain)
- The Brannovices
- The Bellovaci
- The Bituriges (Berry)
- The Parisii
- The Segusiavi (Forez, adjacent to the Arverni)
- The Senones (Sens region)
whose influence thus extended across a large part of Gaul.
Archeologists estimate the population of Beavray between 5,000 and 10,000 inhabitants at its peak.
Commerce
In his History of Gaul,[19] the historian Camille Jullian writes these lines about the Aedui : "Bibracte, I am sure, was the source and the guarantee of their power. Around Bibracte were very good roads, uniting the three biggest basins of France."
So, the Roman products traveling up the Rhône (the waterways were the fastest at the time) and taking after that the Saône, the Loire or the Allier, passed through Aedui territory before joining the basins of the Loire and Seine. The Aedui were located at a commercial crossroads between the Celtic world and Rome. Thus did they allow the diffusion of Roman products through Gaul as soon as the 2nd century BCE, allowing their allies to benefit from their commerce with Rome and definitely with Greek colonies such as Massilia. These exchanges are confirmed by the large quantities of amphoras and ceramics from Italy found in waste tanks and in the paving of houses.
In addition, the Aedui installed a system of customs that taxed the products passing through their territory to increase their wealth as attested in the texts of Julius Caesar : "It was typical of Dumnorix: the man was audacious, his generosity made him popular, and he wanted political change. For years, he has had the control of the customs and all the other taxes of the Aedui, because when he bid, no one dared bid against him."[20] The Aedui and the Sequani fought each other to control the Arar (now the Saône) because the control of the river allowed taxation of all the Roman and Celtic products traveling to the north of the continent via the waterways.
Politics

The political system of the Aedui was essentially reformed according to indications in the Commentaries on the Gallic War. At the head of the Aedui state sat a senate comprising one member of each Aedui aristrocratic family. What is today called executive power was held by the vergobret, the supreme magistrate, who exercised his functions over the course of a year. He was forbidden from leaving the borders of the territory during this period, which prevented him from commanding the army outside the borders.[21] This measure, along with that which authorized only one voice per aristocratic family in the senate, aimed to prevent any individual or their family from monopolizing the reins of power. The vergobret was publicly elected by a council directed by the druids. Among the Aedui, it seems like the vergobret also exercised a judiciary role, since Caesar reports that he had "the right to life and death over his fellow citizens". Finally, it is thought that the vergobret was responsible for the administration of the territory.[21] Caesar adds that the druids were charged with this: "They believe that religion does not allow them to put the material of their education in writing, while for the rest in general, for public and private administrative acts, they used the Greek alphabet."[22] No excavation has permitted the rediscovery of such acts, the backings of which, being wood covered with wax, are perishable.
Furthermore, it is known that the druids held high functions since Diviciacus came to Rome to plead the case of the Aedui during the Germanic invasion led by Ariovistus on the account of the Sequani.;[23] he also directed the Aedui cavalry during the Gallic War after the death of his brother Dumnorix. Therefore, it is thought that some druids held high military positions.
Archeological research on Mont Beuvray
From 1865 to 1895, Gabriel Bulliot identified Bibracte in 1867 and began excavations there (notably the Celtic artisanal neighborhood surrounding the Rebout gate), with the aid of funds allocated by Napoleon III.[6] In fact, having a passion for history, the emperor set off vast campaigns of excavations to uncover sites of the Gallic War in order to write his History of Julius Caesar. The modest "Hotel of the Gauls" which housed the researcher on the premises had been constructed there since. Joseph Déchelette, the nephew of Bulliot, took up his work again from 1895 to 1907. He was killed during World War I. Thus, the excavations fell into neglect. In 1984, the excavations began again under the impetus of François Mitterrand, who proclaimed Bibracte a site of national interest in 1985.[13] This term, invented for the occasion, would permit the site to be subsidized. The label of "national interest" was created afterward in order to designate exhibitions or sites which benefit from a program of diffusion and enlargement of the public by the Minister of Culture. This will always give the necessary impetus to a project of excavations of European scope. Thus, in 1989, the European Archeological Center of Mont Beuvray was created, which will reassemble the site, the museum, and the research center of Glux-en-Glenne. It was inaugurated in 1995. By order on March 21, 1995, the Minister of Culture, on the advice of the National Council of Archeological Research, confirmed the oppidum of Bibracte (Mont-Beuvray, Saint-Léger-sous-Beuvray; Saône-et-Loire; Glux-en-Glenne; Nièvre). The excavations were actually conducted by Vincent Guichard and put into practice by many French and foreign teams; the excavations notably concentrated on the Gallic neighborhood of Rebout, on the vast Gallo-Roman ensemble of the Pasture of the Convent and the Roman residence of the Horse Park.
