1999 LE31
|
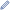
Diagram of the orbit of 1999 LE31 | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Lincoln Laboratory Near-Earth Asteroid Research Team at Socorro |
| Discovery date | June 12, 1999 |
| Designations | |
| damocloid | |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 3 | |
| Observation arc | 409 days (1.12 yr) |
| Aphelion | 11.939 AU (1.7860 Tm) |
| Perihelion | 4.3386 AU (649.05 Gm) |
| 8.1385 AU (1.21750 Tm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.46691 |
| 23.22 yr (8480.41 d) | |
| 266.052° | |
| 0° 2m 32.824s /day | |
| Inclination | 151.812° (retrograde) |
| 292.018° | |
| 32.5005°[2] | |
| Earth MOID | 3.35736 AU (502.254 Gm) |
| Jupiter MOID | 0.527518 AU (78.9156 Gm) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 16.8 km[1] |
Mean radius | 8.4 ± 2.1 km |
| 0.056 ± 0.026[1] | |
| 12.4[1] | |
|
| |
1999 LE31 is a damocloid centaur[1] discovered on June 12, 1999.[3] It is both a Jupiter and Saturn-crossing minor planet.[1]
1999 LE31 spends most of its orbit located in the outer Solar System between Jupiter and Uranus,[4] and like all centaurs, has an unstable orbit caused by the gravitational influence of the giant planets. Due to this, it must have originated from elsewhere, most likely outside Neptune.[4]
Of over half a million known minor planets, 1999 LE31 is one of about 60 that has a retrograde orbit.[5]
1999 LE31 is approximately 16.8 km in diameter.[1][3] It came to perihelion (closest approach to the Sun) in December 1998.[6] It was last observed in 2000, and will next come to perihelion in February 2022.[1]
Observations
This asteroid has been recorded at such observatories as:[2]
- Lincoln Laboratory (1.0-m f/2.15 reflector + CCD) - location of discovery
- Dominion Astrophysical Observatory (1.82-m reflector + CCD)
- Dynic Astronomical Observatory (0.60-m f/3.7 reflector + CCD)
- European Northern Observatory (1.0-m reflector + CCD)
- Farpoint (0.30-m Schmidt-Cassegrain + CCD)
- Kleť Observatory (0.57-m f/5.2 reflector + CCD)
- McDonald Observatory (0.76-m reflector + CCD)
- Roque de los Muchachos Observatory (1.0-m reflector + CCD)
See also
- 20461 Dioretsa a.k.a. 1999 LD31
- 2000 DG8
- List of notable asteroids
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: (1999 LE31)" (last observation: 2000-06-29; arc: 1.12 yr). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 29 March 2016.
- 1 2 "MPEC 1999-M29 : 1999 LE31". Minorplanetcenter.org. Retrieved 2011-07-11.
- 1 2 "BAA Comet Section Comets of 1999". Ast.cam.ac.uk. Retrieved 2011-07-11.
- 1 2 Horner, J.; Evans, N.W.; Bailey, M. E. (2004). "Simulations of the Population of Centaurs I: The Bulk Statistics". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 354 (3): 798–810. arXiv:astro-ph/0407400
 . Bibcode:2004MNRAS.354..798H. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08240.x.
. Bibcode:2004MNRAS.354..798H. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08240.x. - ↑ "JPL Small-Body Database Search Engine: Asteroids and i > 90 (deg)". JPL Solar System Dynamics. Retrieved 2014-11-15.
- ↑ Seiichi Yoshida (2010-07-03). "1999 LE31". Seiichi Yoshida's Comet Catalog. Retrieved 2014-11-15.
External links
- Interactive orbit diagram
- Yanga R. Fernández, David C. Jewitt, and Scott S. Sheppard, Low Albedos Among Extinct Comet Candidates, May 22, 2001
- 1999 LE31 – Seiichi Yoshida @ aerith.net
- 1999 LE31 at the JPL Small-Body Database