2-Bromobutyric acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Bromobutyric acid | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2-Bromobutanoic acid | |
| Other names
2-bromo-butanoicaci;alpha-Bromobytyric acid;Butanoic acid, 2-bromo-;Butyric acid, 2-bromo-;Butyric acid, alpha-bromo-;dl-2-Bromobutyric acid;dl-2-Bromobutyricacid;α-Bromobutyricacid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 80-58-0 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 6403 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.177 |
| PubChem | 6655 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H7BrO2 | |
| Molar mass | 167.00 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | clear, yellow liquid |
| Density | 1.567 g/mL at 25 °C |
| Melting point | −4 °C (25 °F; 269 K) |
| Boiling point | 99 to 103 °C (210 to 217 °F; 372 to 376 K) 10 mmHg |
| 66 g/L (20 °C) | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.0533 Torr |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.95±0.10. Most Acidic Temp: 25 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Causes severe skin burns and eye damage. Causes serious eye damage. Harmful if swallowed. |
| Flash point | > 112 °C (234 °F; 385 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions |
2-Bromobutyride |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Bromobutyric acid is an carboxylic acid with the molecular formula C4H7BrO2. It is a clear, yellow liquid. The 2-position is an asymmetric carbon, so there are two enantiomers of this compound. 2-Bromobutyric acid is mainly used as a building block chemical, such as in the preparation of Levetiracetam, an anticonvulsant medication.[1]
Production
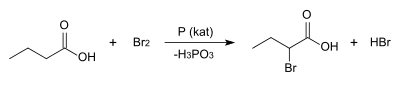
2-Bromobuyric acid may be prepared by the acid-catalyzed Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky reaction, where butyric acid is treated with elemental bromine.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/30/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.