Bizerte
| Bizerte بنزرت | |
|---|---|
| City | |
|
Bizerte City Hall in Belgique Street area | |
 Bizerte Location in Tunisia | |
| Coordinates: 37°16′28″N 9°52′26″E / 37.27444°N 9.87389°E | |
| Country |
|
| Governorate | Bizerte Governorate |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor |
| Area | |
| • Urban | 34[1] km2 (13.127 sq mi) |
| Elevation | + 33[2] m (16 ft) |
| Population (2014[1]) | |
| • City | 142,966[1] |
| • Density | 3.363/km2 (8.712/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 401,144 |
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) |
| Postal code | 7000 |
| Area code(s) | +216 (Tun) 72 (Bizerte) |
| Website | http://www.commune-bizerte.gov.tn |
Bizerte (Arabic: بنزرت ![]() Benzart); historically: Phoenician: 𐤄𐤉𐤁𐤅 𐤀𐤊𐤓𐤀 Hippo Acra, Latin: Hippo Diarrhytus and Hippo Zarytus), also known in English as Bizerta, is a town of Bizerte Governorate in Tunisia and the northernmost city in Africa. Located 65 km (40mil) north of the capital Tunis, the city had 142,966 inhabitants in 2014.
Benzart); historically: Phoenician: 𐤄𐤉𐤁𐤅 𐤀𐤊𐤓𐤀 Hippo Acra, Latin: Hippo Diarrhytus and Hippo Zarytus), also known in English as Bizerta, is a town of Bizerte Governorate in Tunisia and the northernmost city in Africa. Located 65 km (40mil) north of the capital Tunis, the city had 142,966 inhabitants in 2014.
History

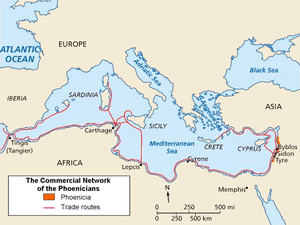

Bizerte is known as the oldest and most European city in Tunisia. It was founded around 1100 BC by Semitic Phoenicians from Tyre.[3] It is also known as the last town to remain under French control after the rest of the country won its independence from France.
Historical names
The city has several very different names in ancient authors. Scylax of Caryanda, who first mentioned the names Hippo Acra and Hippo Polis, these names are derived from the Punic: 𐤄𐤉𐤁𐤅 𐤀𐤊𐤓𐤀 Hippo Acra[3] during the period of the Carthaginians. The name of Hippo is certainly derived from a Phoenician word[3][4] and not Ancient Greek, found in simple or compound state across North Africa to Spain, (as Hippo Regius in Numidia now Annaba in Algeria, not far from Bizerte). According to Polybius, the ancient Greeks added to Hippo, the nickname Diarrhytos, which means: "Divided by the water" (canal of Bizete); Hippo Diarrhytos :("Ἱππὼν διάρρυτος").[4] During the periods of the Romans, the Vandals and the Byzantine Empire ; the city kept its names Hippo Diarrhytus and Hippo Zarytus.[5] Its current Arabic name: (Banzart/بنزرت), drift of a phonetic transformation of its antique name.[3]
Antiquity : (1100 BC to 647 AD)

- Initially a small Phoenician harbor for maritime trading in the western Mediterranean. Located 30 km(18.5 mil)in the north of Utica and 50 km (31 mil) of Carthage, other cities founded by Phoenicians.
Around 950 BC the city came under the influence of Carthage under the leadership of Queen Dido/Elissa; In 309 BC, during the Greek–Punic Wars and after the defeat of Agathocles, the city and sicily returned to Carthaginian Republic, its port is used by several Carthaginian generals in the Punic Wars as Hamilcar Barca, Mago, Hasdrubal and Hannibal.
- In 149 BC, the first Roman raids, the city was then occupied by the Romans, under the name of Hippo Diarrhytus during the period of reign of Julius Caesar, but the new city has regained its prosperity and progress just since the reign of Augustus and it maintains maritime relations followed with Ostia and Rome, as shown by a mosaic decorating its commercial representation in the square of Forum of Corporations, and Christianity spread in the city in this period.
- In 439 AD, Genseric, the king of the Vandals ( East Germanic tribes) and his tribes invaded the city and they used the port to accomplish their invasions of the rest of the Western Roman Empire, the city of Rome and the islands of Sardinia, Malta, Corsica and Sicily.
- From 534 AD to 642 AD, the city returned to eastern Romans under the Byzantine Empire, after a defeat of the vandals in 534, and they build the Fort of Bizerte (now the Fort of Kasba).


