Bandar Seri Begawan
| Bandar Seri Begawan Brunei Town | |
|---|---|
| Other transcription(s) | |
| • Jawi | بندر سري بڬاوان |
|
From top left: Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddin Mosque, Sir Muda Omar Ali Saifuddin Park, Lapau Diraja, Mercu Dirgahayu and Downtown Bandar Seri Begawan. | |
| Nickname(s): Bandar or BSB | |
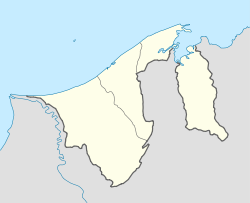 Bandar Seri Begawan | |
| Coordinates: 4°53′25″N 114°56′32″E / 4.89028°N 114.94222°ECoordinates: 4°53′25″N 114°56′32″E / 4.89028°N 114.94222°E | |
| Country |
|
| District | Brunei Muara |
| Bruneian Empire | 7th–18th century |
| Settled by the British | 19th century |
| Land development by the British | 1906 |
| Resettlement of the Sultanate of Brunei administration centre | 1909 |
| Municipality and granted city status | 1920 |
| Area | |
| • City | 100.36 km2 (38.75 sq mi) |
| Population (2015) | |
| • City | 50,000 |
| • Density | 1,395/km2 (3,610/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 279,924 |
| • Demonym | Seri Begawanese / Orang Bandar |
| Time zone | BNT (UTC+8) |
| Area code(s) | +673 02 |
| Website |
www |
Bandar Seri Begawan /ˌbɑːndə sᵻˌriː bᵻˈɡaʊ.ən/ or /ˌbæ-/ BA(H)ND-ə sə-REE bə-GOW-ən (Jawi: بندر سري بڬاوان ; Malay: [ˌbanda səˌri bəˈɡawan]) formerly known as Brunei Town, is the capital and largest city of the Sultanate of Brunei. Bandar Seri Begawan has an estimated population of 50,000,[1] and including the whole Brunei-Muara District, the metro area has an estimated population of 279,924.[2]
Etymology
The original name for this city was "Bandar Brunei" or "Brunei Town" in English. In 1967, Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III abdicated in favour of his eldest son, Hassanal Bolkiah and took the title of "Seri Begawan".[3] Omar was then made the defense minister and on 5 October 1970, the city was renamed to honor him.[3][4][5][6] The word "Begawan" was also used for Bruneian monarchs who have abdicated, the word originally coming from the Sanskrit word for "god": भगवान् bhagavān. Besides that, Seri Begawan was known as "blessed one" in Sanskrit.[4] Seri comes from the honorific Sanskrit word श्री Sri, and Bandar comes from Persian via Indian languages and originally meant "harbour" or "port" or "haven".[4][6] In Malay, the word bandar means "town" or a "city".
History
Human settlement in Brunei can be traced back as far as 6th and 7th century with Malay trading centre and fishing port located near the current site of this city.[4] The first settlement on the banks of the Brunei River can be traced back to the 8th century where there had been settlements similar to those in Kampong Ayer, located near the present site of the Brunei Museum with the modern city on the opposite shore.[7] During the Bruneian Empire period from 15th–17th century, the Sultanate ruled much part of Borneo including the southern part of the Philippines and its capital of Manila,[8][9] with the water settlement near the city area became the third centre of the administration after been moved twice from Kota Batu and Kampong Ayer.[4][5][6][10] When the Sultanate rule declined through the eighteenth century due to the arrival of western powers such as the Spanish, Dutch and the British, this settlement population was totally decreased from its peak of 20,000 inhabitants.[4] From 1888 until its independence in 1984, Brunei was a British protectorate and land development began in 1906 when the British resident encouraged the Sultanate citizens to moved on a reclaimed land on the western bank of the inlet.[10] In 1899, first oil well was drilled at Ayer Bekunchi near Kampung Kasat, Bandar Seri Begawan. Although the oil well was drilled as deep as 259 metres (850 feet), no oil was found in the well. Oil exploration in Brunei later shifted to Seria and Belait District in 1924.[11][12][13] Sultan Muhammad Jamalul Alam II established a new palace on the west bank in 1909 after been persuaded by the British,[5] along with the arriving of Chinese traders to boost the economy. Mosque and government buildings was also built along the western shores in 1920.[4] In the same year, the new settlement was declared as a new capital of Brunei and became a municipal area.[10]

