Battle of Ivankovac
| Battle of Ivankovac | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the First Serbian uprising | |||||||
 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| initially 2,500 men, later reinforced with 5,000 more | 20,000 men | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| less than 1000 dead | approximately 15.000 dead | ||||||
The Battle of Ivankovac (Serbian Cyrillic: Бој на Иванковцу) was the first full-scale confrontation between Serbian revolutionaries and the regular forces of the Ottoman Empire during the First Serbian Uprising. The battle ended with a Serbian victory and prompted Ottoman Sultan Selim III to declare jihad (holy war) against the Serbs.
Background
In the 1790s, the Ottoman Sultan Selim III granted the Serbs in the Sanjak of Smederevo (central Serbia) the right to run their own affairs in exchange for their cooperation with the governor of Belgrade, Hadži Mustafa Pasha. Following the Slaughter of the Knezes in February 1804, a revolt led by Karađorđe Petrović erupted against the Ottoman janissary junta (the "Dahije") in Serbia. The Serbs initially received the support of Selim and managed to defeat the corrupt janissaries by the end of the year.[1] Facing great pressure not to cooperate extensively with his Christian subjects, Selim began to view the Serbs as rebels by the spring of 1805. He appointed the Ottoman governor of Niš, Hafiz Pasha, as the new governor of Belgrade and ordered him to confront the Serbian insurgents.[2][3] The Ottoman Turkish forces were highly trained.[4]
Battle
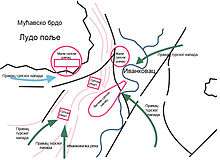
The village of Ivankovac is located near the town of Ćuprija.[5] On 18 August [O.S. 7 August] 1805, the Ottomans attacked the Serbian revolutionaries, commanded by Karađorđe and Milenko Stojković, at Ivankovac. Hafiz Pasha was seriously wounded during the battle and died as a result.[6] The Ottomans were defeated.[7]
Aftermath

The battle was a major victory for the Serbian rebels.[8] It marked the first time that a regular Ottoman Turkish unit was defeated by Serbian revolutionaries during the First Serbian Uprising.[3] Victory meant that the Serbian forces had taken full control of the Belgrade Pashaluk. Smederevo was captured in November and became the first capital of the Serbian revolutionary government, while Belgrade was taken the following year.[2] Defeat in the battle prompted Selim to declare jihad (holy war) against the Serbian revolutionaries fighting to expel the Turks from Serbia.[9][10]
Notes
- ↑ Cox 2002, pp. 39–40.
- 1 2 Jelavich & Jelavich 2000, p. 32.
- 1 2 Radosavljević 2010, p. 175.
- ↑ Axelrod 2003, p. 290.
- ↑ Columbus 1999, p. 127.
- ↑ Morrison 1942, p. xix.
- ↑ Judah 2000, p. 51.
- ↑ Cox 2002, p. 40.
- ↑ Merry 2005, p. 122.
- ↑ Judah 2000, p. 52.
References
Books
- Axelrod, Alan (2003). Profiles in Leadership. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall Press. ISBN 978-0-73520-256-6.
- Columbus, Frank H. (1999). Kosovo–Serbia: A Just War?. Hauppauge, New York: Nova Science Publishers. ISBN 978-1-56072-724-8.
- Cox, John K. (2002). The History of Serbia. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press. ISBN 978-0-313-31290-8.
- Jelavich, Charles; Jelavich, Barbara (2000). The Establishment of the Balkan National States, 1804–1920. 8 (4 ed.). Seattle: University of Washington Press. ISBN 0-295-96413-8.
- Judah, Tim (2000). The Serbs: History, Myth and the Destruction of Yugoslavia (2nd ed.). New Haven, Connecticut: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-08507-5.
- Merry, Robert W. (2005). Sands of Empire: Missionary Zeal, American Foreign Policy, and the Hazards of Global Ambition. New York: Simon and Schuster. ISBN 0-7432-7438-5.
- Morrison, Walter Angus (1942). The Revolt of the Serbs Against the Turks: 1804–1813. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-107-67606-0.
- Radosavljević, Nedeljko (2010). "The Serbian Revolution and the Creation of the Modern State: The Beginning of Geopolitical Changes in the Balkan Peninsula in the 19th Century". In Mitev, Plamen; Parvev, Ivan; Baramova, Maria; Racheva, Vania. Empires and Peninsulas: Southeastern Europe Between Karlowitz and the Peace of Adrianople, 1699–1829. Berlin: LIT Verlag Münster. ISBN 978-3-643-10611-7.
Coordinates: 43°58′25″N 21°26′05″E / 43.97361°N 21.43472°E