Transformation (genetics)
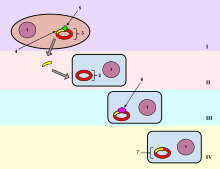
In molecular biology, transformation is the genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the direct uptake and incorporation of exogenous genetic material from its surroundings through the cell membrane(s). For transformation to take place, the recipient bacteria must be in a state of competence, which might occur in nature as a time-limited response to environmental conditions such as starvation and cell density, and may also be induced in a laboratory.[1]
Transformation is one of three processes for horizontal gene transfer, in which exogenous genetic material passes from bacterium to another, the other two being conjugation (transfer of genetic material between two bacterial cells in direct contact) and transduction (injection of foreign DNA by a bacteriophage virus into the host bacterium).[1] In transformation, the genetic material passes through the intervening medium, and uptake is completely dependent on the recipient bacterium.[1]
As of 2014 about 80 species of bacteria were known to be capable of transformation, about evenly divided between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria; the number might be an overestimate since several of the reports are supported by single papers.[1]
"Transformation" may also be used to describe the insertion of new genetic material into nonbacterial cells, including animal and plant cells; however, because "transformation" has a special meaning in relation to animal cells, indicating progression to a cancerous state, the process is usually called "transfection".[2]
History
Transformation in bacteria was first demonstrated in 1928 by British bacteriologist Frederick Griffith.[3] Griffith discovered that a strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae could be made virulent after being exposed to heat-killed virulent strains. Griffith hypothesized that some "transforming principle" from the heat-killed strain was responsible for making the harmless strain virulent. In 1944 this "transforming principle" was identified as being genetic by Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod, and Maclyn McCarty. They isolated DNA from a virulent strain of S. pneumoniae and using just this DNA were able to make a harmless strain virulent. They called this uptake and incorporation of DNA by bacteria "transformation" (See Avery-MacLeod-McCarty experiment). The results of Avery et al.'s experiments were at first skeptically received by the scientific community and it was not until the development of genetic markers and the discovery of other methods of genetic transfer (conjugation in 1947 and transduction in 1953) by Joshua Lederberg that Avery's experiments were accepted.[4]
It was originally thought that Escherichia coli, a commonly used laboratory organism, was refractory to transformation. However, in 1970, Morton Mandel and Akiko Higa showed that E. coli may be induced to take up DNA from bacteriophage λ without the use of helper phage after treatment with calcium chloride solution.[5] Two years later in 1972, Stanley Norman Cohen, Annie Chang and Leslie Hsu showed that CaCl
2 treatment is also effective for transformation of plasmid DNA.[6] The method of transformation by Mandel and Higa was later improved upon by Douglas Hanahan.[7] The discovery of artificially induced competence in E. coli created an efficient and convenient procedure for transforming bacteria which allows for simpler molecular cloning methods in biotechnology and research, and it is now a routinely used laboratory procedure.
Transformation using electroporation was developed in the late 1980s, increasing the efficiency of in-vitro transformation and increasing the number of bacterial strains that could be transformed.[8] Transformation of animal and plant cells was also investigated with the first transgenic mouse being created by injecting a gene for a rat growth hormone into a mouse embryo in 1982.[9] In 1907 a bacterium that caused plant tumors, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, was discovered and in the early 1970s the tumor-inducing agent was found to be a DNA plasmid called the Ti plasmid.[10] By removing the genes in the plasmid that caused the tumor and adding in novel genes, researchers were able to infect plants with A. tumefaciens and let the bacteria insert their chosen DNA into the genomes of the plants.[11] Not all plant cells are susceptible to infection by A. tumefaciens, so other methods were developed, including electroporation and micro-injection.[12] Particle bombardment was made possible with the invention of the Biolistic Particle Delivery System (gene gun) by John Sanford in the 1980s.[13][14][15]
Definitions
Transformation is one of three forms of horizontal gene transfer that occur in nature among bacteria, in which DNA encoding for a trait passes from one bacterium to another and is integrated into the recipient genome by homologous recombination; the other two are transduction, carried out by means of a bacteriophage, and conjugation, in which a gene is passed through direct contact between bacteria.[1] In transformation, the genetic material passes through the intervening medium, and uptake is completely dependent on the recipient bacterium.[1]
Competence refers to a temporary state of being able to take up exogenous DNA from the environment; it may be induced in a laboratory.[1]
It appears to be an ancient process inherited from a common prokaryotic ancestor that is a beneficial adaptation for promoting recombinational repair of DNA damage, especially damage acquired under stressful conditions. Natural genetic transformation appears to be an adaptation for repair of DNA damage that also generates genetic diversity.[1][16]
