BOP reagent
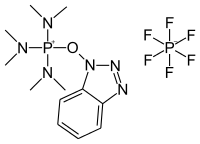 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(Benzotriazol-1-yloxy)tris(dimethylamino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate | |
| Other names
Castro's reagent | |
| Identifiers | |
| 56602-33-6 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 133386 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.054.782 |
| PubChem | 151348 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H22F6N6OP2 | |
| Molar mass | 442.287 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 136 to 140 °C (277 to 284 °F; 409 to 413 K) |
| Partially soluble in cold water reacts (decomposes) | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
BOP reagent is a reagent commonly used in the synthesis of peptides. Its use is discouraged because coupling using BOP liberates HMPA which is carcinogenic, although for small scale use in an organic laboratory this is not a great disadvantage as it is in large scale industrial usage.
See also
- PyBOP, a related reagent
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/20/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.