Later history
Bizerte was taken by Arabs in 647 in their fist invasion, but reverted to Byzantine control until they were defeated and driven from North Africa finally in 695-98, by the troops of Charles V of the Holy Roman Empire in 1535 and then by the Turks in 1574. The city then became a corsair harbour and struggled against the French and the Venetians.
With the occupation of Tunisia in 1881, France gained control of Bizerte and built a large naval harbor in the city.
In 1924, after the French government officially recognized the Soviet Union (USSR), the western military fleet of White Russia that had been kept in the port of Bizerte was returned to the Soviet government. The ships were never moved from the port and finally were sold there as scrap metal.
In March 1939, towards the end of the Spanish Civil War, Spanish Republican Navy Commander Miguel Buiza ordered the evacuation of the bulk of the Republican fleet. Three cruisers, eight destroyers and two submarines left Cartagena harbor and reached Bizerte where they were impounded by the French authorities.[6]
During the Second World War, the German and Italian Army occupied Bizerte until Allied troops defeated them on 7 May 1943. During the fighting between the Allied forces and the German Army, many of the city inhabitants fled to the countryside or Tunis. The city had suffered significant damage during the battle.[7]

Due to Bizerte's strategic location on the Mediterranean, France retained control of the city and her naval base after Tunisian independence in 1956. In 1961 Tunisian forces blockaded the Area of Bizerte and demanded French withdrawal. The face off turned nasty when a French helicopter took off and drew fire. The French brought in reinforcements; when these were fired upon, France took decisive military action against the Tunisian forces. Using state of the art weapons and decisive force the French took Bizerte and Menzel Bourguiba. During the three days, 700 Tunisians died (1200 wounded); the French lost 24 dead (100 wounded).
Meetings at the UN security council, and other international pressure moved France to agreement; the French military finally abandoned Bizerte on 15 October 1963.
Geography
Location
Bizerte is on a section of widened inlet and east-facing coast of the north coast of Tunisia, 15 kilometres from Ras ben Sakka (the northernmost point in Africa on the Mediterranean Sea), 20 kilometers northeast of the Ichkeul lake (a World Heritage Site), 30 kilometers (18 miles) north of the archaeological site of Utica and 65 kilometers north of Tunis.
Bizerte has to the west coastal hills forming an outcrop of the Tell Atlas with well-conserved woods and vantage points. Its associated beaches include Sidi Salem, La Grotte, Rasenjela, and Al Rimel. It is on a section of Mediterranean climate coastline, close to Sardinia and Sicily, as opposed to coasts in the south of the country which have a year-round dry desert climate.
The city is centered on the north shore of the canal of Bizerte linking the Mediterranean Sea to a tidal lake, the Lac de Bizerte which is larger than all parts of the town combined, to the immediate south. Built-up areas are in three directions:
- South-west along the widening canal with jetties at Pecherie and Jarrouba, the latter associated with Bizerte-Sidi Ahmed Air Base adjoining the opening of the lake and military/rescue heliport.
- North are Sidi Salam and Corniche. They are within meters of the coast and on coast-facing slopes of the Ain Berda, a range of hills toward Cap Blanc, a small headland in the Ain Damou Plage natural conservation area.
- Zarzouna, Menzel Jemil and Menzel Abderrahmane are on the south shore of the canal, formed by the locality of Zarzouna and the towns of Menzel Jemil and Menzel Abderrahmane, by a moveable bridge and both Menzels face the lake itself. The rest of the isthmus on which they stand is the gently rising Foret de Remel, reaching a high point east of its forest area at Cap Zebib.
Transport
The bridge leads to the motorway A4 leading to Tunis–Carthage International Airport and the capital. On the town side the P11 passes semi-rural Louata, hugs Ichkeul Lake and branches into a western route, the P7, leading directly to Tabarka on the coast next to the Algerian border. The P11 leads south-west to Béja, a governorate center, in the foothills of the Tell Atlas, forks into several roads at Bou Salem, a small town in a broad fertile plain, and climbs to Firnanah passing two high-altitude lakes and also approaching the north-west border with Algeria.
Climate
Bizerte enjoys a hot-summer mediterranean climate, with mild rainy winters and hot dry summers. The Mediterranean Sea helps moderate temperatures.[8]
| Climate data for Bizerte (1901–1960, extremes 1901–1992) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 27.0 (80.6) |
27.2 (81) |
31.2 (88.2) |
34.2 (93.6) |
39.0 (102.2) |
45.0 (113) |
46.6 (115.9) |
48.0 (118.4) |
45.0 (113) |
37.0 (98.6) |
34.0 (93.2) |
25.3 (77.5) |
48.0 (118.4) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 15.0 (59) |
15.4 (59.7) |
17.5 (63.5) |
20.0 (68) |
23.1 (73.6) |
27.8 (82) |
30.2 (86.4) |
30.9 (87.6) |
29.2 (84.6) |
24.4 (75.9) |
20.6 (69.1) |
16.0 (60.8) |
22.5 (72.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 11.3 (52.3) |
11.6 (52.9) |
13.4 (56.1) |
15.4 (59.7) |
18.4 (65.1) |
22.5 (72.5) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.9 (78.6) |
24.4 (75.9) |
20.4 (68.7) |
16.4 (61.5) |
12.6 (54.7) |
18.1 (64.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 7.7 (45.9) |
7.8 (46) |
9.4 (48.9) |
10.9 (51.6) |
13.4 (56.1) |
17.8 (64) |
20.2 (68.4) |
21.0 (69.8) |
19.6 (67.3) |
16.0 (60.8) |
12.0 (53.6) |
9.2 (48.6) |
13.8 (56.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −3.0 (26.6) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
0.0 (32) |
1.0 (33.8) |
4.0 (39.2) |
8.0 (46.4) |
8.0 (46.4) |
10.0 (50) |
8.9 (48) |
4.9 (40.8) |
0.0 (32) |
0.0 (32) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 112 (4.41) |
79 (3.11) |
56 (2.2) |
44 (1.73) |
24 (0.94) |
12 (0.47) |
4 (0.16) |
7 (0.28) |
34 (1.34) |
70 (2.76) |
92 (3.62) |
119 (4.69) |
653 (25.71) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 16 | 13 | 12 | 9 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 8 | 11 | 13 | 16 | 113 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 83 | 80 | 78 | 78 | 75 | 70 | 68 | 69 | 75 | 78 | 83 | 83 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 142.6 | 163.9 | 217.0 | 237.0 | 303.8 | 330.0 | 384.4 | 356.5 | 267.0 | 207.7 | 153.0 | 133.3 | 2,896.2 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 4.6 | 5.8 | 7.0 | 7.9 | 9.8 | 11.0 | 12.4 | 11.5 | 8.9 | 6.7 | 5.1 | 4.3 | 7.9 |
| Source #1: Deutscher Wetterdienst[9] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: Arab Meteorology Book (humidity and sun)[10] | |||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14.6 °C (58.3 °F) | 14.0 °C (57.2 °F) | 14.3 °C (57.7 °F) | 15.1 °C (59.2 °F) | 17.2 °C (63.0 °F) | 19.9 °C (67.8 °F) | 23.4 °C (74.1 °F) | 24.9 °C (76.8 °F) | 23.8 °C (74.8 °F) | 21.7 °C (71.1 °F) | 18.8 °C (65.8 °F) | 16.2 °C (61.2 °F) |
Economy
Bizerte's economy is very diverse. There are several military bases and year-round tourism. As a tourist centre the region is however not as popular as the eastern coast of Tunisia. There is manufacturing (textile, auto parts, cookware), fishing, fruits and vegetables, and wheat.
Miscellaneous