Thus, specialists, researchers, professors and students from all over Europe mix on the site every summer in order to excavate different parts of the site.[24] These included, among others:
- Austria: University of Vienna
- Belgium: Université Libre de Bruxelles
- Czech Republic: Masaryk University
- France: University of Franche-Comté, University of Burgundy, University of Paris 1 Pantheon-Sorbonne, Pierre and Marie Curie University, François Rabelais University
- Germany: University of Kiel, University of Leipzig, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, University of Mainz
- Hungary: Eötvös Loránd University
- Italy: University of Bologna
- Poland: Rzeszów University
- Slovenia: University of Ljubljana
- Spain: University of Madrid and University of Zaragoza
- Switzerland: University of Lausanne
- United Kingdom: University of Edinburgh
Each university excavates the site in the form of triannual projects which currently depend on the comprehension of the operation of a Celtic city of the La Tène period. Their research consists of several weeks of work on the terrain which is followed by a detailed study of the excavation and of the discovered objects which are then stored at the site's research center.
Archeological prospecting on Mont Beuvray
The prospecting technique used by Bulliot was rudimentary. It consisted of observing the irregularities in the landscape, since the mountain was practically unchanged since the period under study. This allowed him to recreate a plan of the battlements with nearly no excavation. He used this technique to make a scale plan with the help of the army topographers, who made a series of topographical recreations of the landscape. Only the recreation of the Porrey neighborhood exists to this day.[25]
In recent years, the same technique has been used in the same Porrey neighborhood with more precise tools, like theodolites and GPS. In fact, aerial and electromagnetic prospecting is made impossible by the vegetation that reforested the mountain since the end of grazing and the excavations of Joseph Déchelette[25] and the nature of the subsoil. One costly but faster technique, which is to be tested in 2007, is LIDAR, the use of airborne laser scanners, which are unhindered by the vegetation and can recreate in minutes what usually takes weeks to do on the ground. This will be done in order to attempt to make a complete map of the city and to archive the topography of the location.
Organization
The research done by Bulliot and Déchelette at the end of the 19th century and at the beginning of the 20th century recreated an organization of the site into neighborhoods, with construction mostly following a central road from the Gate of Rebout to the Great Gates. This organization differs from that of oppida like Manching, where there is a regular urban framework; this is explained by the relief of the terrain, as the battlements encircle three summits with some relatively steep slopes.
Since 1984, the excavations have seemed to confirm Déchelette's and Bulliot's hypotheses in broad terms, while nevertheless contributing certain nuances.
Battlements

Bibracte was protected by strong Murus Gallicus style battlements, which excavations have made possible to reconstruct. The city had a progression of two different surrounding walls and at least five restorations of the inner surrounding wall, revealed, among other things, by the study of the Rebout gate.[10] Surprisingly, this inner surrounding wall was constructed after the outer wall. The city, therefore, shrank its area from 200 to 135 hectares (494 to 334 acres).