Transformation has been studied in medically important Gram-negative bacteria species such as Helicobacter pylori, Legionella pneumophila, Neisseria meningitidis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Haemophilus influenzae and Vibrio cholerae.[17] It has also been studied in Gram-negative species found in soil such as Pseudomonas stutzeri, Acinetobacter baylyi, and Gram-negative plant pathogens such as Ralstonia solanacearum and Xylella fastidiosa.[17] Transformation among Gram-positive bacteria has been studied in medically important species such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus mutans, Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus sanguinis and in Gram-positive soil bacterium Bacillus subtilis.[16] It has also been reported in at least 30 species of Proteobacteria distributed in the classes alpha, beta, gamma and epsilon.[18] The best studied Proteobacteria with respect to transformation are the medically important human pathogens Neisseria gonorrhoeae (class beta), Haemophilus influenzae (class gamma) and Helicobacter pylori (class epsilon)[16]
"Transformation" may also be used to describe the insertion of new genetic material into nonbacterial cells, including animal and plant cells; however, because "transformation" has a special meaning in relation to animal cells, indicating progression to a cancerous state, the process is usually called "transfection".[19]
Natural competence and transformation
As of 2014 about 80 species of bacteria were known to be capable of transformation, about evenly divided between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria; the number might be an overestimate since several of the reports are supported by single papers.[1]
Naturally competent bacteria carry sets of genes that provide the protein machinery to bring DNA across the cell membrane(s). The transport of the exogenous DNA into the cells may require proteins that are involved in the assembly of type IV pili and type II secretion system, as well as DNA translocase complex at the cytoplasmic membrane.[20]
Due to the differences in structure of the cell envelope between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, there are some differences in the mechanisms of DNA uptake in these cells, however most of them share common features that involve related proteins. The DNA first binds to the surface of the competent cells on a DNA receptor, and passes through the cytoplasmic membrane via DNA translocase.[21] Only single-stranded DNA may pass through, the other strand being degraded by nucleases in the process. The translocated single-stranded DNA may then be integrated into the bacterial chromosomes by a RecA-dependent process. In Gram-negative cells, due to the presence of an extra membrane, the DNA requires the presence of a channel formed by secretins on the outer membrane. Pilin may be required for competence, but its role is uncertain.[22] The uptake of DNA is generally non-sequence specific, although in some species the presence of specific DNA uptake sequences may facilitate efficient DNA uptake.[23]
Natural transformation
Natural transformation is a bacterial adaptation for DNA transfer that depends on the expression of numerous bacterial genes whose products appear to be responsible for this process.[20][24] In general, transformation is a complex, energy-requiring developmental process. In order for a bacterium to bind, take up and recombine exogenous DNA into its chromosome, it must become competent, that is, enter a special physiological state. Competence development in Bacillus subtilis requires expression of about 40 genes.[25] The DNA integrated into the host chromosome is usually (but with rare exceptions) derived from another bacterium of the same species, and is thus homologous to the resident chromosome.
In B. subtilis the length of the transferred DNA is greater than 1271 kb (more than 1 million bases).[26] The length transferred is likely double stranded DNA and is often more than a third of the total chromosome length of 4215 kb.[27] It appears that about 7-9% of the recipient cells take up an entire chromosome.[28]
The capacity for natural transformation appears to occur in a number of prokaryotes, and thus far 67 prokaryotic species (in seven different phyla) are known to undergo this process.[24]
Competence for transformation is typically induced by high cell density and/or nutritional limitation, conditions associated with the stationary phase of bacterial growth. Transformation in Haemophilus influenzae occurs most efficiently at the end of exponential growth as bacterial growth approaches stationary phase.[29] Transformation in Streptococcus mutans, as well as in many other streptococci, occurs at high cell density and is associated with biofilm formation.[30] Competence in B. subtilis is induced toward the end of logarithmic growth, especially under conditions of amino acid limitation.[31]
Transformation, as an adaptation for DNA repair
Competence is specifically induced by DNA damaging conditions. For instance, transformation is induced in Streptococcus pneumoniae by the DNA damaging agents mitomycin C (a DNA crosslinking agent) and fluoroquinolone (a topoisomerase inhibitor that causes double-strand breaks).[32] In B. subtilis, transformation is increased by UV light, a DNA damaging agent.[33] In Helicobacter pylori, ciprofloxacin, which interacts with DNA gyrase and introduces double-strand breaks, induces expression of competence genes, thus enhancing the frequency of transformation[34] Using Legionella pneumophila, Charpentier et al.[35] tested 64 toxic molecules to determine which of these induce competence. Of these only six, all DNA damaging agents, caused strong induction. These DNA damaging agents were mitomycin C (which causes DNA inter-strand crosslinks), norfloxacin, ofloxacin and nalidixic acid (inhibitors of DNA gyrase that cause double-strand breaks[36]), bicyclomycin (causes single- and double-strand breaks[37]), and hydroxyurea (induces DNA base oxidation[38]). UV light also induced competence in L. pneumophila. Charpentier et al.[35] suggested that competence for transformation probably evolved as a DNA damage response.