However, the city prosperity was almost ended when the city was captured by the Japanese in 1941, before been recaptured by the Allied forces in 1945. During the war, most infrastructure was destroyed by Japanese and Allied bombing.[14] The British began reconstructing most of its possessions in Borneo at the end of 1945 with the restoration of the law and order and the reopening of schools.[14] In 1950, Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III, upon his ascension to the throne, negotiated with the British for an increase in corporate taxes, growing from 10% to 30% in 1953. A M$1.2 million (US$0.39 million) allotment to Brunei for war damages during the Japanese occupation increased from M$1 million in 1946 to M$100 million (US$32.6 million) in 1952. A five-year development plan with a total budget of M$100 million was also implemented in 1953, with infrastructure receiving the largest percentage (80%) and the rest going toward social programmes.[14] Together with the expansion of the oil and gas industry, commercialization began to transform Brunei's capital and a large number of public buildings were constructed, along with the development of a central business district in the 1970s and 1980s.[4][5] On 1 August 2007, Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah gave consent for the expansion of the city from 12.87 km2 (4.97 sq mi) to 100.36 km2 (38.75 sq mi).[6]
Capital city
Istana Nurul Iman is the seat of the Brunei government and is the largest residential palace in the world according to Guinness World Records.[15] There are two prime minister offices in the city: one is located inside Istana Nurul Iman and another one is located at Jalan Kumbang Pasang.[16][17]
Local authority and city definition
The city is administered by the Bandar Seri Begawan Municipal Department, a department which was originally responsible to maintain the cleanliness and provide services to the municipality. The city obtained city status in 1920.[18]
With an area of 100.36 square kilometres, the city is located in the most populous district of Brunei namely Brunei-Muara District.[19] The city comprises the following Mukims (subdivisions of a district):[20]
However, 6 mukims are collectively known as Kampong Ayer or Water Village namely: Burong Pinggai Ayer, Sungai Kebun, Sungai Kedayan, Peramu, Saba, and Tamoi.
Geography
Bandar Seri Begawan is located at 4°53'25"N, 114°56'32"E, on the northern bank of the Brunei River.
Climate
Brunei features a tropical rainforest climate which is relatively hot and wet.[21] The city sees heavy precipitation throughout the course of the year with the Northeast Monsoon blows from December to March, while the Southeast Monsoon around June to October.[22]
| Climate data for Bandar Seri Begawan | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 34.1 (93.4) |
35.3 (95.5) |
38.3 (100.9) |
37.6 (99.7) |
36.4 (97.5) |
36.2 (97.2) |
36.2 (97.2) |
37.6 (99.7) |
36.0 (96.8) |
35.3 (95.5) |
34.9 (94.8) |
36.2 (97.2) |
38.3 (100.9) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 30.4 (86.7) |
30.7 (87.3) |
31.9 (89.4) |
32.5 (90.5) |
32.6 (90.7) |
32.5 (90.5) |
32.3 (90.1) |
32.4 (90.3) |
32.0 (89.6) |
31.6 (88.9) |
31.4 (88.5) |
31.0 (87.8) |
31.8 (89.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 23.3 (73.9) |
23.3 (73.9) |
23.5 (74.3) |
23.7 (74.7) |
23.7 (74.7) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.0 (73.4) |
23.1 (73.6) |
23.1 (73.6) |
23.2 (73.8) |
23.2 (73.8) |
23.2 (73.8) |
23.3 (73.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 18.4 (65.1) |
18.9 (66) |
19.4 (66.9) |
20.5 (68.9) |
20.3 (68.5) |
19.2 (66.6) |
19.1 (66.4) |
19.4 (66.9) |
19.6 (67.3) |
20.5 (68.9) |
18.8 (65.8) |
19.5 (67.1) |
