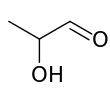
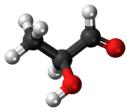
Lactaldehyde
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Hydroxypropanal | |||
| Other names
Hydroxypropionaldehyde | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 598-35-6 3946-09-6 (R) 3913-64-2 (S) | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:18419 | ||
| ChemSpider | 832 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.237.284 | ||
| KEGG | C05999 | ||
| PubChem | 855 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H6O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 74.08 g·mol−1 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related aldehydes |
Glycolaldehyde | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Lactaldehyde is an intermediate in the methylglyoxal metabolic pathway. Methylglyoxal is converted to D-lactaldehyde by glycerol dehydrogenase (gldA). Lactaldehyde is then oxidized to lactic acid by aldehyde dehydrogenase.[1]
Lactaldehyde exists in several forms: in open-chain form and as cyclic hemiacetal; in solution and in crystal forms; as monomer and as dimer. In crystal form, three conformers occur as hemiacetal dimers with a 1,4-dioxane ring skeleton:
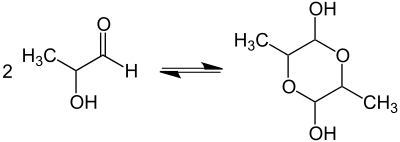
Dimerization of lactaldehyde leads to a mixture of stereoisomeric 1,4-dioxanes.
In equilibrium solution, negligibly small amounts of the monomer and at least one five-membered ring dimer exist.[2]
References
- ↑ Huang PC, Miller ON (1958). "The metabolism of lactaldehyde, page 205" (PDF). J. Biol. Chem. 231 (1): 201–5. PMID 13538961.
- ↑ Takahashi, H (1983). "Conformational studies of DL-lactaldehyde by 1H-NMR, Raman and i.r. spectroscopy". Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular Spectroscopy. 39 (6): 569–572. doi:10.1016/0584-8539(83)80108-1.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/16/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.