Logarithmically growing bacteria differ from stationary phase bacteria with respect to the number of genome copies present in the cell, and this has implications for the capability to carry out an important DNA repair process. During logarithmic growth, two or more copies of any particular region of the chromosome may be present in a bacterial cell, as cell division is not precisely matched with chromosome replication. The process of homologous recombinational repair (HRR) is a key DNA repair process that is especially effective for repairing double-strand damages, such as double-strand breaks. This process depends on a second homologous chromosome in addition to the damaged chromosome. During logarithmic growth, a DNA damage in one chromosome may be repaired by HRR using sequence information from the other homologous chromosome. Once cells approach stationary phase, however, they typically have just one copy of the chromosome, and HRR requires input of homologous template from outside the cell by transformation.[39]
To test whether the adaptive function of transformation is repair of DNA damages, a series of experiments were carried out using B. subtilis irradiated by UV light as the damaging agent (reviewed by Michod et al.[40] and Bernstein et al.[39]) The results of these experiments indicated that transforming DNA acts to repair potentially lethal DNA damages introduced by UV light in the recipient DNA. The particular process responsible for repair was likely HRR. Transformation in bacteria can be viewed as a primitive sexual process, since it involves interaction of homologous DNA from two individuals to form recombinant DNA that is passed on to succeeding generations. Bacterial transformation in prokaryotes may have been the ancestral process that gave rise to meiotic sexual reproduction in eukaryotes (see Evolution of sexual reproduction; Meiosis.)
Methods and mechanisms of transformation in laboratory

Bacterial
Artificial competence can be induced in laboratory procedures that involve making the cell passively permeable to DNA by exposing it to conditions that do not normally occur in nature.[41] Typically the cells are incubated in a solution containing divalent cations (often calcium chloride) under cold conditions, before being exposed to a heat pulse (heat shock).
It has been found that growth of Gram-negative bacteria in 20 mM Mg reduces the number of protein-to-lipopolysaccharide bonds by increasing the ratio of ionic to covalent bonds, which increases membrane fluidity, facilitating transformation.[42] The role of lipopolysaccharides here are verified from the observation that shorter O-side chains are more effectively transformed — perhaps because of improved DNA accessibility.
The surface of bacteria such as E. coli is negatively charged due to phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides on its cell surface, and the DNA is also negatively charged. One function of the divalent cation therefore would be to shield the charges by coordinating the phosphate groups and other negative charges, thereby allowing a DNA molecule to adhere to the cell surface.
DNA entry into E. coli cells is through channels known as zones of adhesion or Bayer’s junction, with a typical cell carrying as many as 400 such zones. Their role was established when cobalamine (which also uses these channels) was found to competitively inhibit DNA uptake. Another type of channel implicated in DNA uptake consists of poly (HB):poly P:Ca. In this poly (HB) is envisioned to wrap around DNA (itself a polyphosphate), and is carried in a shield formed by Ca ions.[42]
It is suggested that exposing the cells to divalent cations in cold condition may also change or weaken the cell surface structure, making it more permeable to DNA. The heat-pulse is thought to create a thermal imbalance across the cell membrane, which forces the DNA to enter the cells through either cell pores or the damaged cell wall.
Electroporation is another method of promoting competence. In this method the cells are briefly shocked with an electric field of 10-20 kV/cm, which is thought to create holes in the cell membrane through which the plasmid DNA may enter. After the electric shock, the holes are rapidly closed by the cell's membrane-repair mechanisms.
