Barakol
For the Kazakhstan lake, see Barak Kol.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
24506-68-1 |
| PubChem (CID) | 3080731 |
| ChemSpider |
2338470 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H12O4 |
| Molar mass | 232.231 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
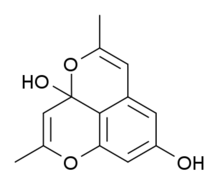
Barakol is a compound found in the plant Senna siamea,[1] which is used in traditional herbal medicine. It has sedative and anxiolytic effects,[2][3] but use for these purposes is now discouraged due to hepatotoxicity.[4]
References
- ↑ Padumanonda, T.; Gritsanapan, W. (March 2006). "Barakol Contents in Fresh and Cooked Senna siamea Leaves". The Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health. 37 (2): 388–393. PMID 17125004.
- ↑ Thongsaard, W.; Pongsakorn, S.; Sudsuang, R.; Bennett, G. W.; Kendall, D. A.; Marsden, C. A. (January 1997). "Barakol, a Natural Anxiolytic, Inhibits Striatal Dopamine Release but Not Uptake in vitro". European Journal of Pharmacology. 319 (2-3): 157–164. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(96)00850-3. PMID 9042586.
- ↑ Sukma, M.; Chaichantipyuth, C.; Murakami, Y.; Tohda, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Watanabe, H. (November 2002). "CNS Inhibitory Effects of Barakol, a Constituent of Cassia siamia Lamk". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 83 (1-2): 87–94. doi:10.1016/S0378-8741(02)00206-4. PMID 12413711.
- ↑ Hongsirinirachorn, M.; Threeprasertsuk, S.; Chutaputti, A. (June 2003). "Acute Hepatitis Associated with Barakol". Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand = Chotmaihet Thangphaet. 86 Suppl. 2: S484–489. PMID 12930029.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/7/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.