18.4 (65.1) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 292.6 (11.52) |
158.9 (6.256) |
118.7 (4.673) |
189.4 (7.457) |
234.9 (9.248) |
210.1 (8.272) |
225.9 (8.894) |
226.6 (8.921) |
264.4 (10.409) |
312.3 (12.295) |
339.9 (13.382) |
339.6 (13.37) |
2,913.3 (114.697) |
| Average rainy days | 16 | 12 | 11 | 16 | 18 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 19 | 21 | 23 | 21 | 205 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 86 | 85 | 84 | 84 | 85 | 84 | 84 | 83 | 84 | 85 | 86 | 86 | 85 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 196 | 191 | 225 | 239 | 236 | 210 | 222 | 218 | 199 | 206 | 205 | 211 | 2,558 |
| Source #1: World Meteorological Organisation,[23] Deutscher Wetterdienst (extremes, 1971–2012 and humidity, 1972–1990)[24] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: NOAA (sun, 1961−1990)[25] | |||||||||||||
Demography
Ethnicity and religion
The Bruneian Census 2011 Report estimated the population of Bandar Seri Begawan is around 20,000, while the metropolitan area has around 279,924.[1][2] The majority of Bruneians are Malays, with Chinese being the most significant minority group.[2] Aboriginal groups such as the Bisaya, Belait, Dusun, Kedayan, Murut and Tutong also exist. They are classified as part of the Malay ethnic groups and have been given the Bumiputera privileges.[1] Large numbers of foreign workers are also found within Brunei and the capital city, with the majority being from Malaysia, Thailand, Philippines, Indonesia (mostly Betawi) and the Indian subcontinent.[26][27]
Places of interest
Mosques

- The Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddin Mosque – Built in 1958, it features a golden dome and an interior of Italian marble walls, carpeting and an elevator. It also has tunnels, which are used by the sultan on journeys through the town. This mosque is considered by some to be one of the world's most beautiful mosques[28]
- Jame'Asr Hassanil Bolkiah Mosque – This mosque is the largest mosque in Brunei. It was built to commemorate the 25th anniversary of the sultan's reign. It is known locally as the Kiarong mosque.
- Al-Ameerah Al-Hajjah Maryam Mosque This green mosque is located just next to Jalan Jerudong.
- Ash Shaliheen Mosque – This mosque is located next to the prime minister's office in Bandar Seri Begawan. The mosque architecture is inspired by Al-Masjid an-Nabawi in Saudi Arabia and Spain's Mosque–Cathedral of Córdoba.
- Surau Brunei International Airport – This surau or small mosque is located just next to Brunei International Airport.
Historical sites
- The Royal Ceremonial Hall or Lapau
- Located in Jalan Kianggeh, the Lapau (Royal Ceremonial Hall) is used for royal traditional ceremonies. It was here that the sultan Hassanal Bolkiah was crowned on 1 August 1968. The interior of the Lapau and sultan's throne are decorated in exquisite gold. Within the precincts of the Lapau is the Dewan Majlis where the legislative assembly used to sit. Official permission is required by visitors to enter this building. With the completion of the new legislative council building in Jalan Mabohai, the Lapau will soon become a symbol of the sultanate's constitutional history.
- Late sultan Bolkiah's tomb in Kota Batu
- Late sultan Sharif Ali's tomb in Kota Batu
- The Royal Mausoleum (Makam Di-Raja)
- Located away from the banks of Brunei River, behind the department store Soon Lee Megamart at Mile One, Jalan Tutong, the Royal Mausoleum and the graveyard have been used by succeeding generations of sultans. Inside the Mausoleum itself are the remains of the last four sultans, Haji Sir Muda Omar Ali Saifuddin (1950–1967), who died in 1986, Ahmad Tajuddin Ibnu Sultan Muhammad Jamalul Alam (1924–1950), Muhammad Jamalul Alam Ibnu Sultan Hashim (1906–1924), and Hashim Jalilul Alam Putera Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddin II (1885–1906). Other members of the royal families from those times are also buried there.