Yeast
Most species of yeast, including Saccharomyces cerevisiae, may be transformed by exogenous DNA in the environment. Several methods have been developed to facilitate this transformation at high frequency in the lab.[43]
- Yeast cells may be treated with enzymes to degrade their cell walls, yielding spheroplasts. These cells are very fragile but take up foreign DNA at a high rate.[44]
- Exposing intact yeast cells to alkali cations such as those of cesium or lithium allows the cells to take up plasmid DNA.[45] Later protocols adapted this transformation method, using lithium acetate, polyethylene glycol, and single-stranded DNA.[46] In these protocols, the single-stranded DNA preferentially binds to the yeast cell wall, preventing plasmid DNA from doing so and leaving it available for transformation.[47]
- Electroporation: Formation of transient holes in the cell membranes using electric shock; this allows DNA to enter as described above for bacteria.[48]
- Enzymatic digestion[49] or agitation with glass beads[50] may also be used to transform yeast cells.
Efficiency – Different yeast genera and species take up foreign DNA with different efficiencies.[51] Also, most transformation protocols have been developed for baker's yeast, S. cerevisiae, and thus may not be optimal for other species. Even within one species, different strains have different transformation efficiencies, sometimes different by 3 orders of magnitude. For instance, when S. cerevisiae strains were transformed with 10 ug of plasmid YEp13, the strain DKD-5D-H yielded between 550 and 3115 colonies while strain OS1 yielded less than 5 colonies.[52]
Plants
A number of methods are available to transfer DNA into plant cells. Some vector-mediated methods are:
- Agrobacterium-mediated transformation is the easiest and most simple plant transformation. Plant tissue (often leaves) are cut into small pieces, e.g. 10x10mm, and soaked for 10 minutes in a fluid containing suspended Agrobacterium. The bacteria will attach to many of the plant cells exposed by the cut. The plant cells secrete wound-related phenolic compounds which in turn act to upregulate the virulence operon of the Agrobacterium. The virulence operon includes many genes that encode for proteins that are part of a Type IV secretion system that exports from the bacterium proteins and DNA (delineated by specific recognition motifs called border sequences and excised as a single strand from the virulence plasmid) into the plant cell through a structure called a pilus. The transferred DNA (called T-DNA) is piloted to the plant cell nucleus by nuclear localization signals present in the Agrobacterium protein VirD2, which is covalently attached to the end of the T-DNA at the Right border (RB). Exactly how the T-DNA is integrated into the host plant genomic DNA is an active area of plant biology research. Assuming that a selection marker (such as an antibiotic resistance gene) was included in the T-DNA, the transformed plant tissue can be cultured on selective media to produce shoots. The shoots are then transferred to a different medium to promote root formation. Once roots begin to grow from the transgenic shoot, the plants can be transferred to soil to complete a normal life cycle (make seeds). The seeds from this first plant (called the T1, for first transgenic generation) can be planted on a selective (containing an antibiotic), or if an herbicide resistance gene was used, could alternatively be planted in soil, then later treated with herbicide to kill wildtype segregants. Some plants species, such as Arabidopsis thaliana can be transformed by dipping the flowers or whole plant, into a suspension of Agrobacterium tumefaciens, typically strain C58 (C=Cherry, 58=1958, the year in which this particular strain of A. tumefaciens was isolated from a cherry tree in an orchard at Cornell University in Ithaca, New York). Though many plants remain recalcitrant to transformation by this method, research is ongoing that continues to add to the list the species that have been successfully modified in this manner.
- Viral transformation (transduction): Package the desired genetic material into a suitable plant virus and allow this modified virus to infect the plant. If the genetic material is DNA, it can recombine with the chromosomes to produce transformant cells. However, genomes of most plant viruses consist of single stranded RNA which replicates in the cytoplasm of infected cell. For such genomes this method is a form of transfection and not a real transformation, since the inserted genes never reach the nucleus of the cell and do not integrate into the host genome. The progeny of the infected plants is virus-free and also free of the inserted gene.
Some vector-less methods include:
- Gene gun: Also referred to as particle bombardment, microprojectile bombardment, or biolistics. Particles of gold or tungsten are coated with DNA and then shot into young plant cells or plant embryos. Some genetic material will stay in the cells and transform them. This method also allows transformation of plant plastids. The transformation efficiency is lower than in Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, but most plants can be transformed with this method.
- Electroporation: Formation of transient holes in cell membranes using electric pulses of high field strength; this allows DNA to enter as described above for bacteria.[53]
Animals
Introduction of DNA into animal cells is usually called transfection, and is discussed in the corresponding article.
Practical aspects of transformation in molecular biology
The discovery of artificially induced competence in bacteria allow bacteria such as Escherichia coli to be used as a convenient host for the manipulation of DNA as well as expressing proteins. Typically plasmids are used for transformation in E. coli. In order to be stably maintained in the cell, a plasmid DNA molecule must contain an origin of replication, which allows it to be replicated in the cell independently of the replication of the cell's own chromosome.