The first wall (the internal wall on the map below), discovered by Bulliot, is a Murus Gallicus that delimits an area of 135 hectares for a length of 5 kilometers (3.1 mi) per battlement. It is estimated that the construction of the wall required imposing quantities in excess of 10,000 cubic meters of wood, between 10,000 and 20,000 cubic meters of earth and about thirty tons of iron.[26]
The second wall, surprisingly outside the first, encircles an area of 200 hectares and was the subject of research beginning in 1992 for initial probing. This archeological research revealed that the battlement had a height between 4 and 5 meters (13 and 16 feet) without its yet unknown top (e.g., palisades or towers) and an identical depth, and was preceded by a ditch between 2 and 4 meters (7 and 13 feet) deep and between 6 and 10 meters (20 and 33 feet) wide. A study was conducted between 1995 and 2002 with many probes along with those by the University of Vienna. The researchers were able to ascertain that this battlement was a Murus Gallicus that had been dismantled in order to construct the inner wall. The dating, however, remains imprecise, and places this event during the 2nd century. These excavations also updated a postern to the level of Porrey, which is the only one currently known for Murus Gallicus type fortifications.[10]
The battlement is punctuated by about fifteen gates, including the famous Gate of Rebout (20 meters (66 feet) in width and 40 meters (131 feet) in depth). The gate of Rebout was the first location excavated by Bulliot, where he worked for 9 weeks, and was the first site for new excavations from 1984 to 1986 which also studied the ditches adjoining the battlements.[27] These excavations revealed the existence of five levels of different restorations, including a palisade from the Neolithic Era (dated with carbon-14). The latter became the object of a reconstruction since 1996 which currently marks the entry into the old oppidum. At the present time, research has not been able to detect a trace of a method for locking the gate or a defensive device for it. Some hypotheses have advanced the idea of a double gate surmounted by a wooden guard tower like that of the Manching oppidum, but nothing can yet confirm this.
The recent research on the battlements, since 2005, has concentrated on a line of fortification downhill from the Gate of Rebout. Dating seems to indicate that this construction took place after that of the gate and therefore constituted an advance fortification. It will be studied over the course of the next excavations. At the same time, some aristocratic tombs have been discovered between the two lines of battlements.[28]
Artisans' neighborhoods of Côme Chaudron and Champlain
The excavations, which were resumed in 2000 in the neighborhoods known as the Côme Cauldron and the Champlain, near the Rebout Gate, revealed a neighborhood dedicated to metalwork and to artisans' lodging. This metalworking seems to have been very specialized, incorporating blacksmiths, bronzeworkers, and enamellers, whose workshops had already been restored by Bulliot, and probably also involved goldsmiths and minters.[29]
Excavations on the site of Beuvray, in the region of the Champlain, and on the surrounding massifs revealed the existence of mines for the extraction of metals, including gold, iron, and tin ore. This research will continue and will attempt to restore the workshops for the smelting of the metals extracted outside the oppidum. In fact, given the specialization of the workshops in Bibracte, it seems that the metals arrived in bars which were therefore cast outside the oppidum.
