AutoSketch
AutoSketch is a 2D vector drawing program by Autodesk. It is less powerful than Autodesk's AutoCAD and does not support 3D models.
AutoSketch uses SKD and SKF, in later versions, as its native format, but can support DWG and DXF. Version 2.1 for Windows supported macros which has been removed in later versions.
History

AutoSketch was developed by Foresight Resources under the name "Drafix" to run under Microsoft DOS, and was one of the first Windows based CAD software products. An Atari version was also available around 1989.[1] Drafix won the first American Institute of Architect's "CAD Shoot-out". Among the features that made the original Drafix stand out when compared to the much more expensive AutoCAD were the ease of learning, the variety of dimensioning available out of the box, including relative dimensions, and being able to draw new primitives (line, circle, square, etc.) relative to existing primitives or points on them using keyboard shortcuts. One limitation of the first DOS release was that it needed to store all of a drawing in RAM, while editing and could not use any sort of swapping. This limited the size of the drawings.[2] In later versions Drafix took advantage of virtual memory available in Windows to edit more complex drawings. One important limitation was that while Drafix was a complete drawing tool at a reasonable price for many industries, especially architecture and industrial design with relatively small drawings, it lacked the extendability AutoCAD had thanks to its LISP interpreter.[3]
Drafix also took advantage of Windows Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) prior to any Autodesk product. This allowed Drafix to offer features to help automate reporting such as cost estimation and part list generation. Autodesk apparently found this product both a threat and opportunity and bought the company.
The final version of Autosketch, version 10, was released on November 14, 2008. Although Autodesk no longer officially supports Autosketch and offers no assistance to run the program on current versions of Windows,[4] the online Knowledge Base still carries a forum, documentation and some technical support.[5]
In use
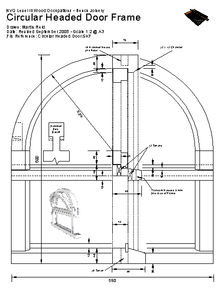
All technical 2D drawings created can be printed to scale from A4 up to A0 size, saved in native AutoCAD file format or exchanged with other CAD programmes using the DXF file format. Accurate 2D drawings can be opened in Google SketchUp and easily 'push - pulled' into 3D models.
The illustrated AutoSketch produced drawing, used by UK Advanced Joinery Students in the practical workshop while demonstrating their skills in the manufacture and production of complex frames.
Using AutoSketch allows students to use and practice 2D CAD techniques on relatively inexpensive software and produce files in the native AutoCAD DWG and DXF file formats that can be used in their workplace and to demonstrating their skills to their employers.
References
- ↑ Chadwick, Ian. "Review Drafix 1.0". ST-Log Issue 30 - April 1989. ST-Log. Archived from the original on October 5, 2008. Retrieved 18 May 2012.
- ↑ Ryan, Dan (2011). History of Computer Graphics. AuthorHouse. p. 303. ISBN 978-1-4567-5115-9.
- ↑ Ryan, Dan (2011). History of Computer Graphics. AuthorHouse. p. 303. ISBN 978-1-4567-5115-9.
- ↑ Autosketch on Windows 10
- ↑ Autodesk Knowledge Base for Autosketch