- The port of Bizerte is being developed into a significant Mediterranean yachting marina that was scheduled to open in May 2012. The superyacht section of the marina will be called Goga Superyacht Marina, and will have berths for yachts of up to 110m in length. It is expected that this will give a significant boost to the local economy as the yacht owners and also the hundreds of professional crew will become year-round consumers. The service industries supplying the yachts will gradually develop and bring additional employment.[11]
- The actor Abdelmajid Lakhal was born in Bizerte.
Titular see
Hippo Diarrhytus is a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church. In 1989–2002 it was held by Mgr. Tadeusz Kondrusiewicz, then by Mgr. Jose Paala Salazar, O.P. in 2002–2004 and by Mrg. Manfred Grothe]since October 14, 2004. The city and see of Hippo Diarrhytus should not be confused with those of Hippo Regius where Saint Augustine of Hippo was the bishop.
Notable residents
- Malek Jaziri, tennis player
International relations
Sister cities
Bizerte is twinned with:
Cooperation agreement
-
 Clermont-Ferrand, France, (a program of rehabilitation of historic centers)
Clermont-Ferrand, France, (a program of rehabilitation of historic centers)
References
- 1 2 3 (French) Mnicipalité de Bizerte Archived January 4, 2010, at the Wayback Machine..
- ↑ City Coordinates (Dateandtime.info)
- 1 2 3 4 Dr Mahmoud ABIDI(french) (2008-02-05). "bizerteyahasra". bizerteyahasra.com. Archived from the original on August 9, 2013. Retrieved 2013-10-13.
- 1 2 Perseus Digital Library.
- ↑ Hippo Zarytus(in Perseus Digital Library).
- ↑ Thomas, Hugh (2001). The Spanish Civil War. London: Penguin Books. p. 877.
- ↑ "To Bizerte With The Ii Corps". History.army.mil. Retrieved 2012-08-04.
- ↑ "Climate Bizerte – Table". Climate–Data.Eu. Retrieved 20 July 2014.
- 1 2 "Klimatafel von Bizerte / Tunesien" (PDF). Baseline climate means (1961-1990) from stations all over the world (in German). Deutscher Wetterdienst. Retrieved 18 October 2016.
- ↑ "Appendix I: Meteorological Data" (PDF). Springer. Retrieved 18 October 2016.
- ↑ Morley Yachts (2009-07-29). "Goga Superyacht Marina". Gogamarina.com. Retrieved 2012-08-04.
External links
- "Encyclopedia of the Orient"
 Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Bizerta". Encyclopædia Britannica. 4 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Bizerta". Encyclopædia Britannica. 4 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. Pétridès, Sophron (1910). "Hippo Diarrhytus". In Herbermann, Charles. Catholic Encyclopedia. 7. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
Pétridès, Sophron (1910). "Hippo Diarrhytus". In Herbermann, Charles. Catholic Encyclopedia. 7. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
Coordinates: 37°16′N 9°52′E / 37.267°N 9.867°E