- Dang Ayang Mausoleum
- A legendary figure who was chased away from Kampong Ayer for committing adultery. Adultery was a taboo in Bruneian society. She died in what we know today as Pusat Bandar (Central City). However some sources say that she was a Queen of Brunei.
- Royal Wharf
Istana Darussalam
This Istana or Palace is located near to the river. It is one of the oldest non-residential palaces in Brunei. This palace was where the Begawan Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddin III resided and where Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah was born. It is not open to the public.
Museums
- Brunei Museum (Muzium Brunei) – Located on an archaeological site at Kota Batu about 5 km (3.1 mi) from Bandar Seri Begawan, this museum is the largest in the country. It was first established in 1965 and occupied its present site since 1970. Officially opened in 1972, the museum focuses on Islamic history, natural history, Brunei artefacts and customs, ceramics and the oil industry of Brunei. of oil, process of drilling, refining, the history of the petroleum industry in Brunei and a map depicting current oil fields..
- Malay Technology Museum – The museum was officially opened in 1988.

- Royal Regalia Building Museum – Located at Jalan Sultan, this museum is devoted to the sultan Hassanal Bolkiah. The main gallery displays the coronation and Silver Jubilee Chariots, gold and silver ceremonial armoury and traditional jewellery encrusted coronation crowns. A collection of documents that chronicles the sultan's life up to the coronation together with the constitutional history gallery is also housed in the same building.
- The Brunei History Centre – Located at Jalan Sultan next to the Royal Regalia building is the Brunei history centre. The centre was opened in 1982 with a brief to research the history of Brunei. Much of that work has been establishing the genealogy and history of the sultans and royal family. The public display has a wealth of information on these subjects including replicas and brass rubbings of tombs. A flow chart giving the entire lineage of the Brunei sultans can be found at the entrance.
- Brunei Stamp Gallery – The recently opened Brunei Stamp Gallery is located inside the post office building in Jalan Sultan.
- Bubongan dua belas – The name which translates to the House of Twelve Roofs is located in Jalan Residency. It was built in 1906 and was formerly the official residence of British residents and high commissioners in Brunei. It is one of the oldest surviving building in Bandar Seri Begawan. It now serves as a gallery that exhibits the long-standing relationship between the sultanate and the United Kingdom
- The Arts and Handicrafts Centre – Located at Jalan Residency it was opened in 1980. Brunei's fine arts and crafts date back to centuries and are part of the nation's proud heritage. The Arts and Handicrafts Centre conducts courses in silverware, brassware, woodcarving, songkok-making, weaving and basketry.
Istana Nurul Iman
The Istana Nurul Iman palace is the residence of the sultan of Brunei. It is located 3 km southwest of the city centre. Its name is taken from Arabic, meaning "Palace of the Light of Faith". The palace was designed by Leandro V. Locsin, and built by the Filipino firm, Ayala Corporation, mixing Malay and Islamic elements in the building architecture.[29] It contains 1,788 rooms, with 257 bathrooms, and a banquet hall that can accommodate up to 5,000 guests. The palace only opens to public during the yearly three-day Hari Raya Adilfitri celebration.[30]
Kampong Ayer
The city's suburb incorporates nearby Kampong Ayer (water village), in which houses were built on stilts and stretches about 8 km (5.0 mi) along the Brunei river. It was founded 1,000 years ago.[31] The village is considered the largest stilt settlement in the world with approximately 30,000 residents and 2,000 houses.[32] "Venice of the East" was coined by Antonio Pigafetta in honour of the water village he encountered at Kota Batu (just east of city's central business district). Pigafetta was on Ferdinand Magellan's last voyages when he visited Brunei in 1521.[33]
Parks and trails
- The Waterfront
- This latest addition to the beautiful Bandar Seri Begawan is strategically overlooking the historical Kg. Ayer. The approximately 1.8-hectare (4.4-acre) site took almost three years to be completed and was officially opened to the public on 28 May 2011. The Waterfront is accessible to everyone as it is open 24 hours where public can enjoy sightseeing and take a break at the outdoor cafes offering varieties of drinks and dishes.
