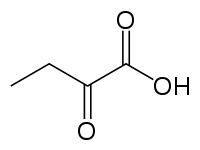
alpha-Ketobutyric acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-oxobutanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 600-18-0 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:30831 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL171246 |
| ChemSpider | 57 |
| DrugBank | DB04553 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.080 |
| KEGG | C00109 |
| MeSH | Alpha-ketobutyric+acid |
| PubChem | 58 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 102.089 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
α-Ketobutyric acid is a product of the lysis of cystathionine. It is also one of the degradation products of threonine, produced by the catabolism of the amino acid by threonine dehydratase. It is also produced by the degradation of homocysteine and the metabolism of methionine.
α-Ketobutyric acid is transported into the mitochondrial matrix, where it is converted to propionyl-CoA by branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex. Further mitochondrial reactions produce succinyl-CoA. This is first through the enzyme mitochondria Propionyl-CoA carboxylase with biotin as a cofactor to produce (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA. This is subsequently converted to (R)-methylmalonyl-CoA by mitochondrial methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase. Finally, mitochondrial methylmalonyl-CoA mutase with cofactor adenosylcobalamin produces succinyl-CoA which enters the citric acid cycle.[1]
Conversion in sotolon in French vin jaune
Vin jaune is marked by the formation of sotolon from alpha-ketobutyric acid.[2][3]
See also
References
- ↑ http://smpdb.ca/
- ↑ Pham TT, Guichard E, Schlich P, Charpentier C (1995). "Optimal Conditions for the Formation of Sotolon from α-Ketobutyric Acid in the French 'Vin Jaune'". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 43 (10): 2616–2619. doi:10.1021/jf00058a012.
- ↑ Guichard E, Pham TT, Etievant P (1993). "Quantitative Determination of Sotolon in Wines by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography". Chromatographia. 37 (9–10): 539–542. doi:10.1007/BF02275793.