Baltic Assembly
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
 Member states of the Baltic Assembly (green).
|
||||
| Headquarter | ||||
| Working languages | ||||
| Type | Intergovernmental organization | |||
| Membership | ||||
| Leaders | ||||
| • | President | Laine Randjärv[1] | ||
| Establishment | ||||
| • | Baltic Assembly | 1991 | ||


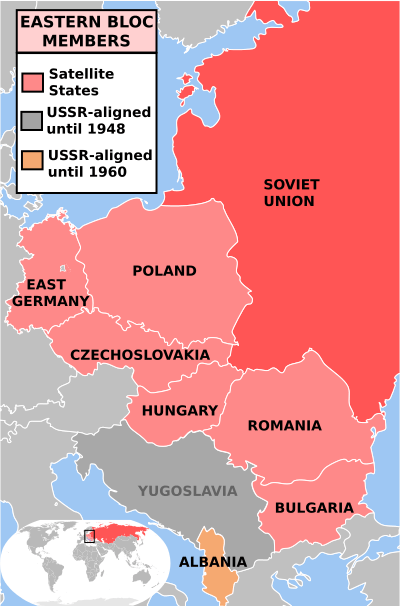
The Baltic Assembly (BA) is a regional organization that promotes intergovernmental cooperation between the Baltic republics of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. It attempts to find a common position in relation to many international issues, including economic, political and cultural issues. The decisions of the assembly are advisory.
The budget of the BA is funded by the three member governments. The official languages of the Baltic Assembly are Estonian, Latvian and Lithuanian. The headquarters and secretariat of the organization are located in Riga, Latvia.
History
Background
The Baltic States, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania were independent states since 1918 after the fall of the Russian Empire. During the outbreak of World War II, under the Ribbentrop-Molotov Pact, they were illegally annexed by the Soviet Union in 1940 and continued on for fifty years.
Under Mikhail Gorbachev, the last Soviet leader, the policies of glasnost and perestroika has led to the restoration of independence between 1990 and 1991 which led the Baltic republics to break away. The Soviet Union itself recognized the independence of the restored Baltic states on 6 September 1991 before its dissolution later that year.
Formation
The organization was formed after a decision to establish it was made in Vilnius on 1 December 1990. It works under regulations approved on 8 November 1991 in Tallinn.[2] On 13 June 1994 the three nations agreed to the structure and rules of the organization.[3]
Achievements
The BA claims the following as its achievements between 1991 and 2003:[4]
- Withdrawal of Russian troops from the member States,
- Formation of the Baltic Council of Ministers as an institution of governmental co-operation,
- Development of common Baltic economic, educational and information technology policies,
- Harmonization of legislation in conformity with requirements of the European Union,
- Improvement of border-crossing procedures,
- The establishment of the Baltic Assembly Prizes for Literature, Arts and Science.
Sessions
There are ordinary and extraordinary Sessions. The ordinary Session is convened once a year, as a concluding forum of a country's presidency, which proceeds according to a yearly rotation principle in Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. Before 2003 there were two Sessions a year – in spring and autumn, and countries - participants had half a year presidency.
Any national delegation may propose that an extraordinary session is held. On 8-9 February 1998 in Helsinki, Finland, following to the 2nd Joint Meeting of the Nordic Council and the Baltic Assembly, the first Extraordinary Session of the Baltic Assembly took place. The second Extraordinary Session of the Baltic Assembly was held on 27-29 April 2005 in Parnu, Estonia, following to the 5th Joint Meeting of the Baltic Assembly and the Nordic Council. [5]
Composition
The BA comprises sixty members. Each of the parliaments of the three States appoints twenty of its members to the Assembly. Each of the national parliaments appoints two of the members to be head and deputy head of the national delegation. The six head delegates and deputy head delegates form the BA’s Presidium. The Chairman of the Presidium is the head of the national delegation of the country hosting the next session of the BA. The heads of the other two national delegations are Vice Chairmen of the Presidium. The Presidium controls the BA between sessions. The Chairman acts as the coordinator of the work of the BA, is its representative with other bodies and liaises with the three members’ governments.
Committees
The following are the standing committees:
- Budget and Audit
- Communications and IT
- Economic and Social Affairs
- Education, Science and Culture
- Environment Protection and Energy
- Legal
- Security and Foreign Affairs
Each member of the BA participates in at least one committee.
Political groupings
The 20 members of the BA from each country are chosen so that their political make-up reflects the proportions within their home parliament. The members may then form cross-national party groupings of at least five members from at least two nations.[6]
As of 2006 the three political groupings are the Conservative-Right Party Group, the Centre Party Group and the Social Democratic Party Group.
Baltic Assembly Prize for Literature, the Arts and Science
Since 1993, the Baltic Assembly gives out an award annually for achievements in literature, the arts and science.
See also
- NB8
- Baltic Entente
- Commonwealth of Independent States
- Eurasian Economic Union
- European Union
- Russian Empire
- Soviet Union
- Post-Soviet states
External links
- Assembly web site
- Flag of the Baltic Assembly at Flags of the World
- Seimas of the Republic of Lithuania
Notes
- ↑ http://baltasam.org/en/structure/presidium/president
- ↑ http://baltasam.org/en/history/pre-history
- ↑ http://baltasam.org/en/history/international-inclusion
- ↑ http://baltasam.org/en/history
- ↑ http://baltasam.org/en/structure/session
- ↑ http://baltasam.org/en/structure/national-delegations