- Persiaran Damuan
- This narrow strip of landscaped park between Jalan Tutong and the Sungei Brunei was created in 1986 as a "Square". It has a permanent display of the work of a sculptor from each of the original ASEAN countries. The 1 km (0.62 mi)-long park has pleasant walkways bordered by shrubs and the mangrove fringed Pulau Ranggu where two species of monkeys live, including the notable proboscis monkey only found in Borneo. The park also offers some of the best views of the Istana Nurul Iman.
- Jalan Tasek Lama
- Located just a few minutes walk from the city centre, this is a popular trekking trail for the local residents of Bandar Seri Begawan. There are well made walkaways through the small park which has benches and picnic spots as well as a waterfall and ponds with water lilies.
- Bukit Subok Recreational Park
- The park offers a great view of the Kampong Ayer and downtown Bandar Seri Begawan. There is a well maintained wooden walkaway with viewing huts along the way. These huts provide a good vantage points of Kampong Ayer and its surroundings.
Transportation

Land
The capital is connected to Bus of Bandar Seri Begawan the western part of the country by road. To get to the eastern part of Brunei (Temburong) it is necessary to travel through Sarawak which is in Malaysia, via the town of Limbang which is accessed by the Kuala Lurah Bus terminal. To get to Bandar Seri Begawan from the west, access is via Miri town in Sarawak via the Sungai Tujuh Bus terminal and then along the coastal highway.
The main bus station in the city is located in Jalan Cator underneath a multi-story car park. There are six bus routes servicing Bandar Seri Begawan area; the Central Line, Circle Line, Eastern Line, Southern Line, Western Line and Northern Line. The buses operate from 6.30 am till 6.00pm except for Bus No. 1 and 20 which have extended to the night. All bus routes begin and terminate their journey at the main bus terminal. Buses heading to other towns in Brunei such as Tutong, Seria and Kuala Belait also depart from the main bus terminal and Taxicab.
Air
Brunei International Airport serves the whole country. It is 11 km (6.8 mi) from the town centre and can be reached in 10 minutes via the Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah Highway. Royal Brunei Airlines, the national airline, has its head office in the RBA Plaza in the city.[34][35]
Water
A water taxi service known as 'penambang' is used for transportation between downtown Bandar Seri Begawan and Kampong Ayer. Water taxis are the most common means of negotiating the waterways of Kampung Ayer. They can be hailed from the numerous "docking parts" along the banks of the Brunei River. Fares are negotiable. Regular water taxi and boat services depart for Temburong between 7:45 am and 4 pm daily, and also serve the Malaysian towns of Limbang, Lawas, Sundar and Labuan. A speedboat is used for passengers travelling to Penambang Ferry Service and from Bangar and Limbang.
Economy
The city produces furniture,[36] textiles, handicrafts, and timber.[37][38]
Shopping
Brunei are known to its shophouses design. These are the shopping areas:
- Gadong Central is where many shopping complexes, shops and restaurants are located (e.g., The Mall Gadong, Western fast food restaurants and Ayamku, the local fast food chain). There is also a night market called Pasar Malam Gadong.
- Serusop Complex, Few small shopping malls and shopping complexes can be found near Brunei International Airport.
- Rimba, a medium-sized mall with Giant supermarket.
- Tungku-link Commercial Complex, various shophouses and local and Korean restaurants, textiles shops, carpet.
- Beribi Complex
- Kiulap Commercial Precinct in Kiarong, Kiulap Mall, private colleges, banks and various restaurants from local, Pakistani and Korean restaurants.
- Abdul Razak Complex and Seri Complex in Jalan Raja Isteri Pengiran Anak Saleha, Kiarong
Traditional markets
- Tamu Kianggeh, The open market brings together numerous small entrepreneurs selling local vegetables, fruits, live chickens and fish, potted plants, assorted food and beverages.
