7-cube
| 7-cube Hepteract | |
|---|---|
 Orthogonal projection inside Petrie polygon The central orange vertex is doubled | |
| Type | Regular 7-polytope |
| Family | hypercube |
| Schläfli symbol | {4,35} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams |
|
| 6-faces | 14 {4,34} |
| 5-faces | 84 {4,33} |
| 4-faces | 280 {4,3,3} |
| Cells | 560 {4,3} |
| Faces | 672 {4} |
| Edges | 448 |
| Vertices | 128 |
| Vertex figure | 6-simplex |
| Petrie polygon | tetradecagon |
| Coxeter group | C7, [35,4] |
| Dual | 7-orthoplex |
| Properties | convex |
In geometry, a 7-cube is a seven-dimensional hypercube with 128 vertices, 448 edges, 672 square faces, 560 cubic cells, 280 tesseract 4-faces, 84 penteract 5-faces, and 14 hexeract 6-faces.
It can be named by its Schläfli symbol {4,35}, being composed of 3 6-cubes around each 5-face. It can be called a hepteract, a portmanteau of tesseract (the 4-cube) and hepta for seven (dimensions) in Greek. It can also be called a regular tetradeca-7-tope or tetradecaexon, being a 7 dimensional polytope constructed from 14 regular facets.
Related polytopes
It is a part of an infinite family of polytopes, called hypercubes. The dual of a 7-cube is called a 7-orthoplex, and is a part of the infinite family of cross-polytopes.
Applying an alternation operation, deleting alternating vertices of the hepteract, creates another uniform polytope, called a demihepteract, (part of an infinite family called demihypercubes), which has 14 demihexeractic and 64 6-simplex 6-faces.
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a hepteract centered at the origin and edge length 2 are
- (±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1)
while the interior of the same consists of all points (x0, x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6) with -1 < xi < 1.
Images
| Coxeter plane | B7 / A6 | B6 / D7 | B5 / D6 / A4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graph |  |
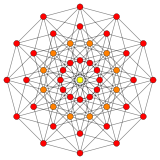 |
 |
| Dihedral symmetry | [14] | [12] | [10] |
| Coxeter plane | B4 / D5 | B3 / D4 / A2 | B2 / D3 |
| Graph |  |
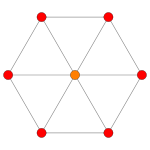 |
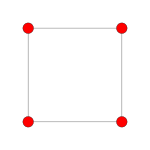 |
| Dihedral symmetry | [8] | [6] | [4] |
| Coxeter plane | A5 | A3 | |
| Graph |  |
 | |
| Dihedral symmetry | [6] | [4] |
Projections
 This hypercube graph is an orthogonal projection. This orientation shows columns of vertices positioned a vertex-edge-vertex distance from one vertex on the left to one vertex on the right, and edges attaching adjacent columns of vertices. The number of vertices in each column represents rows in Pascal's triangle, being 1:7:21:35:35:21:7:1. |
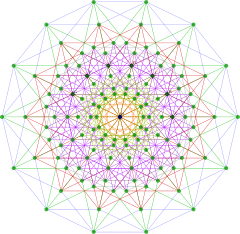 Petrie polygon, skew orthographic projection |
 Another orthogonal projection |

Hepteract 7D simple rotation through 2Pi with 7D perspective projection to 3D.
References
- H.S.M. Coxeter:
- Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, (3rd edition, 1973), Dover edition, ISBN 0-486-61480-8, p. 296, Table I (iii): Regular Polytopes, three regular polytopes in n-dimensions (n≥5)
- H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, 3rd Edition, Dover New York, 1973, p. 296, Table I (iii): Regular Polytopes, three regular polytopes in n-dimensions (n≥5)
- Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter, edited by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995, ISBN 978-0-471-01003-6
- (Paper 22) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi Regular Polytopes I, [Math. Zeit. 46 (1940) 380-407, MR 2,10]
- (Paper 23) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes II, [Math. Zeit. 188 (1985) 559-591]
- (Paper 24) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes III, [Math. Zeit. 200 (1988) 3-45]
- Norman Johnson Uniform Polytopes, Manuscript (1991)
- N.W. Johnson: The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs, Ph.D. (1966)
- Klitzing, Richard. "7D uniform polytopes (polyexa) o3o3o3o3o3o4x - hept".
External links
- Olshevsky, George. "Measure polytope". Glossary for Hyperspace. Archived from the original on 4 February 2007.
- Multi-dimensional Glossary: hypercube Garrett Jones
- Rotation of 7D-Cube www.4d-screen.de
| Fundamental convex regular and uniform polytopes in dimensions 2–10 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family | An | Bn | I2(p) / Dn | E6 / E7 / E8 / E9 / E10 / F4 / G2 | Hn | |||||||
| Regular polygon | Triangle | Square | p-gon | Hexagon | Pentagon | |||||||
| Uniform polyhedron | Tetrahedron | Octahedron • Cube | Demicube | Dodecahedron • Icosahedron | ||||||||
| Uniform 4-polytope | 5-cell | 16-cell • Tesseract | Demitesseract | 24-cell | 120-cell • 600-cell | |||||||
| Uniform 5-polytope | 5-simplex | 5-orthoplex • 5-cube | 5-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform 6-polytope | 6-simplex | 6-orthoplex • 6-cube | 6-demicube | 122 • 221 | ||||||||
| Uniform 7-polytope | 7-simplex | 7-orthoplex • 7-cube | 7-demicube | 132 • 231 • 321 | ||||||||
| Uniform 8-polytope | 8-simplex | 8-orthoplex • 8-cube | 8-demicube | 142 • 241 • 421 | ||||||||
| Uniform 9-polytope | 9-simplex | 9-orthoplex • 9-cube | 9-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform 10-polytope | 10-simplex | 10-orthoplex • 10-cube | 10-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform n-polytope | n-simplex | n-orthoplex • n-cube | n-demicube | 1k2 • 2k1 • k21 | n-pentagonal polytope | |||||||
| Topics: Polytope families • Regular polytope • List of regular polytopes and compounds | ||||||||||||