Another artisanal neighborhood has been found in the region of one of the summits of the site, at the Rock of the Wyvern, an area which had been little investigated at the time of Bulliot and Déchelette's research. This neighborhood will be the object of future excavations which will attempt to determine the function of the neighborhood.[28]
Housing

Predominantly made of wood and earth, the Gallic houses used stone only sparingly, which was saved for the ramparts. Little is known of the houses' structure as wood rots and decomposes. There are, however, stone constructions in the horse Park district, probably aristocratic residences and a public building with columns, near the convent's pasture. These were probably constructed soon after the Gallic Wars.[30]
Horse Park
At the center of Mont Beuvray, the plateau known as the Horse Park holds several Roman-style stone houses which were excavated in the 19th century. The houses there include, in particular, the residence PC1[31] (so named by Bulliot), which is a veritable gold mine for the researchers. In fact, it developed from a wood construction (of Roman inspiration) at a domus with an atrium containing an impluvium, porticos, and thermae heated by hypocaust, along with a system of sewers. In its final stage, the residence measured 55 by 67 meters, covering an area of around 3500 square meters, about four times the size of the domus found on the site of Pompeii. It is estimated that there were about fifteen domus in this area, such as PC2,[32] a smaller residence that faces PC1 on the other side of the central road. There are also homes of the villa rustica type (the Italian rural residences) like PC33.[33] However, it is still not known whether this was a residential neighborhood reserved for only the elite, since excavations have also revealed the presence of forges near the domus.[30]
The fountain and its surroundings

At the center of the main road, in the area of the Pasture of the Monastery, stands a pink granite monumental fountain with a transversal orientation corresponding to the rising sun during the Winter Solstice and to the setting sun during the Summer Solstice. Water left the fountain through the northern opening downstream, continuing through a pipe. The supply of water, however, has not yet been discovered:
- the fountain was waterproofed with a coat of red clay, precluding a feed from a spring
- no supply pipe has been found
The main geometrics of the design are known: the intersection of two circles with connections of precisely the length of a Pythagorean triangle joining the center of the circle, the center of the fountain and one end of the fountain. However, its use is still unknown; it could be a sacred point of the city's founding, or a water shrine. Furthermore, among certain specialists,[34] this manner of carving granite is unusual and rests on the principles of Mediterranean limestone carving. The Aedui doubtlessly employed foreigners to build the fountain. All of this points to the fountain being a monument outside of ordinary Celtic architecture.

Near the fountain, many cellars and certain public buildings that stocked large quantities of cereals[35] and wine imported from the southern countries have been found. One of these wooden cellars has recently been reconstructed. Without a doubt, it was in these buildings that the Aedui centralized their harvests and imports.
Places of worship
The oppidum of Bibracte has about ten springs and five fountains dating from the Gallic or Galloroman periods. The Saint Pierre Fountain was a place of worship and pilgrimage, in which pieces of currency and plagues of thanksgivings were found.[30] At the summit of the mountain, a Celtic place of worship (nemeton) a hectare large has been updated, surrounded by a palisade and concentric ditches.[36] Under the current chapel from the 19th century, the 1988 excavations discovered a Galloroman temple.[37] Furthermore, the abandonment of the city before the beginning of the Christian era was not prevented by pursuit of pilgrimages carried out in its surroundings.
Necropolis
Located below the present-day museum parking lot, the necropolis underwent archaeological excavations, with the aim of saving it, when the museum was created and the route départementale was diverted. Over a surface area of 1.5 hectares, 70 funeral enclosures, used following incineration, were found, each having an eastern entry. The crematorium was found further south. Other funerary urns were discovered at the foot of the Rebout gates, possibly the remains of a local aristocratic family.[28] More cemeteries are presumably situated on the former site access paths, as was the often the case at the time, but have not yet been excavated.
Basilica
In the area of the Convent Pasture, the excavations revealed, under a large domus from the Augustan era, the presence of an exceptional public monument, which was at the time unique for that period in Gaul: a Roman basilica. It appears to have been a basilica with three naves and an internal peristyle with a peripheral ambulatory, displaying four rows of eight columns or eight pilasters. It was connected on the east with a small square, 22 meters on a side, bordered to the north and south with porticoes which were extensions of the walls of annexes of the basilica. On the west it was connected to the main road of Bibracte with another square, 17 meters on the side. Some architectural elements have been found that attest the presence of limestone columns with Attic bases and Doric and Corinthian capitals. These elements form a monumental urban project of the greatest importance. These public buildings were dated to the period between 50 and 40 BCE and between 35 and 25 BCE. At this date, the basilica and the square were carefully leveled and replaced by a large private residence, doubtlessly in connection with the movement of the Aedui capital to Autun. The basilica of Bibracte confirms the exceptional importance of the site and revealed that the Romanization of the Aedui was considerably faster than believed. The basilica of Bibracte is currently the oldest representation of Roman monumental stone architecture in non-Mediterranean Europe[38] · [39] · [40] · .[41]
A window to the Celtic world
Museum of Celtic Civilization

The site hosts the Museum of Celtic Civilization, constructed by Pierre-Louis Faloci and opened to the public in 1996. Pierre-Louis Faloci is also the architect of Bibracte's Center of European Archeological Research, which was opened in 1994. The architectural design corresponds to the evolution of the ages of humanities: it has a base of carved stone, walls of polished pradesh, and a metal roof. One of the facades, which are large picture windows, is hidden by a wall of pradesh (on the valley side), while that which faces the site allows free view to the visitors. The museum has few proper collections, as many of those exhibited are loaned from other museum. During some years, the Coligny calendar and the Gundestrup cauldron can be seen there.