- Pasar Malam (Night Market), located a few metres away from The Mall Gadong, brings together numerous small entrepreneurs just like in Tamu Kianggeh however its more into selling foods such as Sate, Soto, national dishes like Nasi Katok and Ambuyat, fruits and beverages. During the day, it is where local botanist selling their potted plants.
Education
All levels of education are available in Bandar Seri Begawan from kindergarten to the tertiary level.
- The University of Brunei Darussalam, established on 28 October 1985, only a year after the sultanate regained full independence, is located 4.5 km (2.8 mi) from the city centre.[39] It is the oldest and also the largest university in Brunei in terms of student enrolment and curriculum offered.
- The Sultanate's second university, Universiti Islam Sultan Sharif Ali, is also located in Bandar Seri Begawan's suburb of Gadong. It was established on 1 January 2007[40] as an Islamic university.
- Brunei Technological University
- Seri Begawan Religious Teachers University
Higher educational institutes in Bandar Seri Begawan:
- Maktab Sains Paduka Seri Begawan Sultan (Paduka Seri Begawan Sultan College of Science)
- Princess Rashidah Sa'adatul Bolkiah Nursing College
- Maktab Teknik Sultan Saiful Rijal (Sultan Saiful Rijal Technical College)
- Pusat Tingkatan Enam Sengkurong (Sengkurong Sixth Form Centre)
- Pusat Tingkatan Enam Meragang (Meragang Sixth Form Centre).
Private higher educational institutes in Bandar Seri Begawan:
- KEMUDA Institute – established since 2004 that offers Foundation courses, Diploma and Advanced Diploma.
Secondary schools in the capital:
- Chung Hwa Middle School
- St. George's School
- St. Andrew's School
- International School Brunei
- Jerudong International School
- Institut Tahfiz Al Quran Sultan Haji Hassanal Bolkiah (ITQSHHB) (Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah Institute of Tahfiz Al-Quran)
International relations
Several countries have set up their embassies, commissions or consulates in Bandar Seri Begawan, including Australia,[41] Bangladesh,[42] Belgium, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burma,[43] Cambodia, Canada,[44] Chile, China,[45] Finland,[46] France,[47] Germany,[48] India,[49] Indonesia,[50] Japan,[51] Laos, Malaysia,[52] Netherlands, New Zealand, North Korea, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines, Poland, Russia, Saudi Arabia,[53] Singapore,[54] South Korea, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, Thailand,[55] United Kingdom,[56] United States[57] and Vietnam.[58][59]
Development
Recently there have been plans to develop Bandar Seri Begawan to look more Urban (similar to Jakarta). Redevelopment has taken place. The municipality is executing a BSB Master-plan with the support of both locals and government. Bandar Seri Begawan looking for more monuments such as Monas-style Brunei National Monument.
Sister city
Bandar Seri Begawan currently has only six sister city:
-
 Nanjing, China.[60]
Nanjing, China.[60] -
 Seoul, South Korea.
Seoul, South Korea. -
 Pyongyang, North Korea.
Pyongyang, North Korea. -
 Havana, Cuba.
Havana, Cuba. -
 Santiago de Cuba, Cuba.
Santiago de Cuba, Cuba.  Jakarta, Indonesia.
Jakarta, Indonesia.
Gallery
|
References
- 1 2 3 "Brunei Darussalam Statistical Yearbook (Brunei Darussalam – An Introduction)" (PDF). Department of Statistics, Brunei. Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister's Office. 2011. pp. 28/2 and 39/9. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 May 2015. Retrieved 4 May 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Population and Housing Census Report (Demographic Characteristics)" (PDF). Department of Economic Planning and Development. 2011. pp. 4/10. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 May 2015. Retrieved 4 May 2015.
- 1 2 Oxford Business Group (2009). The Report: Brunei Darussalam 2009. Oxford Business Group. pp. 215–. ISBN 978-1-907065-09-5.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Marshall Cavendish Corporation (2007). World and Its Peoples: Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, and Brunei. Marshall Cavendish. pp. 1206–. ISBN 978-0-7614-7642-9.
