Aeronautical mobile-satellite service
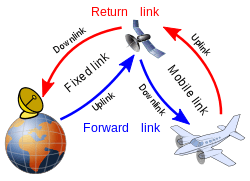
Aeronautical mobile-satellite service (short: AMSS; | also: aeronautical mobile-satellite radiocommunication service) is – according to Article 1.35 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR)[1] – defined as «A mobile-satellite service in which mobile earth stations are located on board aircraft; survival craft stations and emergency position-indicating radiobeacon stations may also participate in this service. . »
- See also
- Main articles: Radio station and Radiocommunication service
Classification
This radiocommunication service is classified in accordance with ITU Radio Regulations (article 1) as follows:
Mobile service (article 1.24)
- Aeronautical mobile service (article 1.32)
- Aeronautical mobile-satellite service
- Aeronautical mobile-satellite (R)° service (article 1.36)
- Aeronautical mobile-satellite (OR)°° service (article 1.37)
- Aeronautical mobile-satellite service
(R)° = abbreviation to route flights (route)
(OR)°° = abbreviation to flights others than on routs (off-route)
Frequency allocation
The allocation of radio frequencies is provided according to Article 5 of the ITU Radio Regulations (edition 2012).[2]
In order to improve harmonisation in spectrum utilisation, the majority of service-allocations stipulated in this document were incorporated in national Tables of Frequency Allocations and Utilisations which is with-in the responsibility of the appropriate national administration. The allocation might be primary, secondary, exclusive, and shared.
- primary allocation: is indicated by writing in capital letters (see example below)
- secondary allocation: is indicated by small letters
- exclusive or shared utilization: is within the responsibility of administrations
- Example of frequency allocation
| Allocation to services | ||
| Region 1 | Region 2 | Region 3 |
5 000–5 010 MHz
| ||
References / sources
- ↑ ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.35, definition: aeronautical mobile-satellite service / aeronautical mobile-satellite radiocommunication service
- ↑ ITU Radio Regulations, CHAPTER II – Frequencies, ARTICLE 5 Frequency allocations, Section IV – Table of Frequency Allocations