Bacillibactin
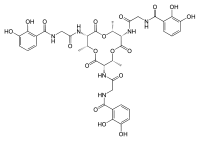 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N,N’,N’’-{[(2R,3S,6R,7S,10R,11S)-2,6,10-Trimethyl-4,8,12-trioxo-1,5,9-trioxacyclododecane-3,7,11-triyl]tris[imino(2-oxo-2,1-ethanediyl)]}tris(2,3-dihydroxybenzamide) | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 111553 |
| PubChem | 125349 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C39H42N6O18 | |
| Molar mass | 882.79 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Bacillibactin is a catechol-based siderophore secreted by members of the genus Bacillus, including Bacillus anthracis and Bacillus subtilis. It is involved in the chelation of ferric iron (Fe3+) from the surrounding environment and is subsequently transferred into the bacterial cytoplasm via the use of ABC transporters.[1]
References
- ↑ Hotta, K; Kim, CY; Fox, DT; Koppisch, AT (July 2010). "Siderophore-mediated iron acquisition in Bacillus anthracis and related strains.". Microbiology (Reading, England). 156 (Pt 7): 1918–25. doi:10.1099/mic.0.039404-0. PMID 20466767.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/7/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.