- 1 2 3 4 Trudy Ring; Noelle Watson; Paul Schellinger (12 November 2012). Asia and Oceania: International Dictionary of Historic Places. Routledge. pp. 161–. ISBN 978-1-136-63979-1.
- 1 2 3 4 Shirleen Cambridge (5 October 2014). Ultimate Handbook Guide to Bandar Seri Begawan : (Brunei) Travel Guide. MicJames. pp. 8–. GGKEY:16PGAE1LKCQ.
- ↑ Roman Adrian Cybriwsky (23 May 2013). Capital Cities around the World: An Encyclopedia of Geography, History, and Culture: An Encyclopedia of Geography, History, and Culture. ABC-CLIO. pp. 32–. ISBN 978-1-61069-248-9.
- ↑ "List of Brunei Sultans". Government of Brunei (in Malay). Brunei Historical Centre. Archived from the original on 15 April 2015. Retrieved 15 April 2015.
- ↑ Nigel Hicks (2007). The Philippines. New Holland Publishers. pp. 34–. ISBN 978-1-84537-663-5.
- 1 2 3 Jatswan S. Sidhu (22 December 2009). Historical Dictionary of Brunei Darussalam. Scarecrow Press. pp. 32–. ISBN 978-0-8108-7078-9.
- ↑ "History of Oil & Gas". Brunei Shell Petroleum Company Sendirian Berhad (BSP). Archived from the original on 2 June 2015. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ Rozan, Yunos. "How oil was discovered in Brunei". bruneiresources.com. Archived from the original on 19 October 2014. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "Exploration history". Brunei Shell Petroleum Company Sendirian Berhad (BSP). Archived from the original on 2 June 2015. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- 1 2 3 Marie-Sybille de Vienne (9 March 2015). Brunei: From the Age of Commerce to the 21st Century. NUS Press. pp. 105–108. ISBN 978-9971-69-818-8.
- ↑ "Largest residential palace". Guinness World Records. Archived from the original on 30 May 2015. Retrieved 30 May 2015.
- ↑ "Overview – Prime Minister's Office". Prime Minister's Office of Brunei Darussalam. Archived from the original on 30 May 2015. Retrieved 30 May 2015.
- ↑ "Kompleks Bangunan Jabatan Perdana Menteri, Brunei (Prime Minister Office Building Complex, Brunei)". Boehme systems. Archived from the original on 23 September 2014. Retrieved 30 May 2015.
- ↑ "Jabatan Bandaran Bandar Seri Begawan" (in Malay). Jabatan Bandaran – Bandar Seri Begawan. Archived from the original on 1 May 2015. Retrieved 1 May 2015.
- ↑ Gwillim Law (30 October 2013). "Districts of Brunei Darussalam". Statoids. Archived from the original on 11 May 2015. Retrieved 11 May 2015.
- ↑ Za'im Zaini; Sonia K (23 July 2007). "Brunei capital to become nearly ten times bigger". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the People's Republic of China, Embassy of the People's Republic of China in Bandar Seri Begawan. Archived from the original on 1 May 2015. Retrieved 1 May 2015.
- ↑ Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc (1 May 2014). Britannica Student Encyclopedia. Encyclopedia Britannica, Inc. pp. 1–. ISBN 978-1-62513-172-0.
- ↑ Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (1999). Irrigation in Asia in Figures. Food & Agriculture Org. pp. 65–. ISBN 978-92-5-104259-5.
- ↑ "World Weather Information Service - Bandar Seri Begawan". World Meteorological Organisation. Retrieved 14 May 2010.
- ↑ "Klimatafel von Bandar Seri Begawan (Int. Flugh.) / Brunei" (PDF). Baseline climate means (1961-1990) from stations all over the world (in German). Deutscher Wetterdienst. Retrieved 22 November 2016.
- ↑ "Brunei Darussalam Climate Normals 1961−1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 29 November 2013.
- ↑ "Foreign Workers Information". Brunei Resources. 2005. Archived from the original on 11 May 2015. Retrieved 11 May 2015.
