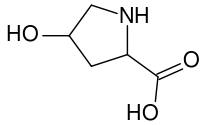
Hydroxyproline
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S,4R)-4-hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 51-35-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 5605 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.084 |
| MeSH | Hydroxyproline |
| PubChem | 5810 |
| UNII | RMB44WO89X |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H9NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 131.13 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
(2S,4R)-4-Hydroxyproline, or L-hydroxyproline (C5H9O3N), is a common non-proteinogenic amino acid, abbreviated as Hyp, e.g., in Protein Data Bank.
Structure and discovery
In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer isolated hydroxyproline from hydrolyzed gelatin. In 1905, Hermann Leuchs synthesized a racemic mixture of 4-hydroxyproline.[1]
Hydroxyproline differs from proline by the presence of a hydroxyl (OH) group attached to the gamma carbon atom.
Production and function
Hydroxyproline is produced by hydroxylation of the amino acid proline by the enzyme prolyl hydroxylase following protein synthesis (as a post-translational modification). The enzyme catalysed reaction takes place in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. Although it is not directly incorporated into proteins, hydroxyproline comprises roughly 4% of all amino acids found in animal tissue, an amount greater than seven other amino acids that are translationally incorporated.[2]
Hydroxyproline is a major component of the protein collagen,[3] comprising roughly 13.5% of mammalian collagen. Hydroxyproline and proline play key roles for collagen stability.[4] They permit the sharp twisting of the collagen helix.[5] In the canonical collagen Xaa-Yaa-Gly triad (where Xaa and Yaa are any amino acid), a proline occupying the Yaa position is hydroxylated to give a Xaa-Hyp-Gly sequence. This modification of the proline residue increases the stability of the collagen triple helix. It was initially proposed that the stabilization was due to water molecules forming a hydrogen bonding network linking the prolyl hydroxyl groups and the main-chain carbonyl groups.[6] It was subsequently shown that the increase in stability is primarily through stereoelectronic effects and that hydration of the hydroxyproline residues provides little or no additional stability.[7] In addition to collagen, the mammalian proteins elastin and argonaute 2 have collagen-like domains in which hydroxyproline is formed. Some snail poisons, conotoxins, contain hydroxyproline, but lack collagen-like sequences.[2]
Hydroxylation of proline has been shown to be involved in targeting Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) alpha subunit (HIF-1 alpha) for degradation by proteolysis. Under normoxia (normal oxygen conditions) EGLN1 protein hydroxylates the proline at the 564 position of HIF-1 alpha, which allows ubiquitylation by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor (pVHL) and subsequent targeting for proteasome degradation.[8]
Hydroxyproline is found in few proteins other than collagen. For this reason, hydroxyproline content has been used as an indicator to determine collagen and/or gelatin amount.
Hydroxyproline rich glycoproteins are also found in plant cell walls.[9]
Clinical significance
Proline hydroxylation requires ascorbic acid (vitamin C). The most obvious, first effects (gingival and hair problems) of absence of ascorbic acid in humans come from the resulting defect in hydroxylation of proline residues of collagen, with reduced stability of the collagen molecule, causing scurvy.
Increased serum and urine levels of hydroxyproline have also been demonstrated in Paget's disease.[10]
Other hydroxyprolines
Other hydroxyprolines also exist in nature. The most notable ones are 2,3-cis-, 3,4-trans-, and 3,4-dihydroxyproline, which occurs in diatom cell walls[11] and are postulated to have a role in silica deposition. Hydroxyproline is also found in the walls of oomycetes, fungus-like protists related to diatoms.[12] (2S,4S)-cis-4-Hydroxyproline is found in the toxic cyclic peptides from Amanita mushrooms (e.g., alpha-amanitin and phalloidin).[13]
See also
References
- ↑ R.H.A. Plimmer (1912) [1908]. R.H.A. Plimmer; F.G. Hopkins, eds. The chemical composition of the proteins. Monographs on biochemistry. Part I. Analysis (2nd ed.). London: Longmans, Green and Co. p. 132. Retrieved January 18, 2010.
- 1 2 Gorres, Kelly L.; Raines, Ronald T. (April 2010). "Prolyl 4-hydroxylase". Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 45 (2): 106–124. doi:10.3109/10409231003627991. PMC 2841224
 . PMID 20199358.
. PMID 20199358. - ↑ Szpak, Paul (2011). "Fish bone chemistry and ultrastructure: implications for taphonomy and stable isotope analysis". Journal of Archaeological Science. 38 (12): 3358–3372. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2011.07.022.
- ↑ Nelson, D. L. and Cox, M. M. (2005) Lehninger's Principles of Biochemistry, 4th Edition, W. H. Freeman and Company, New York.
- ↑ Brinckmann, J., Notbohm, H. and Müller, P.K. (2005) Collagen, Topics in Current Chemistry 247, Springer, Berlin.
- ↑ Bella, J; Eaton, M; Brodsky, B; Berman, HM (1994). "Crystal and molecular structure of a collagen-like peptide at 1.9 A resolution". Science. 266 (5182): 75–81. doi:10.1126/science.7695699. PMID 7695699.
- ↑ Kotch, F.W.; Guzei, I.A.; Raines, R.T. (2008). "Stabilization of the Collagen Triple Helix by O-Methylation of Hydroxyproline Residues". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 130 (10): 2952–2953. doi:10.1021/ja800225k. PMC 2802593
 . PMID 18271593.
. PMID 18271593. - ↑ Jaakkola, P.; Mole, D.R.; Tian, Y.M.; Wilson, M.I.; Gielbert, J.; Gaskell, S.J.; Kriegsheim, A.V.; Hebestreit, H.F.; et al. (2001). "Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation". Science. 292 (5516): 468–72. doi:10.1126/science.1059796. PMID 11292861.
- ↑ Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998. 49:281–309 PLANT CELL WALL PROTEINS Gladys I. Cassab
- ↑ http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/pagets_disease
- ↑ Nakajima, T.; Volcani, B.E. (1969). "3,4-Dihydroxyproline: a new amino acid in diatom cell walls". Science. 164 (3886): 1400–1401. doi:10.1126/science.164.3886.1400. PMID 5783709.
- ↑ Alexopoulos, C.J., Mims C.W. and Blackwell, M. (1996). Introductory Mycology (4th ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 687–688. ISBN 0-471-52229-5.
- ↑ Wieland, T. (1986). Peptides of Poisonous Amanita Mushrooms. Springer.