Permanent exhibits
The 2000 square meters of the exhibit in the museum are laid out over two stages. The first stage (and the first in the tour) recounts the discovery of the site and the place of Bibracte in the global context of the European Celtic culture. The majority of the following subjects are covered: war, the age of oppida, Mediterranean commerce, and agriculture. The ground floor, which consists of several alcoves, recounts the life of the Aedui at Bibracte. Objects of daily life, jewelry, funereal urns, and artisanal workshops are reconstructed or exhibited there.
Temporary exhibits

Several summer exhibits have been featured at the museum, each addressing a precise subject of the Celtic world:[42]
- 1995: Celtic Europe at the time of Bibracte
- 1996: History seen from above
- 1997: A look at the Celts in Slovenia
- 1998: At the border of East and West[43]
- 1999: The tombs of the last Celtic aristocrats
- 2000: The Gallic druids[44]
- 2001: The time of the Gauls in the provinces
- 2002: On Caesar's trail
- 2003: Blacksmiths and metal merchants
- 2004: The white gold of Hallstatt
- 2005: Wine, the nectar of the Gods
- 2006: The treasures of women
- 2007: A round trip between Bibracte and Kathmandu
- 2008: Situlae, images of a vanished world
- 2009: La Tène
- 2010: The Gauls do the head
Research center
Located 4 kilometers from Mont Beuvray, in the commune of Glux-en-Glenne (Nièvre), is one of the most important libraries on the Celtic world, regularly funded by European researchers who take their counterparts there. There is also an archeological depot there, the administration of the archeological park, several technical establishments, a lecture hall, and, in the village, a dining hall and a several gîtes. In this center, archeologists, students, and researchers congregate from all over Europe to excavate the site of Bibracte. In several months, the research center will expand to accommodate the regional center for preservation of relics and archeological collections, becoming the reference center of Burgundy in this field.
See also
- Network of the Great Sites of France
- Jacques Gabriel Bulliot
- Joseph Déchelette
- Christian Goudineau
- Murus Gallicus
- Oppidum
- Aedui
- Dumnorix
- Diviciacos
References
- ↑ Maschner, H.D.G.; Southern Illinois University at Carbondale. Center for Archaeological Investigations (1996). New Methods, Old Problems: Geographic Information Systems in Modern Archaeological Research. Center for Archaeological Investigations, Southern Illinois University at Carbondale. ISBN 9780881040791. Retrieved 2015-06-27.
- ↑ McIntosh, J. (2009). Handbook to Life in Prehistoric Europe. Oxford University Press. p. 158. ISBN 9780195384765. Retrieved 2015-06-27.
- ↑ Pierre-Yves Lambert, La langue gauloise, éditions errance 1994.