- ↑ "Business Guide – Employment and Immigration". Brunei Economic Development Board. Archived from the original on 11 May 2015. Retrieved 11 May 2015.
- ↑ "60 Unbelievable Beautiful Mosques Around The World". DesignFollow. 13 May 2011. Retrieved 16 September 2013.
- ↑ "Istana Nurul Iman". Lonely Planet. Archived from the original on 2 June 2015. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "World's Largest Palace : Istana Nurul Iman, Brunei". ASEAN Book of Records. Archived from the original on 8 November 2014. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ Yunos, Rozan (25 April 2011). "Tracing the history of today's Kampong Ayer". The Brunei Times. Archived from the original on 2 June 2013. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ↑ Piri, Sally (22 October 2011). "Kampong Ayer in Brunei and Borneo". The Brunei Times. Archived from the original on 8 June 2015. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ↑ "Kampung Ayer". Lonely Planet. Archived from the original on 7 June 2014. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ↑ "Contact Us." Royal Brunei Airlines. Retrieved on 10 November 2010.
- ↑ "World Wide Offices Brunei." Royal Brunei Airlines. Retrieved on 10 November 2010. "Bandar Seri Begawan Details: RBA Address: Royal Brunei Airlines. RBA Plaza, Jalan Sultan, Bandar Seri Begawan BS 8811, Brunei Darussalam."
- ↑ "Furniture Manufacturers in Bandar Seri Begawan, BN". Yellow Pages. Archived from the original on 2 November 2012. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "Timber Retail in Bandar Seri Begawan, BN". Yellow Pages. Archived from the original on 1 November 2012. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "The 4th China-ASEAN Expo Review". China-ASEAN EXPO Secretariat. Archived from the original on 19 March 2014. Retrieved 30 May 2015.
- ↑ "UBD in Brief". Universiti Brunei Darussalam. Retrieved 26 October 2009.
- ↑ "About Us". Universiti Islam Sultan Sharif Ali. Retrieved 26 October 2009.
- ↑ "Australian High Commission Bandar Seri Begawan". Australian High Commission. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "Bangladesh High Commission Brunei Darussalam". Bangladesh High Commission. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "Embassy of the Republic of the Union of Myanmar, Bandar Seri Begawan". Myanmar Embassy. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "High Commission of Canada in Brunei Darussalam". Canada International. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "Embassy of the People's Republic of China in Negara Brunei Darussalam". China Embassy. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "Contact information: Finland´s Honorary Consulate, Bandar Seri Begawan (Brunei Darussalam)". Ministry for Foreign Affairs (Finland). Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "Embassy of France in Brunei Darussalam". Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Development (France). Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "German Embassy Bandar Seri Begawan". German Embassy. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "The High Commission of India Brunei Darussalam". Japan Embassy. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "Embassy of the Republic of Indonesia in Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam". Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Indonesia). Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "Embassy of Japan in Brunei Darussalam". Japan Embassy. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "Official Website of the High Commission of Malaysia, Bandar Seri Begawan". Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Malaysia). Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "Embassy of Saudi Arabia – Bandar Seri Begawan". Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Saudi Arabia). Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "High Commission of the Republic of Singapore Bandar Seri Begawan". Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Singapore). Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "Royal Thai Embassy, Bandar Seri Begawan Brunei Darussalam". Thailand Embassy. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "British High Commission Bandar Seri Begawan". Government of the United Kingdom. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "Embassy of the United States in Bandar Seri Begawan". US Embassy. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "Embassy of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam in Brunei Darussalam". Vietnam Embassy. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "Foreign Embassies and Consulates in Brunei (36 Foreign Embassies and Consulates in Brunei)". GoAbroad.com. Archived from the original on 26 April 2015. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ Daljit Singh; Pushpa Thambipillai (10 May 2012). Southeast Asian Affairs 2012. Institute of Southeast Asian Studies. pp. 98–. ISBN 978-981-4380-23-2.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bandar Seri Begawan. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Bandar Seri Begawan. |