The efficiency with which a competent culture can take up exogenous DNA and express its genes is known as transformation efficiency and is measured in colony forming unit (cfu) per μg DNA used. A transformation efficiency of 1×108 cfu/μg for a small plasmid like pUC19 is roughly equivalent to 1 in 2000 molecules of the plasmid used being transformed.
In calcium chloride transformation, the cells are prepared by chilling cells in the presence of Ca2+
(in CaCl
2 solution), making the cell become permeable to plasmid DNA. The cells are incubated on ice with the DNA, and then briefly heat-shocked (e.g., at 42 °C for 30–120 seconds). This method works very well for circular plasmid DNA. Non-commercial preparations should normally give 106 to 107 transformants per microgram of plasmid; a poor preparation will be about 104/μg or less, but a good preparation of competent cells can give up to ~108 colonies per microgram of plasmid.[54] Protocols, however, exist for making supercompetent cells that may yield a transformation efficiency of over 109.[55] The chemical method, however, usually does not work well for linear DNA, such as fragments of chromosomal DNA, probably because the cell's native exonuclease enzymes rapidly degrade linear DNA. In contrast, cells that are naturally competent are usually transformed more efficiently with linear DNA than with plasmid DNA.
The transformation efficiency using the CaCl
2 method decreases with plasmid size, and electroporation therefore may be a more effective method for the uptake of large plasmid DNA.[56] Cells used in electroporation should be prepared first by washing in cold double-distilled water to remove charged particles that may create sparks during the electroporation process.
Selection and screening in plasmid transformation
Because transformation usually produces a mixture of relatively few transformed cells and an abundance of non-transformed cells, a method is necessary to select for the cells that have acquired the plasmid. The plasmid therefore requires a selectable marker such that those cells without the plasmid may be killed or have their growth arrested. Antibiotic resistance is the most commonly used marker for prokaryotes. The transforming plasmid contains a gene that confers resistance to an antibiotic that the bacteria are otherwise sensitive to. The mixture of treated cells is cultured on media that contain the antibiotic so that only transformed cells are able to grow. Another method of selection is the use of certain auxotrophic markers that can compensate for an inability to metabolise certain amino acids, nucleotides, or sugars. This method requires the use of suitably mutated strains that are deficient in the synthesis or utility of a particular biomolecule, and the transformed cells are cultured in a medium that allows only cells containing the plasmid to grow.
In a cloning experiment, a gene may be inserted into a plasmid used for transformation. However, in such experiment, not all the plasmids may contain a successfully inserted gene. Additional techniques may therefore be employed further to screen for transformed cells that contain plasmid with the insert. Reporter genes can be used as markers, such as the lacZ gene which codes for β-galactosidase used in blue-white screening. This method of screening relies on the principle of α-complementation, where a fragment of the lacZ gene (lacZα) in the plasmid can complement another mutant lacZ gene (lacZΔM15) in the cell. Both genes by themselves produce non-functional peptides, however, when expressed together, as when a plasmid containing lacZ-α is transformed into a lacZΔM15 cells, they form a functional β-galactosidase. The presence of an active β-galactosidase may be detected when cells are grown in plates containing X-gal, forming characteristic blue colonies. However, the multiple cloning site, where a gene of interest may be ligated into the plasmid vector, is located within the lacZα gene. Successful ligation therefore disrupts the lacZα gene, and no functional β-galactosidase can form, resulting in white colonies. Cells containing successfully ligated insert can then be easily identified by its white coloration from the unsuccessful blue ones.
Other commonly used reporter genes are green fluorescent protein (GFP), which produces cells that glow green under blue light, and the enzyme luciferase, which catalyzes a reaction with luciferin to emit light. The recombinant DNA may also be detected using other methods such as nucleic acid hybridization with radioactive RNA probe, while cells that expressed the desired protein from the plasmid may also be detected using immunological methods.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Johnston C, Martin B, Fichant G, Polard P, Claverys JP (2014). "Bacterial transformation: distribution, shared mechanisms and divergent control". Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 12 (3): 181–96. doi:10.1038/nrmicro3199. PMID 24509783.
- ↑ Alberts, Bruce; et al. (2002). Molecular Biology of the Cell. New York: Garland Science. p. G:35. ISBN 978-0-8153-4072-0.
- ↑ Griffith, F. 1928. The significance of pneumococcal types. J. Hyg. 27: 113–159, .