- ↑ Christian Goudineau et Christian Peyre, Bibracte et les Éduens, À la découverte d'un peuple gaulois, éditions errance, 1993, p15
- ↑ D'un point de vue phonétique également, Biffractus aurait donné *Beffray et non pas Beuvray.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Christian Goudineau et Christian Peyre, Bibracte et les Éduens, À la découverte d'un peuple gaulois, éditions Errance, pp 1–6 1993
- 1 2 3 4 Christian Goudineau, Regards sur la Gaule, éditions Errance, 1998, pp. 65–82
- ↑ Stephan Fichtl, La ville celtique, Les oppida de 150 av. J.-C. à 15 ap. J.-C., éditions Errance, 2005, p. 17
- ↑ Christian Goudineau et Christian Peyre, Bibracte et les Éduens, À la découverte d'un peuple gaulois, éditions Errance, 1993, p27
- 1 2 3 Anne-Marie Romero, Bibracte Archéologie d'une ville gauloise, Bibracte-Centre archéologique européen, 2006, p.60
- ↑ Julius Caesar, Commentaries on the Gallic War, Book I, 23
- ↑ Julius Caesar, Commentaries on the Gallic War, Book VII, 63
- 1 2 3 Anne-Marie Romero, Bibracte Archéologie d'une ville gauloise, Bibracte-Centre archéologique européen, 2006, p16
- ↑ Julius Caesar, Commentaries on the Gallic War, Book VII, 90, Book VIII, 2
- ↑ Strabo, Geography, Book IV, 3, 2
- ↑ Stephan Fichtl, La ville celtique, Les oppida de 150 av. J.-C. à 15 ap. J.-C., éditions Errance, 2005, pp 191–198
- ↑ Julius Caesar, Commentaries on the Gallic War, Book I, 33
- ↑ Modélisation des connaissances temporelles en archéologie (page 5)
- ↑ Histoire de la Gaule, 8 vol, Camille Jullian
- ↑ Julius Caesar, Commentaries on the Gallic War, Book I, 18
- 1 2 Christian Goudineau et Christian Peyre, Bibracte et les Éduens, À la découverte d'un peuple gaulois, éditions Errance, 1993, pp 81–83
- ↑ Julius Caesar, Commentaries on the Gallic War, Book VI, 14
- ↑ Julius Caesar, Commentaries on the Gallic War, Book I
- ↑ Anne-Marie Romero, Bibracte Archéologie d'une ville gaulois, Bibracte-Centre archéologique européen, 2006, pp 63–64
- 1 2 Anne-Marie Romero, Bibracte Archéologie d'une ville gauloise, Bibracte-Centre archéologique européen, 2006, pp 98–99
- ↑ Stephan Fichtl, La ville celtique, Les oppida de 150 av. J.-C. à 15 ap. J.-C., éditions Errance, 2005, pp. 62–63 (évaluation réalisée d'après les calculs de Déchelette et rectifiés par les données fournies lors de la reconstruction du rempart à la porte du Rebout).
- ↑ Anne-Marie Romero, Bibracte Archéologie d'une ville gauloise, Bibracte-Centre archéologique européen, 2006, pp 56–57
- 1 2 3 Ideal Productions. "parc archéologique et centre de recherche – Bibracte en Bourgogne (Mont Beuvray) : archéologie gauloise / celtique, fouilles, musée". bibracte.fr. Retrieved 2015-06-27.
- ↑ Anne-Marie Romero, Bibracte Archéologie d'une ville gauloise, Bibracte-Centre archéologique européen, 2006, pp 67–69
- 1 2 3 (French) Anne-Marie Romero, Bibracte Archéologie d'une ville gauloise, Bibracte-Centre archéologique européen, 2006, pp 87–89
- ↑ PC1, for Parc aux Chevaux 1. Bulliot gave designations to the excavations by indicating the initials of the place of discovery, then giving a number for each building in an individual location
- ↑ Parc au Chevaux 2
- ↑ Parc aux Chevaux 33
- ↑ M.Almagro-Gorbea et J.Gran-Aymerich, El estanque Monumental de Bibracte, Madrid, Editorial Complutense, 1991, pp. 237–238
- ↑ Anne-Marie Romero, Bibracte Archéologie d'une ville gauloise : Des graines carbonisées ont été retrouvées dans une cave qui a brûlé.
- ↑ Christian Goudineau et Christian Peyre, Bibracte et les Éduens, À la découverte d'un peuple gaulois, éditions Errance, 1993, pp 90–94
- ↑ Christian Goudineau et Christian Peyre, Bibracte et les Éduens, À la découverte d'un peuple gaulois, éditions Errance, 1993, pp 84–89
- ↑ M. Szabo, L. Timar, D. Szabo, « La basilique de Bibracte : un témoignage de l’architecture romaine en Gaule centrale », Archäologisches Korrespondenzblatt, 2007, 37, 3, pp. 389–408.
