Antichthones
Antichthones, in geography, are those peoples who inhabit the antipodes, regions on opposite sides of the Earth. The word is compounded of the Greek ὰντὶ ("opposed") and χθών ("earth").
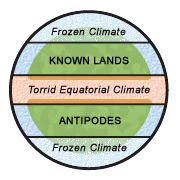
Classical and Medieval Europe considered the Earth to be divided by the equator into two hemispheres, the northern and southern; those who inhabited one of these hemispheres were said to be antichthones to those of the other. This idea was expounded by Mela and other Classical authors, though Christian writers, who believed that all people on earth must be descended from Adam, denied the possibility that any southern land, if it existed, could be inhabited by humans. St. Augustine, arguing from a position of scriptural inerrancy, wrote in his City of God "it is too absurd to say, that some men might have taken ship and traversed the whole wide ocean, and crossed from this side of the world to the other, and that thus even the inhabitants of that distant region are descended from that one first man."[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Dods, Marcus (translator); St. Augustine (1890). "Book XVI, Chapter 9.—Whether We are to Believe in the Antipodes.". In Philip Schaff. St. Augustine's City of God and Christian Doctrine. A Select Library of the Nicene and Post-Nicene Fathers of the Christian Church. 2. New York, New York: The Christian Literature Publishing Co. Archived from the original on July 2, 2003. Retrieved August 24, 2016.
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chambers, Ephraim, ed. (1728). "Antichthones". Cyclopædia, or an Universal Dictionary of Arts and Sciences (first ed.). James and John Knapton, et al.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chambers, Ephraim, ed. (1728). "Antichthones". Cyclopædia, or an Universal Dictionary of Arts and Sciences (first ed.). James and John Knapton, et al.