- ↑ Lederberg, Joshua (1994). The Transformation of Genetics by DNA: An Anniversary Celebration of AVERY, MACLEOD and MCCARTY(1944) in Anecdotal, Historical and Critical Commentaries on Genetics. The Rockfeller University, New York, New York 10021-6399. PMID 8150273.
- ↑ Mandel, Morton; Higa, Akiko (1970). "Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection". Journal of Molecular Biology. 53 (1): 159–162. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. PMID 4922220.
- ↑ Cohen, Stanley N.; Chang, Annie; Hsu, Leslie (1972). "Nonchromosomal Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria: Genetic Transformation of Escherichia coli by R-Factor DNA". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 69 (8): 2110–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. PMC 426879
 . PMID 4559594.
. PMID 4559594. - ↑ Hanahan, D. (1983). "Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids". Journal of Molecular Biology. 166 (4): 557–580. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(83)80284-8. PMID 6345791.
- ↑ Wirth R, Friesenegger A, Fiedler S (March 1989). "Transformation of various species of gram-negative bacteria belonging to 11 different genera by electroporation". Mol. Gen. Genet. 216 (1): 175–7. doi:10.1007/BF00332248. PMID 2659971.
- ↑ Palmiter, Richard; Ralph L. Brinster; Robert E. Hammer; Myrna E. Trumbauer; Michael G. Rosenfeld; Neal C. Birnberg; Ronald M. Evans (1982). "Dramatic growth of mice that develop from eggs microinjected with metallothionein−growth hormone fusion genes". Nature. 300 (5893): 611–5. doi:10.1038/300611a0. PMID 6958982.
- ↑ Nester, Eugene. "Agrobacterium: The Natural Genetic Engineer (100 Years Later)". Retrieved 14 January 2011.
- ↑ Zambryski, P.; Joos, H.; Genetello, C.; Leemans, J.; Montagu, M. V.; Schell, J. (1983). "Ti plasmid vector for the introduction of DNA into plant cells without alteration of their normal regeneration capacity". The EMBO Journal. 2 (12): 2143–2150. PMC 555426
 . PMID 16453482.
. PMID 16453482. - ↑ Peters, Pamela. "Transforming Plants - Basic Genetic Engineering Techniques". Retrieved 28 January 2010.
- ↑ "Biologists invent gun for shooting cells with DNA" (PDF). Cornell Chronicle. 14 May 1987. p. 3.
- ↑ Sanford JC, et al. (1987). "Delivery of substances into cells and tissues using a particle bombardment process". Journal of Particulate Science and Technology. 5: 27–37. doi:10.1080/02726358708904533.
- ↑ Klein TM, Wolf ED, Wu R, Sanford JC (7 May 1987). "High-velocity microprojectiles for delivering nucleic acids into living cells". Nature. 327 (6117): 70–73. doi:10.1038/327070a0.
- 1 2 3 Michod RE, Bernstein H, Nedelcu AM (2008). "Adaptive value of sex in microbial pathogens". Infect. Genet. Evol. 8 (3): 267–85. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2008.01.002. PMID 18295550.
- 1 2 Seitz P, Blokesch M (2013). "Cues and regulatory pathways involved in natural competence and transformation in pathogenic and environmental Gram-negative bacteria". FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 37 (3): 336–63. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2012.00353.x. PMID 22928673.
- ↑ Johnsborg O, Eldholm V, Håvarstein LS (2007). "Natural genetic transformation: prevalence, mechanisms and function". Res. Microbiol. 158 (10): 767–78. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2007.09.004. PMID 17997281.
- ↑
- 1 2 Chen I, Dubnau D (March 2004). "DNA uptake during bacterial transformation". Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2 (3): 241–9. doi:10.1038/nrmicro844. PMID 15083159.
- ↑ Lacks, S.; Greenberg, B.; Neuberger, M. (1974). "Role of a Deoxyribonuclease in the Genetic Transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 71 (6): 2305–2309. doi:10.1073/pnas.71.6.2305. PMC 388441
 . PMID 4152205.
. PMID 4152205. - ↑ Long, C. D.; Tobiason, D. M.; Lazio, M. P.; Kline, K. A.; Seifert, H. S. (2003). "Low-Level Pilin Expression Allows for Substantial DNA Transformation Competence in Neisseria gonorrhoeae". Infection and immunity. 71 (11): 6279–6291. doi:10.1128/iai.71.11.6279-6291.2003. PMC 219589
 . PMID 14573647.