- ↑ V. Guichard, « Chroniques des recherches sur le Mont Beuvray », RAE, 56, 2007, pp. 127–152 lire en ligne
- ↑ M. Reddé, « La Gaule Chevelue entre César et Auguste », dans M. Christol et D. Darde dir., L’expression du pouvoir au début de l’Empire. Autour de la Maison Carrée à Nîmes. Paris, 2009, pp. 85–96 en particulier p. 91
- ↑ Ideal Productions. "parc archéologique et centre de recherche – Bibracte en Bourgogne (Mont Beuvray) | Résumé de la dernière campagne de fouille". bibracte.fr. Archived from the original on 2015-06-30. Retrieved 2015-06-27.
- ↑ Anne-Marie Romero, Bibracte Archéologie d'une ville gauloise, Bibracte-Centre archéologique européen, 2006, pp 136–142
- ↑ protohistoric art in Hungary in the 1st millennium BCE
- ↑ Note that Diviciacos, an Aedui druid, is the only one whose name is known
Bibliography
Reference works
- Christian Goudineau and Christian Peyre, Bibracte et les Éduens, À la découverte d'un peuple gaulois, éditions Errance, 1993
- Christian Goudineau, Regards sur la Gaule, éditions Errance, 1998, pp. 65–82
- Anne-Marie Romero, Bibracte. Archéologie d'une ville gauloise, Bibracte-Centre archéologique européen, 2006
- Stephan Fichtl, La ville celtique, Les oppida de 150av. J.-C. à 15ap. J.-C., éditions Errance, 2005
- K. Gruel et D. Vitali, L'oppidum de Bibracte. Un bilan de onze années de recherches (1984–1996), Gallia, 55, 1998, pp. 1–140 Read online
- "Bibracte, capitale des Éduens", L'Archéologue-Archéologie nouvelle, 4, mars 1994, pp. 36–45 et 6, juin 1994, pp. 62–72
Old works
- Jacques Gabriel Bulliot, Fouilles du Mont-Beuvray (ancienne Bibracte) de 1867 à 1895, Dejussieu (Autun), 2volumes, 1899
- Joseph Déchelette, Les fouilles du Mont-Beuvray de 1897 à 1901, Picard (Paris), Dejussieu (Autun), 1904
- Joseph Déchelette, L'oppidum de Bibracte. Guide du touriste et de l'archéologue au Mont Beuvray et au Musée de l'Hôtel Rolin, Picard (Paris), Dejussieu (Autun), 1903
- Joseph Déchelette, Manuel d'archéologie préhistorique, celtique et gallo-romaine, éditions Picard, Collection Grands manuels Picard, 2000
Works from the collection Archeological Excavations of Bibracte
- Guillaumet J.-P., Szabo M. (sous la direction de), Études sur Bibracte, Glux-en-Glenne : BIBRACTE, 2005, 313 p.,
- Paunier D., Luginbühl T., Les site de la maison 1 du Parc aux Chevaux (PC 1). Des origines de l’oppidum au règne de Tibère, Glux-en-Glenne : Bibracte, 2004, 472 p.
- Olmer F., Les amphores de Bibracte, 2. Le commerce du vin chez les Eduens d’après les timbres d’amphores, Glux-en-Glenne : Bibracte, 2003, 375 p.
- Buchsenschutz O., Guillaumet J.-P., Ralston I. (sous la direction de), La Porte du Rebout, Glux-en-Glenne : Centre *Archéologique Européen du Mont Beuvray (CAE), 1999, 320 p.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bibracte. |
- Bibracte website (in English)
- Athena Review article "Bibracte"
- Bibracte, a city of the Gauls
- (French) Bibracte, site archéologique, centre de recherche et musée