Administrative divisions of Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia had various administrative divisions in different time periods.
1918–1922

From 1918 to 1922, Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes continued to be subdivided into the pre–World War I divisions (districts, counties and kingdoms) of the Habsburg Monarchy and the formerly independent Balkan kingdoms of Serbia and Montenegro.
1922–1929

The Vidovdan Constitution of 1921 established the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes as a unitary state and, in 1922, 33 new administrative oblasts (provinces) ruled from the center were instituted:
- Oblast of Banja Luka
- Oblast of Belgrade
- Oblast of Bihać
- Oblast of Bitola
- Oblast of Cetinje (Zeta Oblast)
- Oblast of Čačak (Raška Oblast)
- Oblast of Ćuprija
- Oblast of Dubrovnik
- Oblast of Karlovec
- Oblast of Kragujevac (Šumadija Oblast)
- Oblast of Kruševac
- Oblast of Ljubljana
- Oblast of Maribor
- Oblast of Mostar
- Oblast of Niš
- Oblast of Novi Sad (Bačka Oblast)
- Oblast of Osijek
- Oblast of Požarevac
- Oblast of Pristina (Kosovo Oblast)
- Oblast of Sarajevo
- Oblast of Smederevo (Podunavlje Oblast)
- Oblast of Split
- Oblast of Skopje
- Oblast of Šabac (Podrinje Oblast)
- Oblast of Štip
- Oblast of Travnik
- Oblast of Tuzla
- Oblast of Užice (Zlatibor Oblast?)
- Oblast of Valjevo
- Oblast of Vranje
- Oblast of Vukovar (Syrmia Oblast)
- Oblast of Zagreb
- Oblast of Zaječar (Timok Oblast)
1929–1941


From 1929, the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes was renamed Kingdom of Yugoslavia and was subdivided into nine new provinces called banovinas. Their borders were intentionally drawn so that they would not correspond either to boundaries between ethnic groups, or to pre–World War I imperial borders. They were named after various geographic features, mostly rivers. Slight changes to their borders were made in 1931 with the new Yugoslav Constitution. The banovinas were as follow:
- Drava Banovina (Dravska banovina), with its capital in Ljubljana (1929–1941)
- Sava Banovina (Savska banovina), with its capital in Zagreb (1929–1939)
- Littoral Banovina (Primorska banovina), with its capital in Split (1929–1939)
- Vrbas Banovina (Vrbaska banovina), with its capital in Banja Luka (1929–1941)
- Drina Banovina (Drinska banovina), with its capital in Sarajevo (1929–1941)
- Zeta Banovina (Zetska banovina), with its capital in Cetinje (1929–1941)
- Danube Banovina (Dunavska banovina), with its capital in Novi Sad (1929–1941)
- Morava Banovina (Moravska banovina), with its capital in Niš (1929–1941)
- Vardar Banovina (Vardarska banovina), with its capital in Skopje (1929–1941)
- The City Administration of Belgrade, together with Zemun and Pančevo was also an administrative unit.
As an accommodation to Yugoslav Croats, the Banovina of Croatia (Banovina Hrvatska) was formed in 1939 from a merger of the Maritime and Sava Banovinas, with some additional territory from the Vrbas and Zeta Banovinas. Like Sava, its capital was Zagreb.
1941–1944

During World War II, Kingdom of Yugoslavia was occupied and partitioned by the Axis powers and was divided into 3 Axis puppet states:
- Independent State of Croatia
- Italian governorate of Montenegro (later German occupied territory of Montenegro)
- the Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia (including autonomous German-ruled Banat)
Other parts of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia were occupied by German, Italian, Hungarian, Bulgarian and Albanian Axis troops.
1945–1992
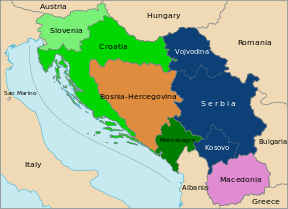
Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was divided into 6 republics and two autonomous provinces:
- Serbia (including autonomous provinces of Vojvodina and Kosovo)
- Montenegro
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Croatia
- Slovenia
- Macedonia
Successor states
After dissolution of Yugoslavia, in 1991–1992, five successor states were formed:
- Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1992–2003), in 2003 transformed into state union of Serbia and Montenegro, which in 2006 was dissolved into independent states of Serbia and Montenegro, in 2008 Kosovo[lower-alpha 1] declared its independence from Serbia.
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Croatia
- Slovenia
- Republic of Macedonia
Notes
- ↑ Kosovo is the subject of a territorial dispute between the Republic of Kosovo and the Republic of Serbia. The Republic of Kosovo unilaterally declared independence on 17 February 2008, but Serbia continues to claim it as part of its own sovereign territory. The two governments began to normalise relations in 2013, as part of the Brussels Agreement. Kosovo has received recognition as an independent state from 110 out of 193 United Nations member states.