. PMID 14573647. - ↑ Sisco, K. L.; Smith, H. O. (1979). "Sequence-specific DNA uptake in Haemophilus transformation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 76 (2): 972–976. doi:10.1073/pnas.76.2.972. PMC 383110
 . PMID 311478.
. PMID 311478. - 1 2 Johnsborg O, Eldholm V, Håvarstein LS (December 2007). "Natural genetic transformation: prevalence, mechanisms and function". Res. Microbiol. 158 (10): 767–78. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2007.09.004. PMID 17997281.
- ↑ Solomon JM, Grossman AD (April 1996). "Who's competent and when: regulation of natural genetic competence in bacteria". Trends Genet. 12 (4): 150–5. doi:10.1016/0168-9525(96)10014-7. PMID 8901420.
- ↑ Saito Y, Taguchi H, Akamatsu T (March 2006). "Fate of transforming bacterial genome following incorporation into competent cells of Bacillus subtilis: a continuous length of incorporated DNA". J. Biosci. Bioeng. 101 (3): 257–62. doi:10.1263/jbb.101.257. PMID 16716928.
- ↑ Saito Y, Taguchi H, Akamatsu T (April 2006). "DNA taken into Bacillus subtilis competent cells by lysed-protoplast transformation is not ssDNA but dsDNA". J. Biosci. Bioeng. 101 (4): 334–9. doi:10.1263/jbb.101.334. PMID 16716942.
- ↑ Akamatsu T, Taguchi H (April 2001). "Incorporation of the whole chromosomal DNA in protoplast lysates into competent cells of Bacillus subtilis". Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 65 (4): 823–9. doi:10.1271/bbb.65.823. PMID 11388459.
- ↑ Goodgal SH, Herriott RM (July 1961). "Studies on transformations of Hemophilus influenzae. I. Competence". J. Gen. Physiol. 44 (6): 1201–27. doi:10.1085/jgp.44.6.1201. PMC 2195138
 . PMID 13707010.
. PMID 13707010. - ↑ Aspiras MB, Ellen RP, Cvitkovitch DG (September 2004). "ComX activity of Streptococcus mutans growing in biofilms". FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 238 (1): 167–74. doi:10.1016/j.femsle.2004.07.032. PMID 15336418.
- ↑ Anagnostopoulos C, Spizizen J (May 1961). "Requirements for transformation in Bacillus subtilis". J. Bacteriol. 81 (5): 741–6. PMC 279084
 . PMID 16561900.
. PMID 16561900. - ↑ Claverys JP, Prudhomme M, Martin B (2006). "Induction of competence regulons as a general response to stress in gram-positive bacteria". Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 60: 451–75. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.60.080805.142139. PMID 16771651.
- ↑ Michod RE, Wojciechowski MF, Hoelzer MA (January 1988). "DNA repair and the evolution of transformation in the bacterium Bacillus subtilis". Genetics. 118 (1): 31–9. PMC 1203263
 . PMID 8608929.
. PMID 8608929. - ↑ Dorer MS, Fero J, Salama NR (2010). Blanke, Steven R, ed. "DNA damage triggers genetic exchange in Helicobacter pylori". PLoS Pathog. 6 (7): e1001026. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001026. PMC 2912397
 . PMID 20686662.
. PMID 20686662. - 1 2 Charpentier X, Kay E, Schneider D, Shuman HA (March 2011). "Antibiotics and UV radiation induce competence for natural transformation in Legionella pneumophila". J. Bacteriol. 193 (5): 1114–21. doi:10.1128/JB.01146-10. PMC 3067580
 . PMID 21169481.
. PMID 21169481. - ↑ Albertini S, Chételat AA, Miller B, et al. (July 1995). "Genotoxicity of 17 gyrase- and four mammalian topoisomerase II-poisons in prokaryotic and eukaryotic test systems". Mutagenesis. 10 (4): 343–51. doi:10.1093/mutage/10.4.343. PMID 7476271.
- ↑ Washburn RS, Gottesman ME (January 2011). "Transcription termination maintains chromosome integrity". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108 (2): 792–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.1009564108. PMC 3021005
 . PMID 21183718.
. PMID 21183718. - ↑ Sakano K, Oikawa S, Hasegawa K, Kawanishi S (November 2001). "Hydroxyurea induces site-specific DNA damage via formation of hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide". Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 92 (11): 1166–74. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2001.tb02136.x. PMID 11714440.
