Pied heron
| Pied heron | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Adult in breeding plumage in Queensland, Australia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Pelecaniformes |
| Family: | Ardeidae |
| Genus: | Ardea |
| Species: | A. picata |
| Binomial name | |
| Ardea picata (Gould, 1845)[2] | |
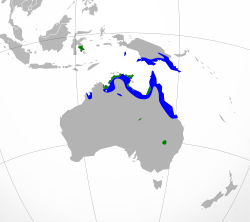 | |
| Distribution. Green: year-round breeding, blue: nonbreeding. | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The pied heron (Ardea picata), also known as the pied egret[4] is a bird found in coastal and subcoastal areas of monsoonal northern Australia as well as some parts of Wallacea and New Guinea.
Taxonomy
_-_Fogg_Dam_-_Middle_Point_-_Northern_Territory_-_Australia.jpg)
The species was originally described by ornithologist John Gould in 1845. Some taxonomists put this species in the genus Egretta. There are no recognised subspecies.[5]


Description
It is a small heron, 43–55 cm long, with dark slaty wings, body, and crested head, with a white throat and neck. The appearance is similar to the white-necked heron.[4] Males (247–280 g) are heavier than females (225–242 g), but the two are similar in appearance.[6]
Immature birds lack the crest as well as the dark colouring on the head and may look like small versions of the white-necked heron. The juveniles were once classified as a separate species.[6]
Distribution and habitat
Its habitat mainly comprises a range of wetlands and wet grasslands.
Behaviour
Call
The call of the pied heron is a loud 'awk' or 'ohrk' in flight.[4] Soft cooing is given around the nest.[6] Little else is known about vocalisations.[6]
Breeding
Breeding takes place from February to May.[4] It nests in trees above the water, including mangroves, often colonially with other species of heron. 1–2 blue-green eggs are laid in a shallow platform of sticks.[4]
Feeding
It feeds on insects, frogs, crabs, fish and other small aquatic animals. Insects are the most important source of food.[6] It may feed alone or in groups of up to a thousand individuals.[6]
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2012). "Ardea picata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2008). "Ardea picata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2008. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 9 February 2009. Database entry includes justification for why the species is listed as least concern.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2006) Species factsheet: Ardea picata. Downloaded from http://www.birdlife.org/datazone/species/index.html?action=SpcHTMDetails.asp&sid=3727 on 25/02/2010
- 1 2 3 4 5 Pizzey, Graham; Knight, Frank (1997). Field Guide to the Birds of Australia. Sydney, Australia: HarperCollinsPublishers. p. 111. ISBN 0-207-18013-X.
- ↑ "Pied Heron, Egretta picata, Taxonomy". Retrieved 25 February 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Kushlan, James Anthony; Hancock, James; Thelwell, David (2005). The Herons. Oxford University Press. p. 170. ISBN 0-19-854981-4.
Bibliography
- Marchant, S.; & Higgins, P.J. (Coordinators). (2000). Handbook of Australian, New Zealand and Antarctic Birds. Vol.1: Ratites to Ducks. Oxford University Press: Melbourne. ISBN 978-0-19-553068-1
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ardea picata. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Ardea picata |
