Ascomycin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| |
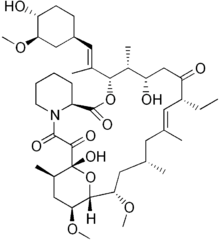
| Synonyms | 17-ethyl-1,14-dihydroxy-12-[2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-cyclohexyl)-1-methyl-vinyl]-23,25-dimethoxy-13,19,21,27-tetramethyl-11,28-dioxa-4-aza-tricyclo[22.3.1.04,9]octacos-18-ene-2,3,10,16-tetraone |
| CAS Number |
11011-38-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 5282071 |
| ChemSpider |
4445297 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:29582 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL8597 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C43H69NO12 |
| Molar mass | 792.01 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Ascomycin, also called Immunomycin, FR-900520, FK520, is an ethyl analog of tacrolimus (FK506) with strong immunosuppressant properties. It has been researched for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and skin diseases, and to prevent rejection after an organ transplant.
Ascomycin acts by binding to immunophilins, especially macrophilin-12. It appears that Ascomycin inhibits the production of Th1 (interferon- and IL-2) and Th2 (IL-4 and IL-10) cytokines. Additionally, ascomycin preferentially inhibits the activation of mast cells, an important cellular component of the atopic response. Ascomycin produces a more selective immunomodulatory effect in that it inhibits the elicitation phase of allergic contact dermatitis but does not impair the primary immune response when administered systemically.
Ascomycin is produced by the fermentation of Streptomyces hygroscopicus.
In fiction
Ascomycin is also the name of a fictional "antiagathic" (anti-aging) drug in James Blish's future history Cities in Flight.
Related compounds
References
- Griffiths CE. Ascomycin: an advance in the management of atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2001. Apr;144(4):679-81.
- Kawai, M., et al., Structure-activity profiles of macrolactam immunosuppressant FK-506 analogues. FEBS Lett. 1993. 316(2): 107-13.
- Zuberbier T, Chong SU, Grunow K, Guhl S, Welker P, Grassberger M, Henz BM. The ascomycin macrolactam pimecrolimus (Elidel, SDZ ASM 981) is a potent inhibitor of mediator release from human dermal mast cells and peripheral blood basophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001. Aug;108(2): 275-80.
- Mollison KW, Fey TA, Krause RA, Thomas VA, Mehta AP, Luly JR. Comparison of FK-506, rapamycin, ascomycin, and cyclosporine in mouse models of host-versus-graft disease and heterotopic heart transplantation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993. Jun 23; 685:55-7.
- Morisaki M, Arai T., Related Articles, Identity of immunosuppressant FR-900520 with ascomycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1992. Jan;45(1):126-8.
- Paul C., Graeber M, Stuetz A., Ascomycins: promising agents for the treatment of inflammatory skin diseases. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2000. Jan;9(1):69-77.#Mrowietz U., Macrolide immunosuppressants. Eur J Dermatol. 1999. Jul-Aug;9(5):346-51.
External links
- Exciting New Eczema Treatment Expected This Year By Jane Schwanke, WebMD Medical News March 17, 2000 (San Francisco)