- 1 2 Bernstein H, Bernstein C, Michod RE (2012). "Chapter 1". In Sakura Kimura and Sora Shimizu. DNA repair as the primary adaptive function of sex in bacteria and eukaryotes. DNA Repair: New Research. Nova Sci. Publ., Hauppauge, N.Y. pp. 1–49. ISBN 978-1-62100-808-8.
- ↑ Michod RE, Bernstein H, Nedelcu AM (May 2008). "Adaptive value of sex in microbial pathogens". Infect. Genet. Evol. 8 (3): 267–85. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2008.01.002. PMID 18295550. http://www.hummingbirds.arizona.edu/Faculty/Michod/Downloads/IGE%20review%20sex.pdf
- ↑ Donahue RA, Bloom FR (July 1998). "Large-volume transformation with high-throughput efficiency chemically competent cells" (PDF). Focus. 20 (2): 54–56. OCLC 12352630.
- 1 2 Srivastava, Sheela (2013). Genetics of Bacteria (PDF). India: Springer-Verlag. doi:10.1007/978-81-322-1090-0. ISBN 978-81-322-1089-4.
- ↑ Kawai, Shigeyuki; Hashimoto, Wataru; Murata, Kousaku (1 November 2010). "Transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and other fungi: methods and possible underlying mechanism.". Bioengineered Bugs. 1 (6): 395–403. doi:10.4161/bbug.1.6.13257.
- ↑ Hinnen, A; Hicks, JB; Fink, GR (April 1978). "Transformation of yeast.". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 75 (4): 1929–33. doi:10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. PMID 347451.
- ↑ Ito, H; Fukuda, Y; Murata, K; Kimura, A (January 1983). "Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations". Journal of Bacteriology. 153 (1): 163–8. PMC 217353
 . PMID 6336730.
. PMID 6336730. - ↑ Gietz, RD; Woods, RA (2002). "Transformation of yeast by lithium acetate/single-stranded carrier DNA/polyethylene glycol method". Methods in enzymology. Methods in Enzymology. 350: 87–96. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(02)50957-5. ISBN 9780121822538. PMID 12073338.
- ↑ Gietz, RD; Schiestl, RH; Willems, AR; Woods, RA (Apr 15, 1995). "Studies on the transformation of intact yeast cells by the LiAc/SS-DNA/PEG procedure". Yeast. 11 (4): 355–60. doi:10.1002/yea.320110408. PMID 7785336.
- ↑ Schiestl, Robert H.; Manivasakam, P.; Woods, Robin A.; Gietzt, R.Daniel (1 August 1993). "Introducing DNA into Yeast by Transformation". Methods. 5 (2): 79–85. doi:10.1006/meth.1993.1011.
- ↑ Spencer, F.; Ketner, G.; Connelly, C.; Hieter, P. (1 August 1993). "Targeted Recombination-Based Cloning and Manipulation of Large DNA Segments in Yeast". Methods. 5 (2): 161–175. doi:10.1006/meth.1993.1021.
- ↑ Costanzo, MC; Fox, TD (November 1988). "Transformation of yeast by agitation with glass beads". Genetics. 120 (3): 667–70. PMC 1203545
 . PMID 3066683.
. PMID 3066683. - ↑ Dohmen, R. J.; Strasser, A. W.; Höner, C. B.; Hollenberg, C. P. (1991). "An efficient transformation procedure enabling long-term storage of competent cells of various yeast genera". Yeast. 7 (7): 691–2. doi:10.1002/yea.320070704. PMID 1776359.
- ↑ Hayama, Y; Fukuda, Y; Kawai, S; Hashimoto, W; Murata, K (2002). "Extremely simple, rapid and highly efficient transformation method for the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae using glutathione and early log phase cells". Journal of bioscience and bioengineering. 94 (2): 166–71. PMID 16233287.
- ↑ V.Singh and D.K.Jain (2014). "Applications of recombinant DNA". ISC BIOLOGY. Nageen Prakashan. p. 840.
- ↑ Bacterial Transformation
- ↑ Inoue, H.; Nojima, H.; Okayama, H. (1990). "High efficiency transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids". Gene. 96 (1): 23–28. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(90)90336-P. PMID 2265755.
- ↑ Donahue RA, Bloom FR (September 1998). "Transformation efficiency of E. coli electroporated with large plasmid DNA" (PDF). Focus. 20 (3): 77–78. Archived from the original on September 3, 2011.
External links
- Bacterial Transformation (a Flash Animation)
- "Ready, aim, fire!" At the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Plant Physiology in Potsdam-Golm plant cells are ‘bombarded’ using a particle gun